热门标签
热门文章
- 1鸿蒙系列--组件介绍之其他基础组件(下)_鸿蒙scrollbar组件讲解
- 2新版 Microsoft Edge浏览器 使用Alt+Tab 键 切换 窗口显示多个Edge浏览器页面_edge alt+tab
- 3IOS面试题object-c 146-150
- 4Error while executing: am start -n错误解决方案_error while executing: am start -n "com.example.ls
- 5【HarmonyOS】1、HarmonyOS应用开发基础详解(持续更新)
- 6(10-2)大模型优化算法和技术:模型并行和数据并行_大模型并行计算什么意思
- 7java project clean_如何在Java maven项目的命令提示符中执行'project> clean'
- 8使用Jan下载AI模型失败_download failedmodelundefined downloadfailed:conne
- 9python各种空变量问题_python中检测多个变量中哪一个或多个变量为空
- 10Android-dp、sp等像素单位以及48dp调和原则_48dp dp单位
当前位置: article > 正文
c++学习——(4)构造函数初始化列表以及拷贝构造函数_在初始化列表中未调用拷贝构造函数
作者:凡人多烦事01 | 2024-03-08 04:07:56
赞
踩
在初始化列表中未调用拷贝构造函数
一.初始化列表
1.构造函数初始化列使用方法

如图所示的类中只有两个数据成员,语法:构造函数后面要用冒号隔开,对于多个数据成员之间要用逗号隔开,赋值的时候要有括号而不能用等于号复制。
2.初始化列表特性
初始化列表由于构造函数执行:编译器会先给初始列表的成员。
赋值再执行构造函数的代码。
初始化列表只适用于构造函数。
初始化列表可以初始化多个成员数据。
3.初始化列表的必要性
大家可能会想初始化列表的工作构造函数完全能够完成,为什么还要存在初始化列表呢!下面看一个例子。
- 1
用构造函数来给常量赋值会发生语法错误

但是用初始化列表却可以完成这个工作。
4.代码实例
main函数文件:
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string> #include"teacher.h" using namespace std; /****************************************************************/ /*自定义Teacher类 *自定义有参默认构造函数 *使用初始化列表初始化数据 *数据成员: * 名字 * 年龄 *成员函数 * 数据成员的封装函数 *扩展 #定义可以带最多学生个数,此为常量 /****************************************************************/ int main(void) { Teacher t1("Merry",2,1000); cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getAge() <<" "<<t1.getMax()<< endl; //cout << t2.getName() << " " << t2.getAge() << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
Teacher.h文件
#include<string> using namespace std; class Teacher { public: Teacher(string _name ="Jim", int _age = 1,int m=100); void setName(string _name); string getName(); void setAge(int _age); int getAge(); int getMax(); private: string m_strName; int m_iAge; const int m_iMax; };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
Teacher.cpp文件(初始化列表)
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string> #include "Teacher.h" using namespace std; Teacher::Teacher(string _name, int _age,int m):m_strName(_name),m_iAge(_age),m_iMax(m) { cout << "Teacher(string _name,int _age)" << endl; } int Teacher::getMax() { return m_iMax; } void Teacher::setName(string _name) { m_strName = _name; } string Teacher::getName() { return m_strName; } void Teacher::setAge(int _age) { m_iAge = _age; } int Teacher::getAge() { return m_iAge; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
可以尝试不用初始化列表初始化const常量会发现错误
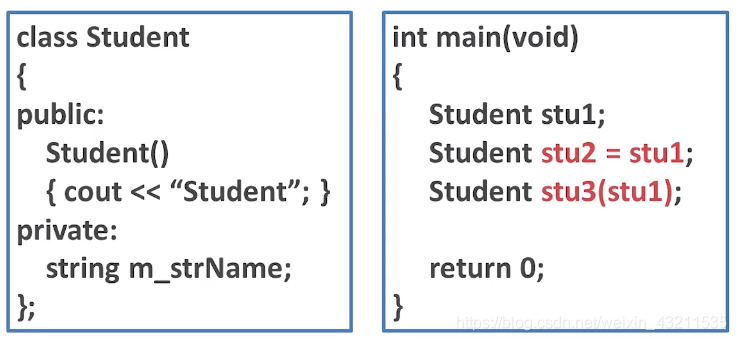
二.拷贝构造函数
1.拷贝构造函数的用途
如图当我们实例化对象stu1、stu2、stu3时本应该自动调用构造函数就会打印出三个Student的,但是事实是只打印了一个。原因就是后面两个调用的是拷贝构造函数。
2.拷贝构造函数的定义以及其特点

特点:
*拷贝构造函数的参数是固定的不可以重载
*如果有自定义拷贝构造函数则系统会自动生成一个默认的拷贝构造函数
*当采用直接初始化或者复制初始化实例对象时系统会自动调用拷贝构造函数
3.代码实例
main函数文件:
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string> #include"teacher.h" using namespace std; /****************************************************************/ /*自定义Teacher类 *自定义拷贝构造函数 *数据成员: * 名字 * 年龄 *成员函数 * 数据成员的封装函数 /****************************************************************/ int main(void) { Teacher t1; Teacher t2 = t1; Teacher t3(t1); system("pause"); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Teacher.h文件
#include<string> using namespace std; class Teacher { public: Teacher(string _name = "Jim", int _age = 1); Teacher(const Teacher &tea); void setName(string _name); string getName(); void setAge(int _age); int getAge(); private: string m_strName; int m_iAge; };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
Teacher.cpp文件
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string> #include "Teacher.h" using namespace std; Teacher::Teacher(string _name, int _age):m_strName(_name),m_iAge(_age) { cout << "Teacher(string _name,int _age)" << endl; } Teacher::Teacher(const Teacher &tea) { cout << "Teacher(const Teacher &tea)" << endl; } void Teacher::setName(string _name) { m_strName = _name; } string Teacher::getName() { return m_strName; } void Teacher::setAge(int _age) { m_iAge = _age; } int Teacher::getAge() { return m_iAge; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
运行结果显示t2、t3的实例化都调用的是拷贝构造函数。
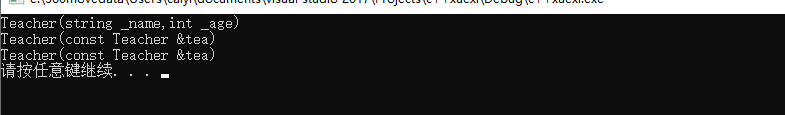
**注意:**拷贝构造函数不仅在前面实例化对象的时候会被调用,当出现参数传递的时候一样会自动调用拷贝构造函数。如图当test函数引用t1的时候一样会自动调用拷贝构造函数。

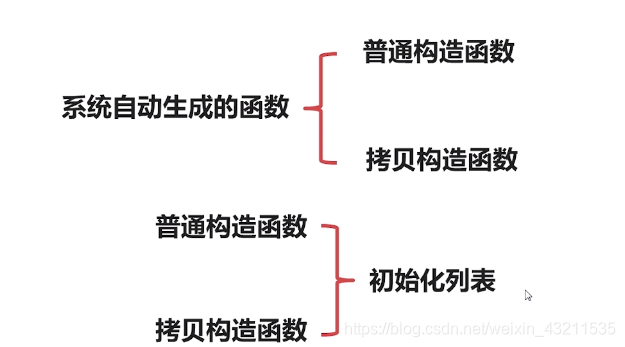
三.构造函数总结

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/凡人多烦事01/article/detail/209057
推荐阅读
相关标签



