热门标签
热门文章
- 1HTTP状态码_http422ka
- 2我的字节跳动Android面试初体验——稀里糊涂结束战斗,阿里p8面试题
- 3如何保障 MySQL 和 Redis 的数据一致性?_等保合规 mysql redis
- 4裸辞考研成功那一刻,我在想值得吗?_学习分享驿站
- 5Mac 电脑安装putty_putty mac
- 6免费AI开源引擎:在电力电网工单系统中智能解析的应用场景_开源电力分析系统
- 7常见的Linux操作系统_linux操作系统有哪些
- 8【数据结构】排序(插入、选择、交换、归并) -- 详解_关于插入交换选择和归并排序算法比较
- 9大数据学习06:Java访问HDFS_java普通类加载hdfs文件
- 10《 构造/析构/内联/构造/静态成员函数 》——在什么情况下是否可以是虚函数?_构造成员函数可以是虚函数吗
当前位置: article > 正文
二叉树 - (前序,中序,后序,层序 遍历实现)_本关任务:以顺序结构存储二叉树,编写前序、中序、后序及层次顺序遍历二叉树的算法
作者:你好赵伟 | 2024-06-19 20:37:09
赞
踩
本关任务:以顺序结构存储二叉树,编写前序、中序、后序及层次顺序遍历二叉树的算法
目录
一 . 什么是树
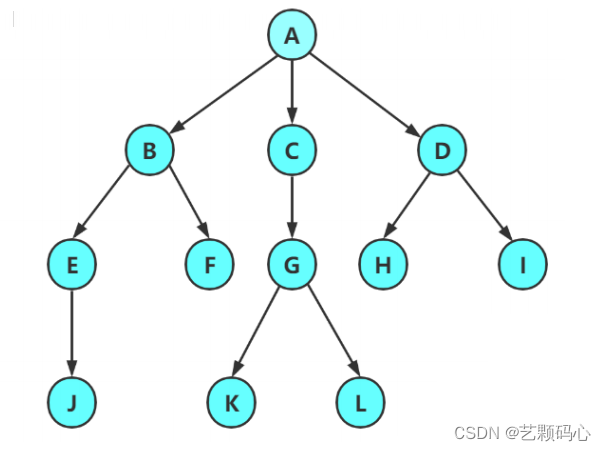
注意 :
1.子树是不相交的.

2.除了根节点以外,每个节点有且仅有一个父节点
3,一棵N个节点的树有N-1条边.
树的概念
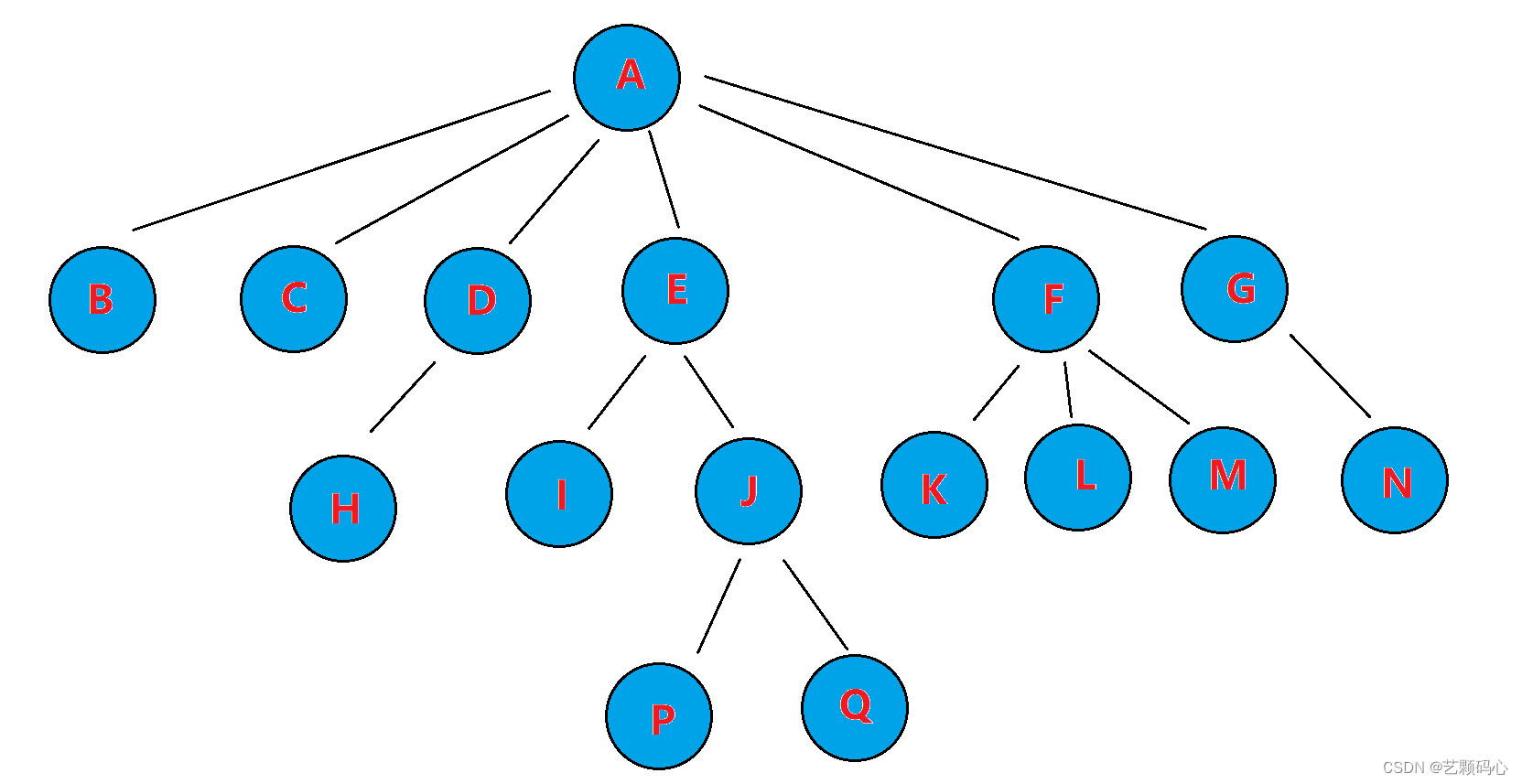
