- 1VS2015+QT5.9.2开发一个adb_tool.exe工具(二)_com.tencent.qqmusic.third.dispacheractivityforthir
- 2TCP三次握手详解:传输控制块TCB以及积极和消极的连接建立方式
- 3来自异国的客人【华为OD机试JAVA&Python&C++&JS题解】_有位客人来自异国,在该国使用m进制计数
- 4MAC - Burpsuite+Proxifier实现小程序抓包_mac 小程序抓包
- 5Python爬虫:教你四种姿势解析提取数据_python爬数据
- 6MySQL大表优化方案(应该是最完整最全的了)_mysql大表查询优化方案
- 7Android Studio Build窗口出现中文乱码问题_android studio 乱码
- 8[SD必备知识18]修图扩图AI神器:ComfyUI+Krita加速修手抽卡,告别低效抽卡还原光滑细腻双手,写真无需隐藏手势_comfyui 手部修复
- 9Maven构建JavaWeb项目_首先,使用maven构建一个基本的java web项目,添加servlet和mybatis的依赖。
- 10sql查看各表大小
读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock源码分析
赞
踩
一、ReentrantReadWriteLock结构


二、读写状态的设计
设计的精髓:用一个变量如何维护多种状态 在 ReentrantLock 中,使用 Sync ( 实际是 AQS )的 int 类型的 state 来表示同步状态,表示锁被一个线程重复获取的次数。但是,读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 内部维护着一对读写锁,如果要用一个变量维护多种状态,需要采用“按位切割使用”的方式来维护这个变量,将其切分为两部分:高16为表示读,低16为表示写。
分割之后,读写锁是如何迅速确定读锁和写锁的状态呢?通过位运算。假如当前同步状态为S,那么:
- 写状态,等于 S & 0x0000FFFF(将高 16 位全部抹去)。 当写状态加1,等于S+1.
- 读状态,等于 S >>> 16 (无符号补 0 右移 16 位)。当读状态加1,等于S+(1<<16),也就是S+0x00010000
根据状态的划分能得出一个推论:S不等于0时,当写状态(S&0x0000FFFF)等于0时,则读状态(S>>>16)大于0,即读锁已被获取。

代码实现:java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock.Sync

- exclusiveCount(int c) 静态方法,获得持有写状态的锁的次数。
- sharedCount(int c) 静态方法,获得持有读状态的锁的线程数量。不同于写锁,读锁可以同时被多个线程持有。而
每个线程持有的读锁支持重入的特性,所以需要对每个线程持有的读锁的数量单独计数,这就需要用到 HoldCounter 计数器
三、HoldCounter 计数器
读锁的内在机制其实就是一个共享锁。一次共享锁的操作就相当于对HoldCounter 计数器的操作。获取共享锁,则该计数器 + 1,释放共享锁,该计数器 - 1。只有当线程获取共享锁后才能对共享锁进行释放、重入操作。

