- 1Parallels® Desktop 19 for Mac在 Mac 上运行 Windows,简单,强大,无缝。_pd19
- 2Android12上实现双以太网卡共存同时访问外网_android 12 以太网与wifi共存修改
- 3AI的Prompt是什么_aiprompt
- 4Android实战技巧之十六:getprop与dumpsys命令
- 5映美精黑白相机IFrameQueueBuffer转halcon的HObject
- 6跌倒检测算法笔记
- 7【HarmonyOS】根据文本内容动态测算文本控件宽高_鸿蒙 获取控件宽度
- 8Java之 Spring Cloud 微服务搭建网关SpringCloud Gateway微服务网关GateWay(第三个阶段)【二_java spring boot 自己实现gateway
- 92019CVPR单目深度估计综述_recurrent neural network for (un-) supervised lear
- 10Docker学习笔记 —— Dockerfile_dockerfile 提取文件名
java温习——2024年5月2日_2024学java学8还是21
赞
踩
1.java下载
作用:编程语言,下载了才可以进行编程
其实项目学习基本java8够用了,用最新的稳定版java21也可以。
下载地址
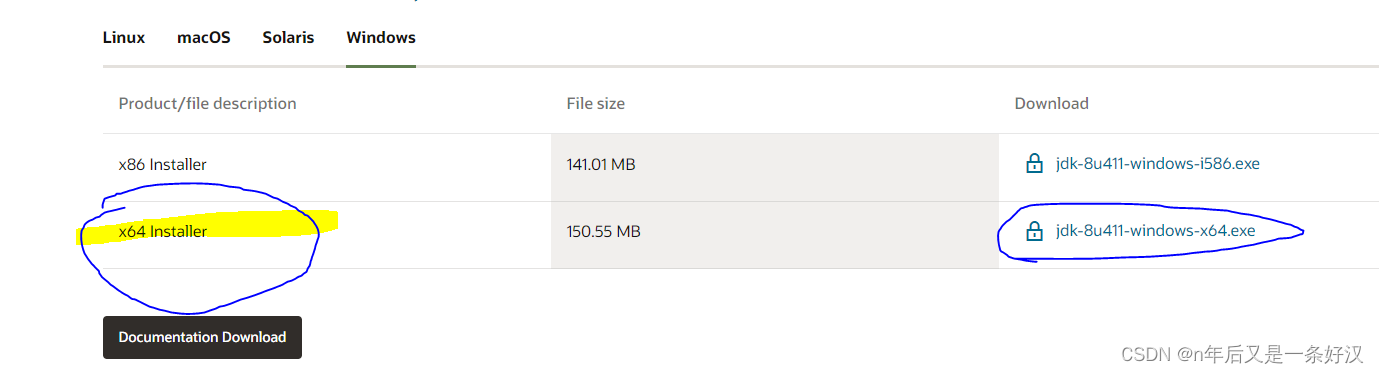