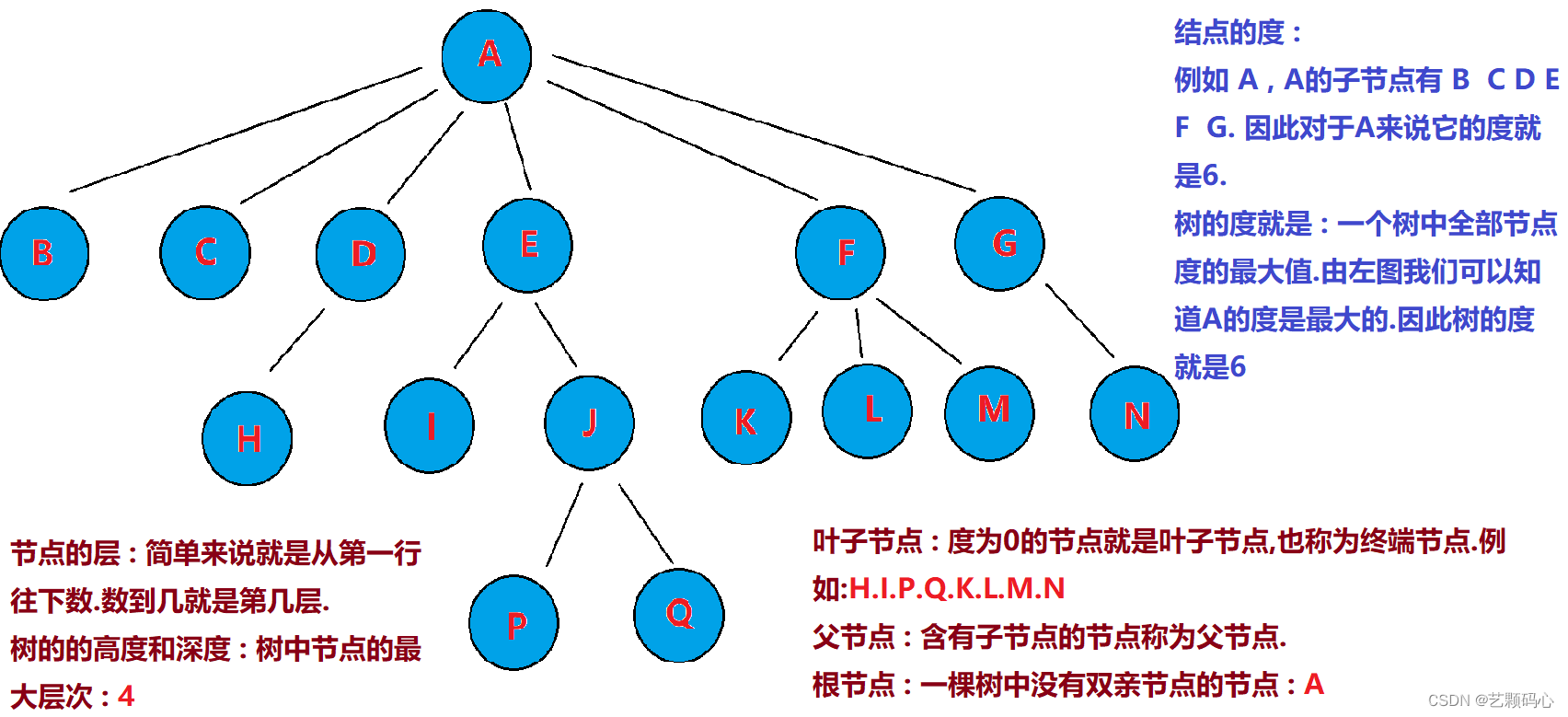
1. 结点的度:一个结点含有子树的个数称为该结点的度; 如上图:A的度为6
2. 树的度:一棵树中,所有结点度的最大值称为树的度; 如上图:树的度为6
3. 叶子结点或终端结点
:度为
0
的结点称为叶结点; 如上图:
B
、
C
、
H
、
I...
等节点为叶结点
4. 双亲结点或父结点
:若一个结点含有子结点,则这个结点称为其子结点的父结点; 如上图:
A
是
B
的父结点
5. 孩子结点或子结点
:一个结点含有的子树的根结点称为该结点的子结点; 如上图:
B
是
A
的孩子结点
6. 根结点
:一棵树中,没有双亲结点的结点;如上图:
A
7. 结点的层次
:从根开始定义起,根为第
1
层,根的子结点为第
2
层,以此类推
8. 树的高度或深度:树中结点的最大层次; 如上图:树的高度为4
树的表示形式
树的表示方式有很多 , 如 : 双亲表示法,孩子表示法,孩子双亲表示法,孩子兄弟表示法.
我们采用最常用的孩子兄弟表示法.
比较简单 : 就像我们之前学的链表一样.
对于二叉树来说 : 有三个值域 : 分别存储 : 值, 左孩子节点地址, 右孩子节点地址
- public class Node {
- public int val;
- public Node left;
- public Node right;
-
- public Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
二. 二叉树
1. 概念 :
二叉树的每个节点的度不能超过2.