通过 ThreadLocalHoldCounter 类,HoldCounter 与线程进行绑定。HoldCounter 是绑定线程的一个计数器,而 ThreadLocalHoldCounter 则是线程绑定的 ThreadLocal。
HoldCounter是用来记录读锁重入数的对象ThreadLocalHoldCounter是ThreadLocal变量,用来存放不是第一个获取读锁的线程的其他线程的读锁重入数对象
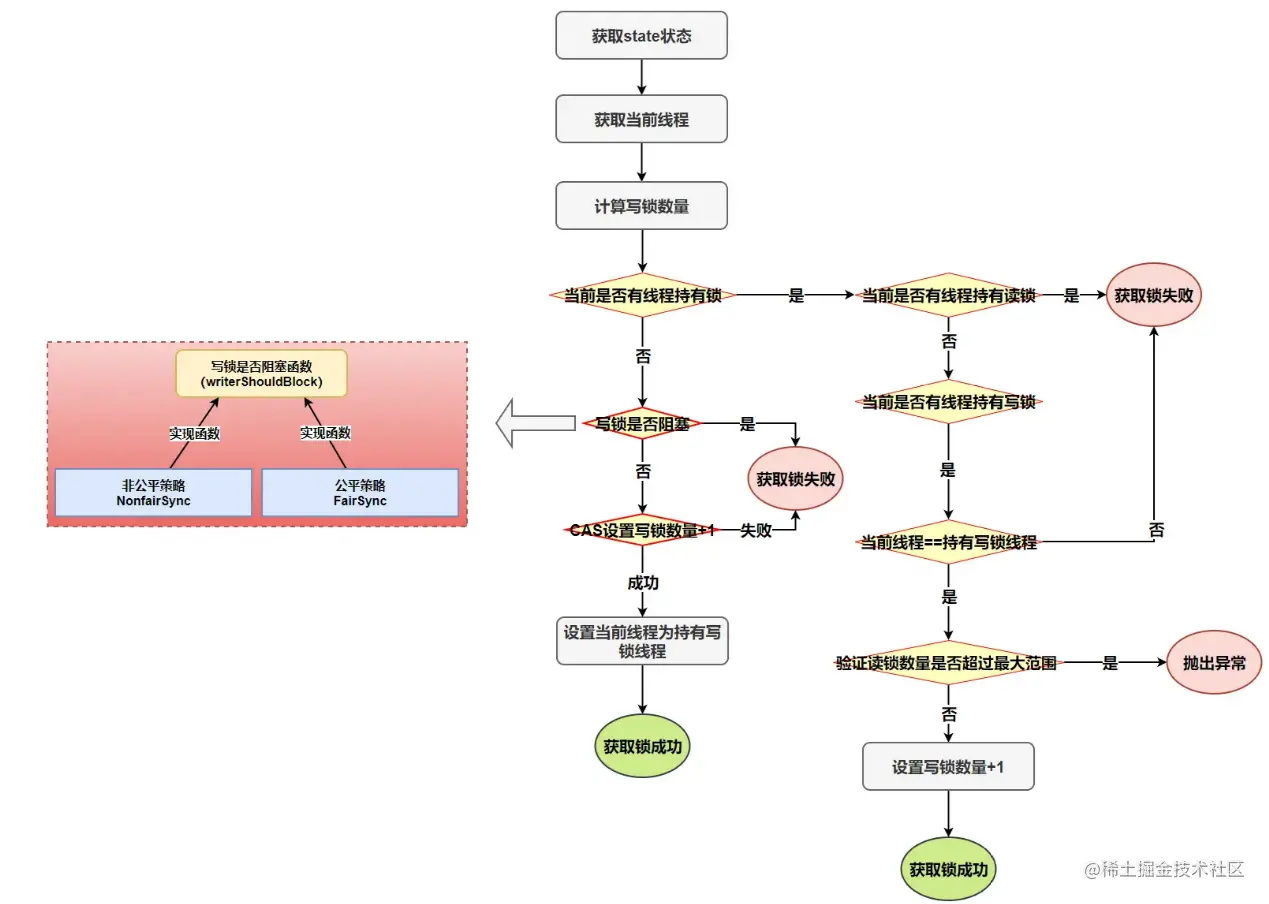
四、写锁的获取
写锁是一个支持重进入的排它锁。如果当前线程已经获取了写锁,则增加写状态。如果当前线程在获取写锁时,读锁已经被获取(读状态不为0)或者该线程不是已经获取写锁的线程, 则当前线程进入等待状态。
写锁的获取是通过重写AQS中的tryAcquire方法实现的。
- protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
- //当前线程
- Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
- //获取state状态 存在读锁或者写锁,状态就不为0
- int c = getState();
- //获取写锁的重入数
- int w = exclusiveCount(c);
- //当前同步状态state != 0,说明已经有其他线程获取了读锁或写锁
- if (c != 0) {
- // c!=0 && w==0 表示存在读锁
- // 当前存在读锁或者写锁已经被其他写线程获取,则写锁获取失败
- if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
- return false;
- // 超出最大范围 65535
- if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
- throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
- //同步state状态
- setState(c + acquires);
- return true;
- }
- // writerShouldBlock有公平与非公平的实现, 非公平返回false,会尝试通过cas加锁
- //c==0 写锁未被任何线程获取,当前线程是否阻塞或者cas尝试获取锁
- if (writerShouldBlock() ||
- !compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
- return false;
-
- //设置写锁为当前线程所有
- setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
- return true;
- 复制代码