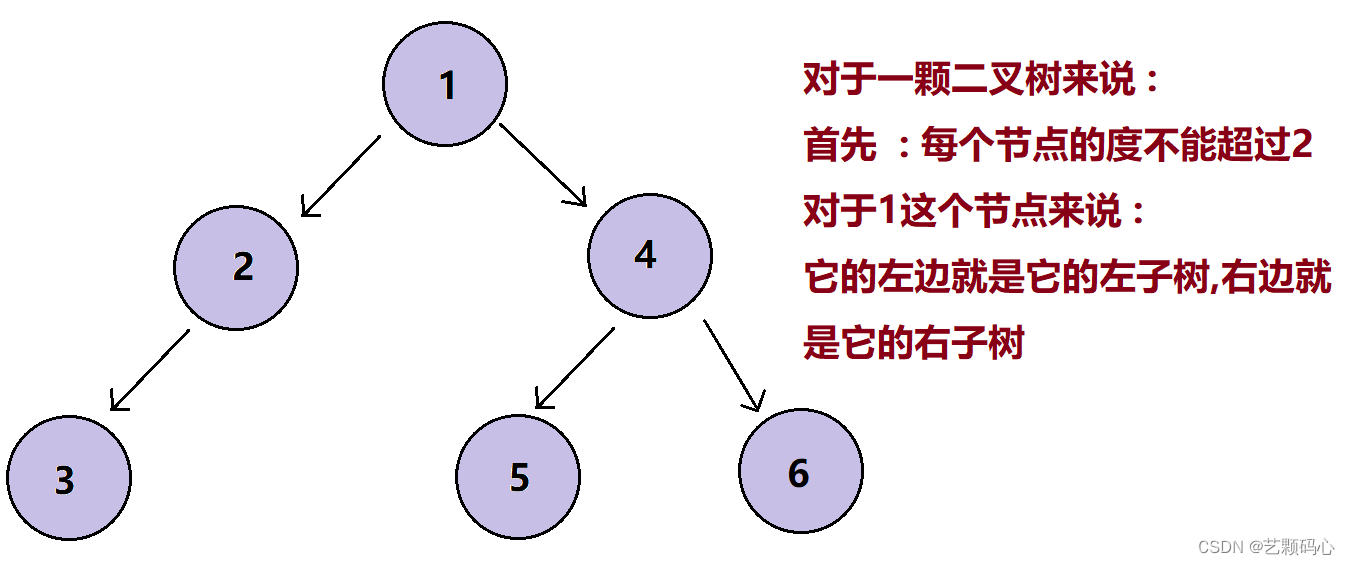
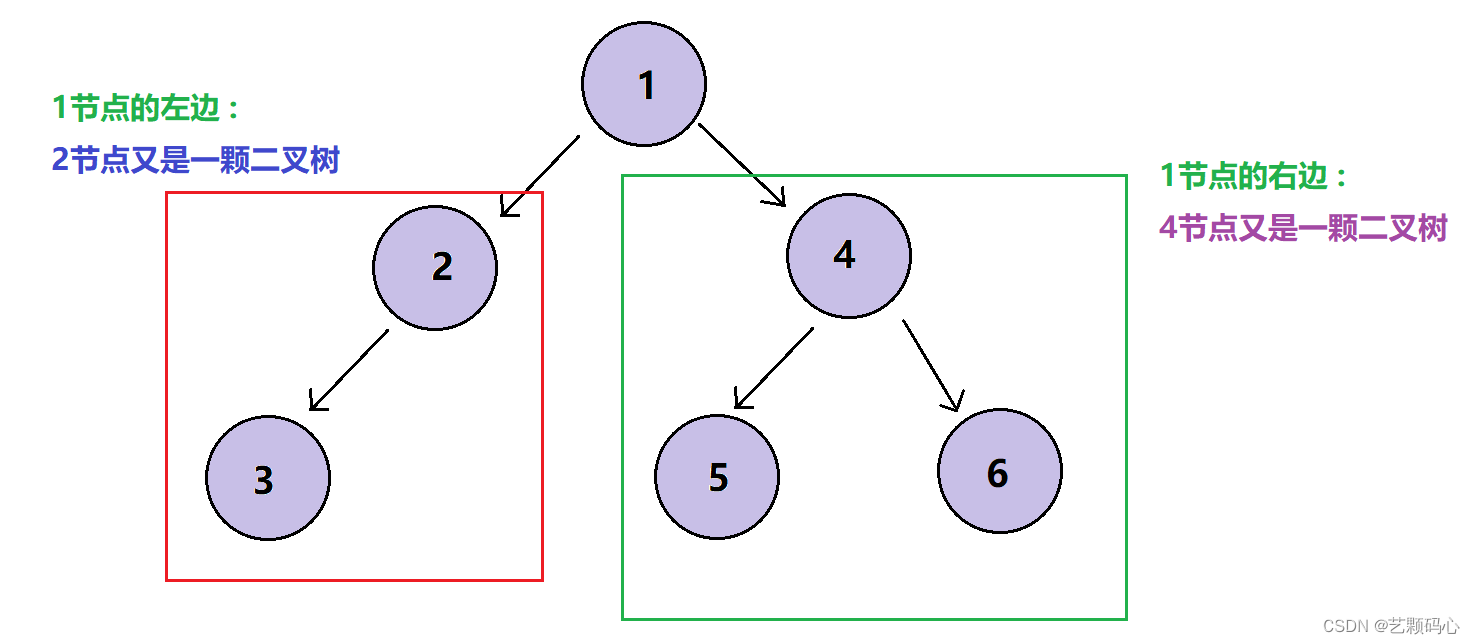
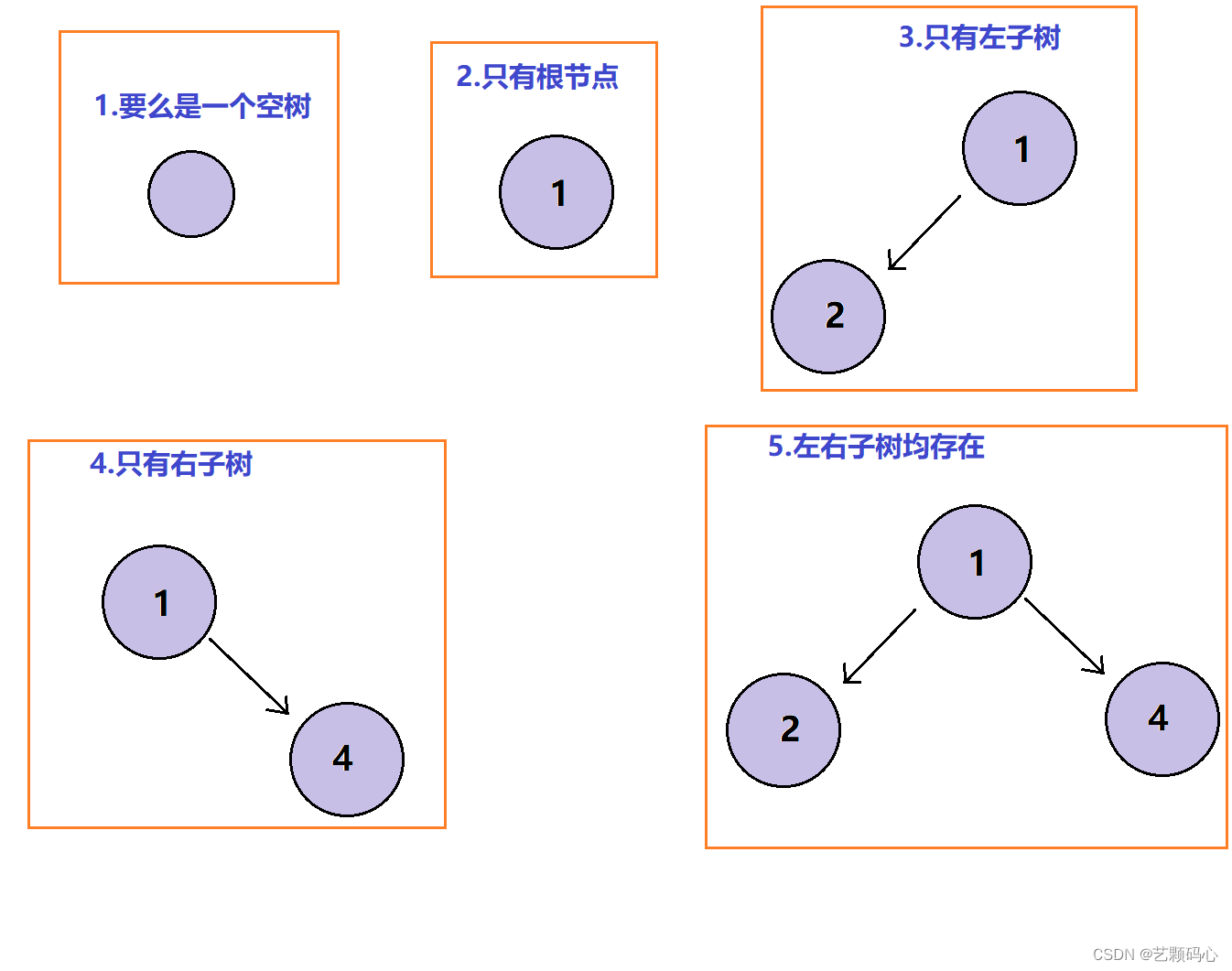
注意 : 对于任意二叉树都是由以下几种情况复合而成的 :
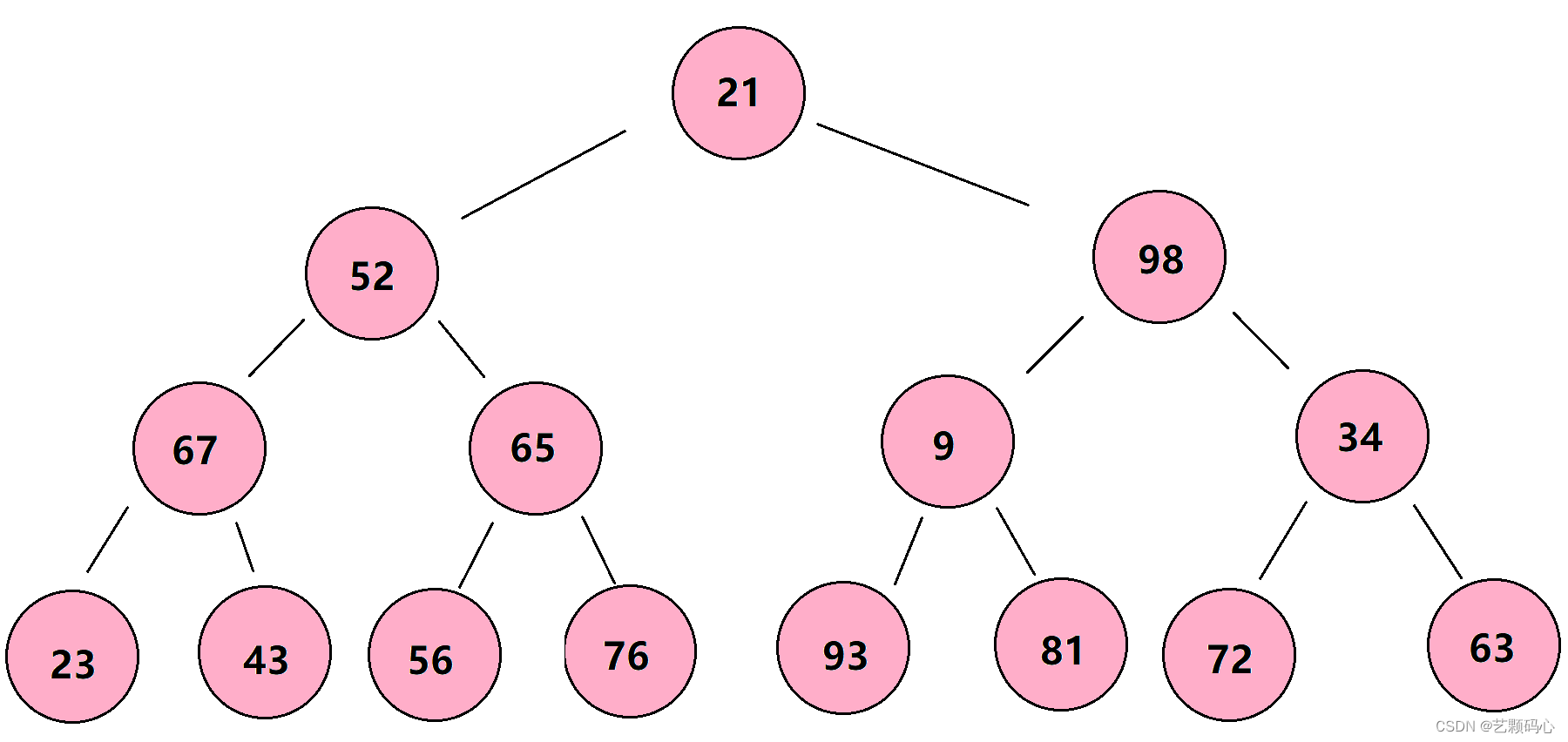
2. 两种特殊的二叉树
1.