通过源码我们可以知道:
- 读写互斥
- 写写互斥
- 写锁支持同一个线程重入
- writerShouldBlock写锁是否阻塞实现取决公平与非公平的策略(FairSync和NonfairSync
五、写锁的释放
写锁释放通过重写AQS的tryRelease方法实现
- protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
- //若锁的持有者不是当前线程,抛出异常
- if (!isHeldExclusively())
- throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
- int nextc = getState() - releases;
- //当前写状态是否为0,为0则释放写锁
- boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
- if (free)
- setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
- setState(nextc);
- return free;
- 复制代码

六、读锁的获取
实现共享式同步组件的同步语义需要通过重写AQS的tryAcquireShared方法和tryReleaseShared方法。读锁的获取实现方法为:
- protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
- Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
- int c = getState();
- // 如果写锁已经被获取并且获取写锁的线程不是当前线程,当前线程获取读锁失败返回-1 判断锁降级
- if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
- getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
- return -1;
- //计算出读锁的数量
- int r = sharedCount(c);
- /**
- * 读锁是否阻塞 readerShouldBlock()公平与非公平的实现
- * r < MAX_COUNT: 持有读锁的线程小于最大数(65535)
- * compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT) cas设置获取读锁线程的数量
- */
- if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
- r < MAX_COUNT &&
- compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { //当前线程获取读锁
-
- if (r == 0) { //设置第一个获取读锁的线程
- firstReader = current;
- firstReaderHoldCount = 1; //设置第一个获取读锁线程的重入数
- } else if (firstReader == current) { // 表示第一个获取读锁的线程重入
- firstReaderHoldCount++;
- } else { // 非第一个获取读锁的线程
- HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
- if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
- cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
- else if (rh.count == 0)
- readHolds.set(rh);
- rh.count++; //记录其他获取读锁的线程的重入次数
- }
- return 1;
- }
- // 尝试通过自旋的方式获取读锁,实现了重入逻辑
- return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
- 复制代码

七、读锁的释放
获取到读锁,执行完临界区后,要记得释放读锁(如果重入多次要释放对应的次数),不然会阻塞其他线程的写操作。
读锁释放的实现主要通过方法tryReleaseShared:
- protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
- Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
- //如果当前线程是第一个获取读锁的线程
- if (firstReader == current) {
- // assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
- if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
- firstReader = null;
- else
- firstReaderHoldCount--; //重入次数减1
- } else { //不是第一个获取读锁的线程
- HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
- if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
- rh = readHolds.get();
- int count = rh.count;
- if (count <= 1) {
- readHolds.remove();
- if (count <= 0)
- throw unmatchedUnlockException();
- }
- --rh.count; //重入次数减1
- }
- for (;;) { //cas更新同步状态
- int c = getState();
- int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
- if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
- // Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
- // but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
- // both read and write locks are now free.
- return nextc == 0;
- }
- 复制代码


- 读锁共享,读读不互斥
- 读锁可重入,每个获取读锁的线程都会记录对应的重入数
- 读写互斥,锁降级场景除外
- 支持锁降级,持有写锁的线程,可以获取读锁,但是后续要记得把读锁和写锁读释放
- readerShouldBlock读锁是否阻塞实现取决公平与非公平的策略(FairSync和NonfairSync)