满二叉树:
一棵二叉树,如果
每层的结点数都达到最大值,则这棵二叉树就是满二叉树
。也就是
说,
如果一棵
二叉树的层数为
K
,且结点总数是
2 ^ k - 1
,则它就是满二叉树
。
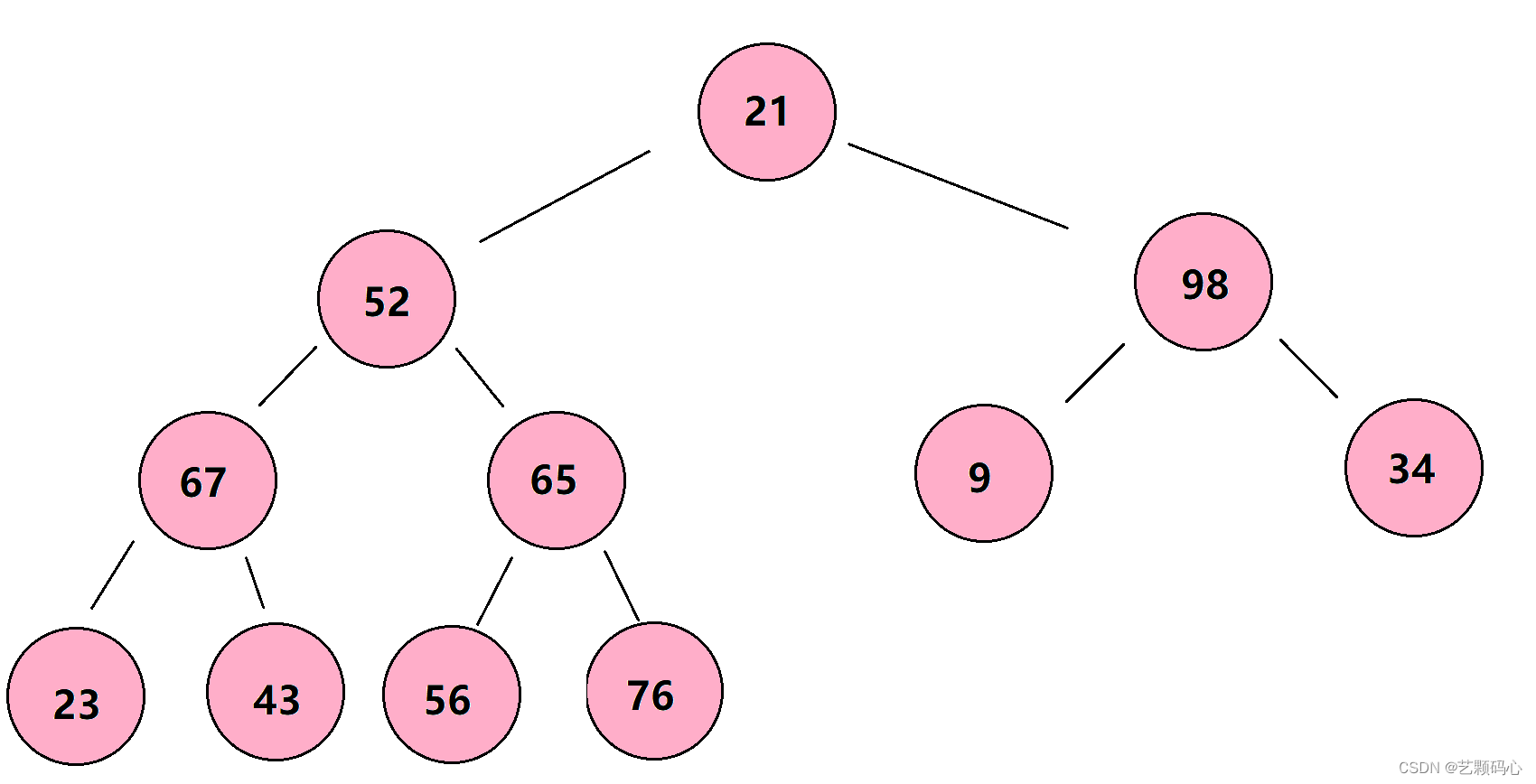
2.
完全二叉树:
完全二叉树是效率很高的数据结构,完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。对于深
度为
K
的 , 有
n 个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K
的满二叉树中编号从
0
至
n-1
的
结点一一对应时称之为完全二叉树。 要注意的是
满二叉树是一种特殊的完全二叉树
。

3. 二叉树的性质
1.
若规定
根结点的层数为
1
,则一棵
非空二叉树的第
i
层上最多有
2 ^ (i - 1) (i>0)个结点.
2.
若规定只有
根结点的二叉树的深度为
1
,则
深度为
K
的二叉树的最大结点数是
(2^k) - 1(k>=0)
3.
对任何一棵二叉树
,
如果其
叶结点个数为
n0,
度为
2
的非叶结点个数为
n2,
则有
n0
=
n2
+
1
4.
具有
n
个结点的完全二叉树的深度
k
为 log(n+1)
上取整
5. 对于具有n个结点的完全二叉树,如果按照从上至下从左至右的顺序对所有节点从0开始编号,则对于序号为i的结点有:
1. 若i>0
,
双亲序号:
(i-1)/2
;
i=0
,
i
为根结点编号
,无双亲结点
2. 若2i+1<n
,左孩子序号:
2i+1
,否则无左孩子
3. 若2i+2<n
,右孩子序号:
2i+2, 否则无右孩子
4. 二叉树的存储
二叉树的存储结构
分为:
顺序存储
和
类似于链表的链式存储
。
顺序存储用于堆中. 在这里我们使用链式存储
二叉树的遍历
1. 前序遍历
首先我们先用穷举的办法来建一个二叉树 :
为了方便操作 我们定义一个成员变量root
- public class TreeNode {
- static class Node {
- public int val;
- public Node left;
- public Node right;
-
- public Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
- Node root = null;
- //创建树
- public void createTree() {
- Node n1 = new Node(11);
- Node n2 = new Node(21);
- Node n3 = new Node(31);
- Node n4 = new Node(41);
- Node n5 = new Node(51);
- Node n6 = new Node(61);
- n1.left = n2;
- n1.right = n3;
- n2.left = n4;
- n2.right = n5;
- n3.right = n6;
- this.root = n1;
- }
- }

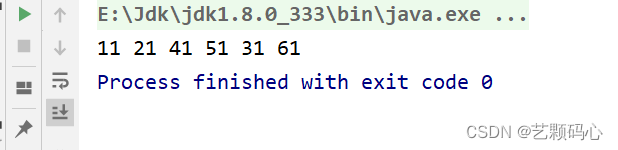
将上面的代码 图形化 :

前序遍历 : 根 左 右 依次去遍历

对于二叉树的遍历,使用递归是最好的办法
- package demo1;
-
- public class TreeNode {
- static class Node {
- public int val;
- public Node left;
- public Node right;
-
- public Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
- Node root = null;
- //创建树
- public Node createTree() {
- Node n1 = new Node(11);
- Node n2 = new Node(21);
- Node n3 = new Node(31);
- Node n4 = new Node(41);
- Node n5 = new Node(51);
- Node n6 = new Node(61);
- n1.left = n2;
- n1.right = n3;
- n2.left = n4;
- n2.right = n5;
- n3.right = n6;
- return n1;
- }
- public void preorder(Node root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- System.out.print(root.val + " ");
- preorder(root.left);
- preorder(root.right);
- }
- }
-
-
- package demo1;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode();
- TreeNode.Node root = treeNode.createTree();
- treeNode.preorder(root);
- }
- }

接下来我们来看一下OJ上这道前序遍历的题 : 144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(Leetcode)
- public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
-
- }
它的返回值类型是List<Integer>
解决的思路有两种 :
1. 遍历思路
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(Node root) {
- pre(root);
- return list;
- }
- public void pre(Node root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- list.add(root.val);
- pre(root.left);
- pre(root.right);
- }
2. 子问题思路
- public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(Node root) {
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- if (root == null) {
- return list;
- }
- list.add(root.val);
- List<Integer> left = preorderTraversal(root.left);
- list.addAll(left);
- List<Integer> right = preorderTraversal(root.right);
- list.addAll(right);
-
- return list;
- }
2. 中序遍历
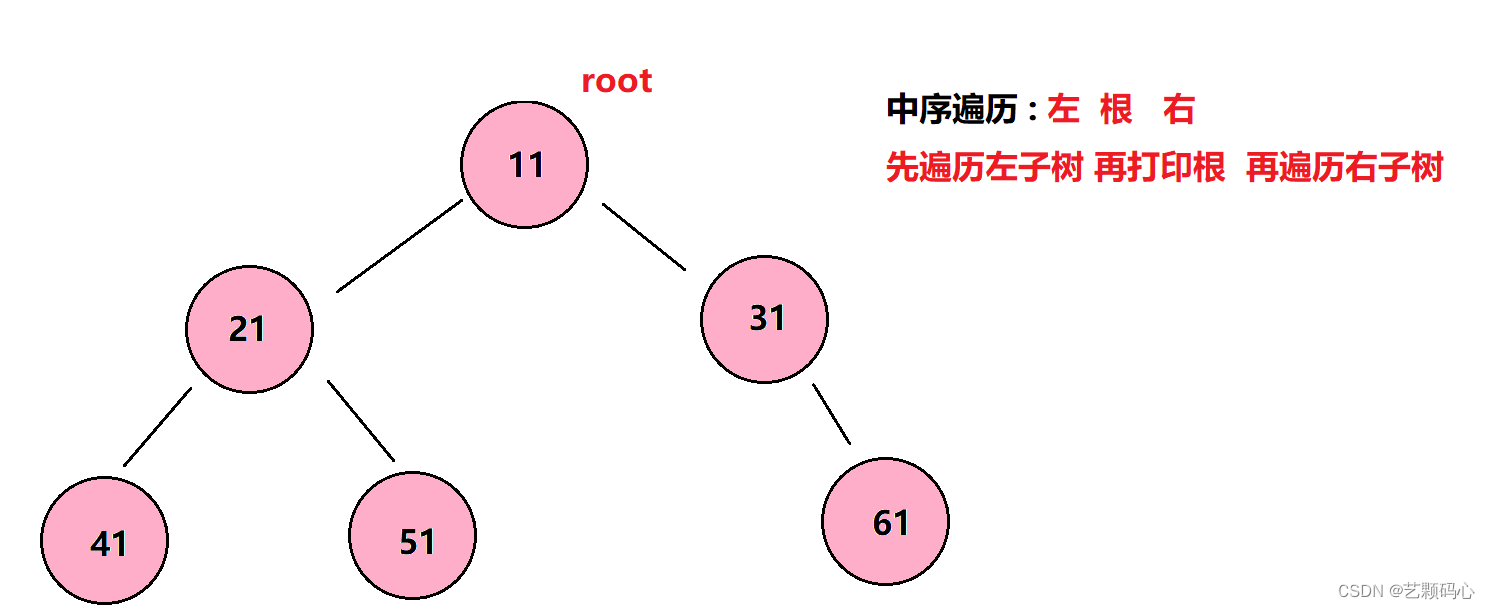
1. 遍历思路解决
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(Node root) {
- inorder(root);
- return list;
- }
- public void inorder(Node root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- inorder(root.left);
- list.add(root.val);
- inorder(root.right);
- }
2. 子问题思路解决
- public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- if (root == null) {
- return list;
- }
- List<Integer> left = inorderTraversal(root.left);
- list.addAll(left);
- list.add(root.val);
- List<Integer> right = inorderTraversal(root.right);
- list.addAll(right);
- return list;
- }
3 . 后序遍历
遍历思路 : 左 右 根
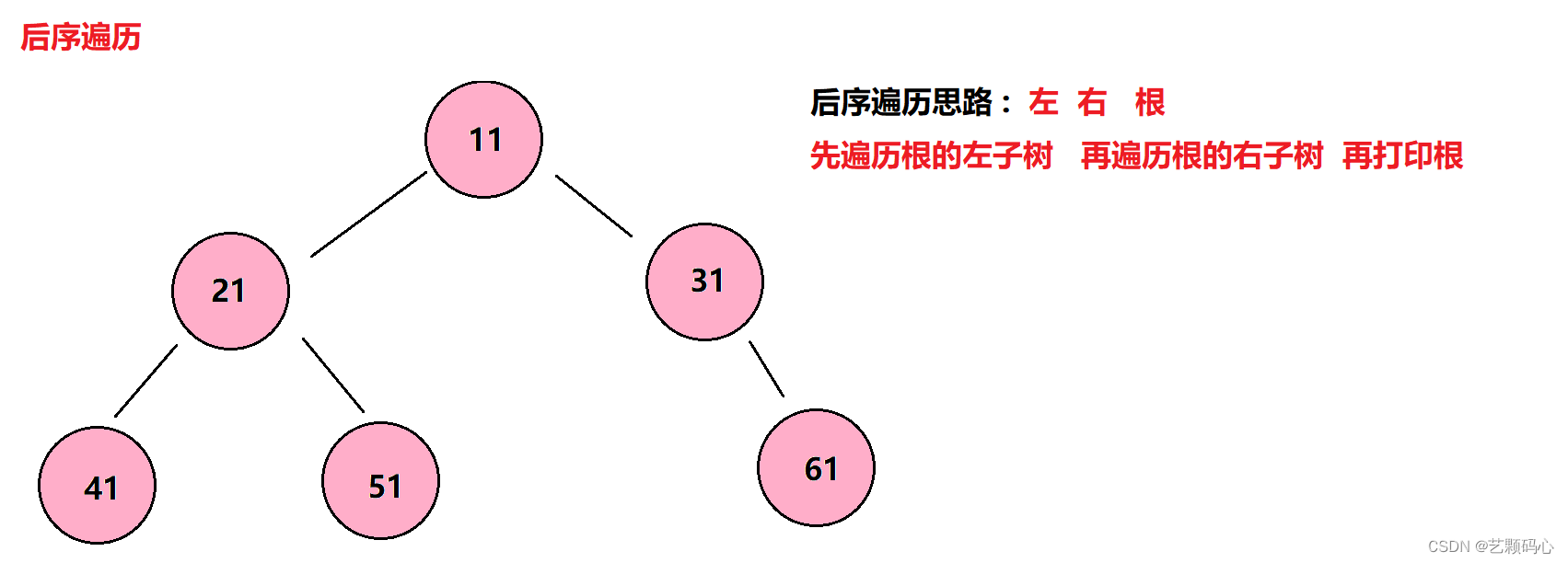
1. 遍历思路
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- postorder(root);
- return list;
- }
- public void postorder(TreeNode root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- postorder(root.left);
- postorder(root.right);
- list.add(root.val);
- }
2. 子问题思路
- public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- if (root == null) {
- return list;
- }
- List<Integer> left = postorderTraversal(root.left);
- list.addAll(left);
- List<Integer> right = postorderTraversal(root.right);
- list.addAll(right);
- list.add(root.val);
- return list;
- }
二叉树的基本操作
- package demo2;
-
- public class BinaryTree {
- static class Node {
- public int val;
- public Node left;
- public Node right;
-
- public Node(int val) {
- this.val = val;
- }
- }
- Node root = null;
- //创建树
- public Node createTree() {
- Node n1 = new Node(11);
- Node n2 = new Node(21);
- Node n3 = new Node(31);
- Node n4 = new Node(41);
- Node n5 = new Node(51);
- Node n6 = new Node(61);
- n1.left = n2;
- n1.right = n3;
- n2.left = n4;
- n2.right = n5;
- n3.right = n6;
- return n1;
- }
- int count = 0;
- // 获取树中节点的个数
- int size(Node root) {
- preorder(root);
- return count;
- }
- public void preorder(Node root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return;
- }
- count++;
- preorder(root.left);
- preorder(root.right);
- }
- // 获取叶子节点的个数
- // 子问题思路-求叶子结点个数
- int getLeafNodeCount(Node root) {
- if (root == null){
- return 0;
- }
- if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
- return 1;
- }
- return getLeafNodeCount(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount(root.right);
- }
-
- // 获取第K层节点的个数
- int getKLevelNodeCount(Node root,int k) {
- if (root == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- if (k == 1) {
- return 1;
- }
- return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);
- }
- // 获取二叉树的高度
- int getHeight(Node root) {
- if (root == null) {
- return 0;
- }
- int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
- int rightHeight = getHeight(root.left);
- return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
- }
- // 检测值为value的元素是否存在
- Node find(Node root, int val) {
- if (root == null) {
- return null;
- }
- if (root.val == val) {
- return root;
- }
- Node left = find(root.left,val);
- if (left != null) {
- return left;
- }
- Node right = find(root.right,val);
- if (right != null) {
- return right;
- }
- return null;
- }
- }

- package demo2;
-
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
- BinaryTree.Node root = binaryTree.createTree();
- System.out.print("树的节点个数 : ");
- System.out.println(binaryTree.size(root));
- System.out.print("树的叶子节点个数 : ");
- System.out.println(binaryTree.getLeafNodeCount(root));
- System.out.print("第3层的节点个数 : ");
- System.out.println(binaryTree.getKLevelNodeCount(root,3));
- System.out.print("树的高度 : ");
- System.out.println(binaryTree.getHeight(root));
- System.out.println("找到21这个节点 : ");
- BinaryTree.Node node = binaryTree.find(root,21);
- System.out.println(node.val);
- }
- }


层序遍历
思路 : 从上往下 从左往右 依次遍历
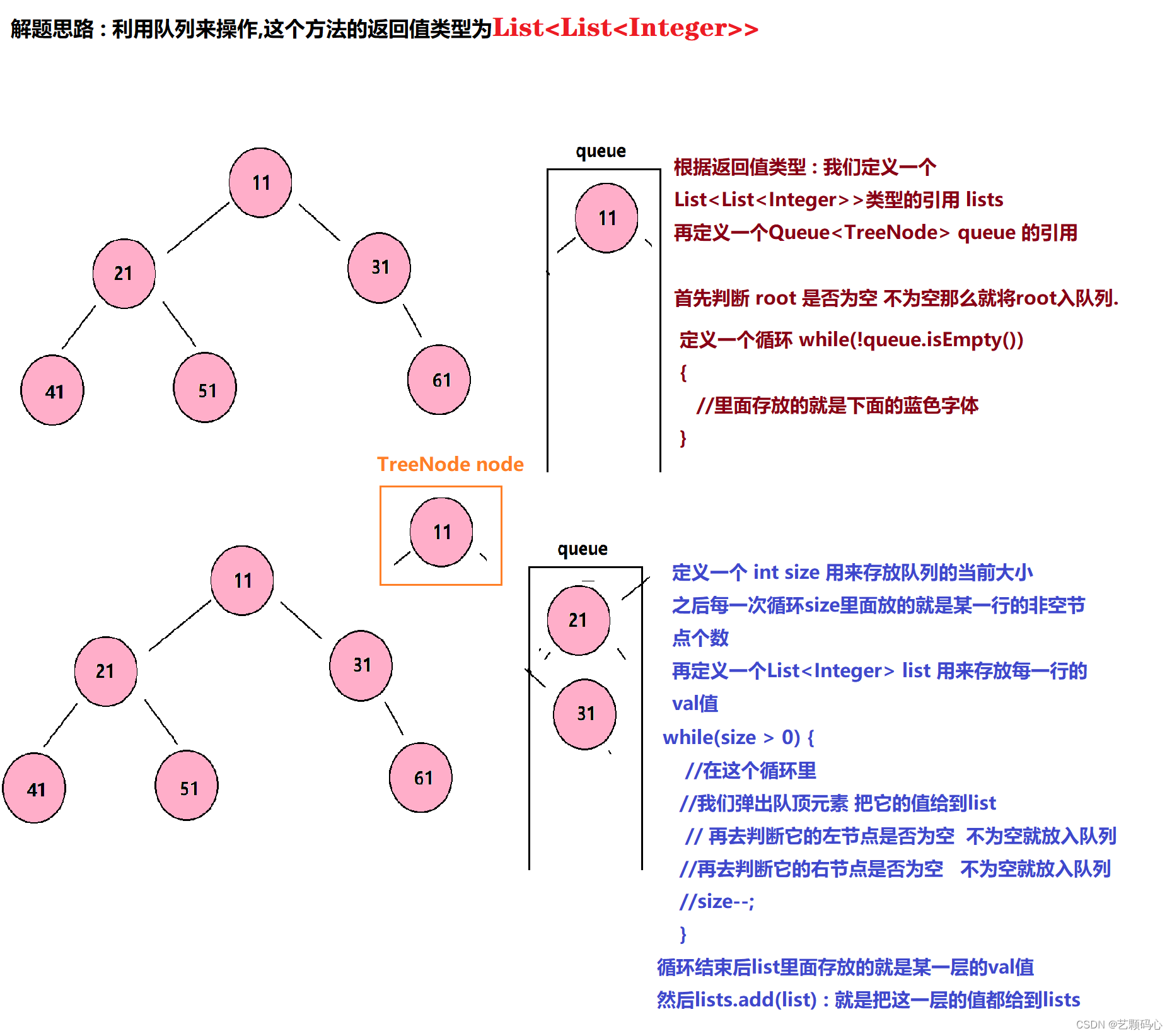
- public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
- List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>();
- Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
- if (root != null) {
- queue.offer(root);
- }
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- int size = queue.size();
- List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- while (size-- > 0) {
- TreeNode node = queue.poll();
- list.add(node.val);
- if (node.left != null) {
- queue.offer(node.left);
- }
- if (node.right != null) {
- queue.offer(node.right);
- }
- }
- lists.add(list);
- }
- return lists;
- }

判断完全二叉树
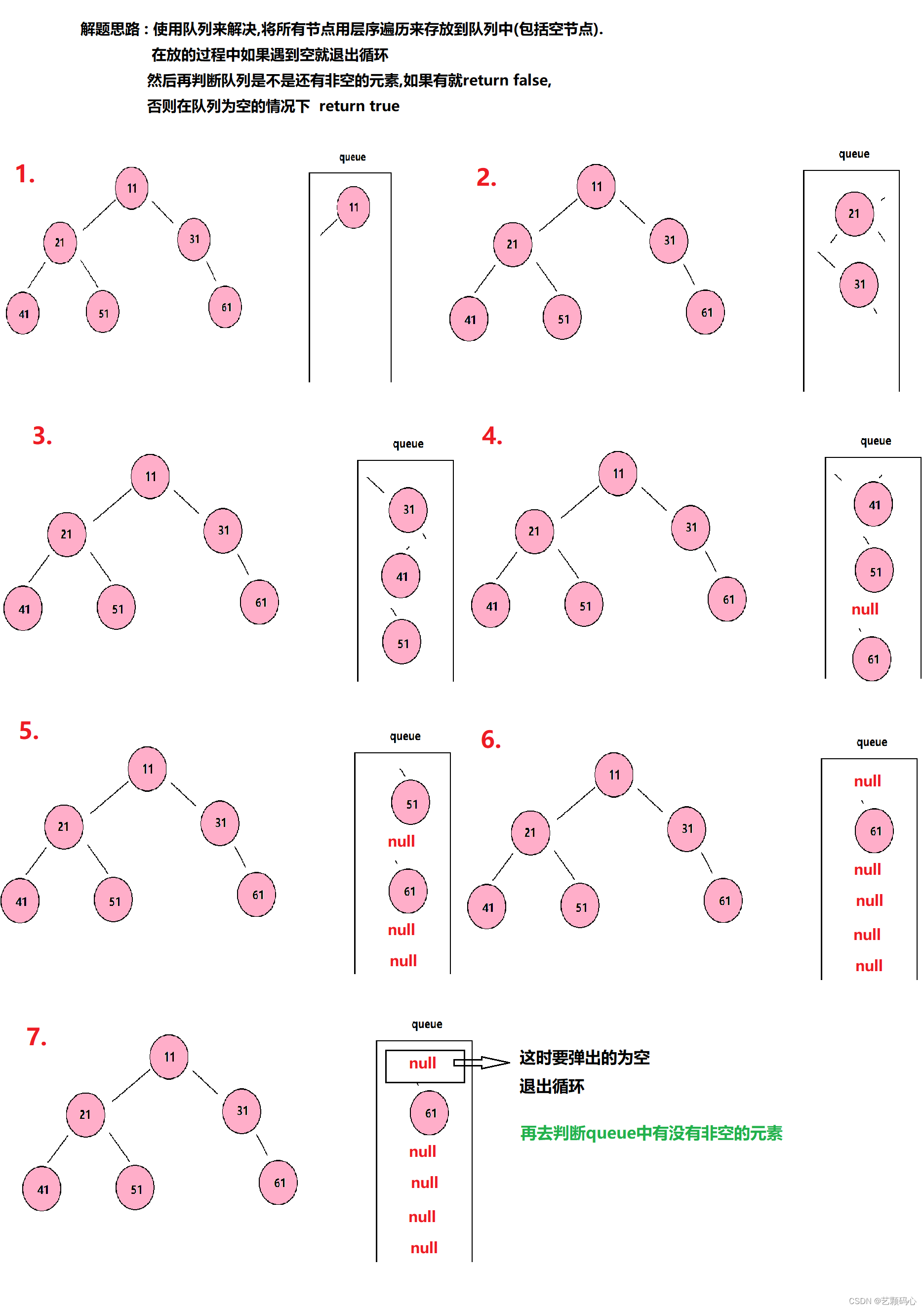
- // 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
- boolean isCompleteTree(Node root) {
- Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
- if (root == null) {
- return true;
- }
- queue.offer(root);
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- BinaryTree.Node node = queue.poll();
- if (node == null) {
- break;
- }
- queue.offer(node.left);
- queue.offer(node.right);
- }
- while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
- if (queue.poll() != null) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }

希望可以帮到大家~~~~~
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/你好赵伟/article/detail/737590
推荐阅读
相关标签