网盘自取:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qx8Fpi8rKnA0lYAvnW60kA?pwd=w9kr 提取码: w9kr 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
配置环境变量
变量值因路径而不同。
原因:可以在任意目录下使用java javac 命令
JAVA_HOME 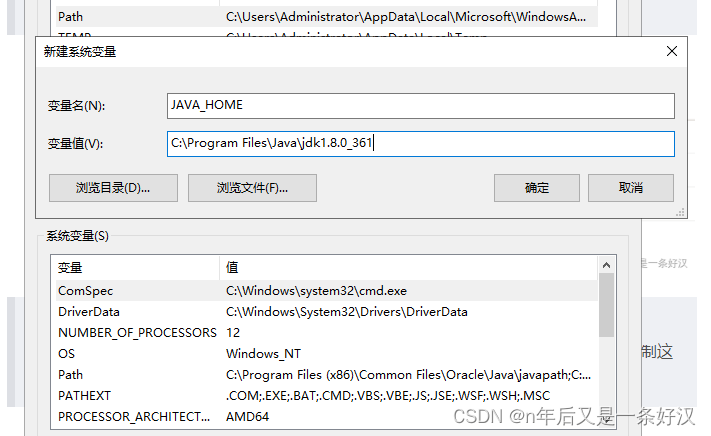
%JAVA_HOME%\bin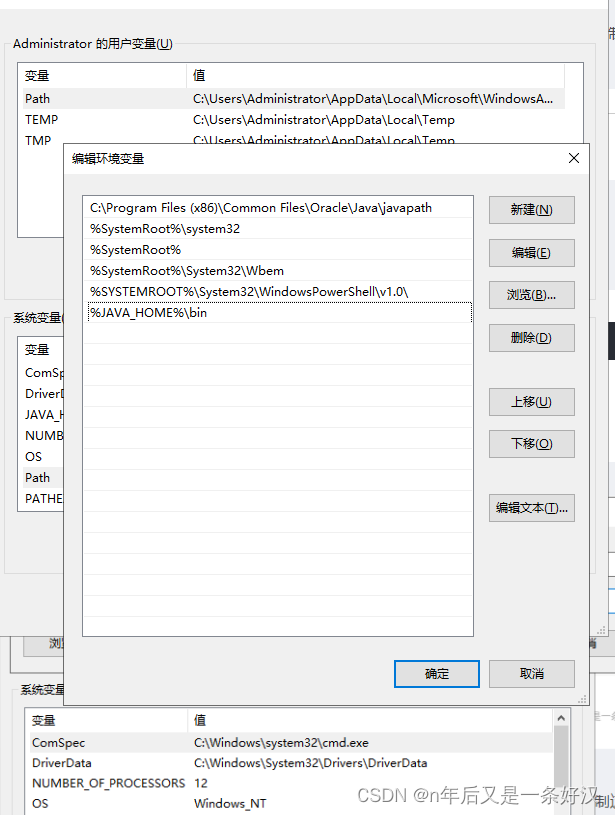
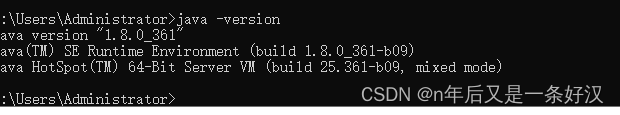
验证是否安装成功
cmd窗口打开
2.idea下载
作用:方便进行java编程的工具
安装idea前提是java环境需要配置好,否则打不开idea
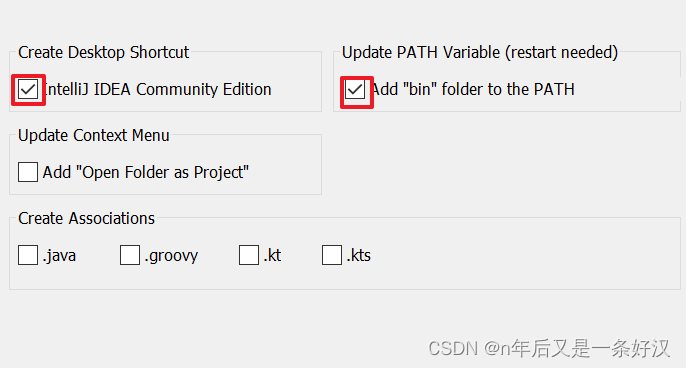
记得勾选
全局配置: (一定是首页面进行的配置才是全局配置)
1.编码配置UTF-8
2.
idea使用:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1UleEXSaZQgLap8G5yukhnQ?pwd=envy
提取码:envy
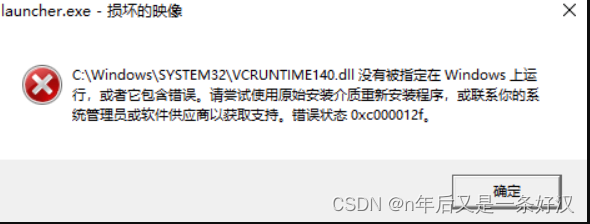
idea打不开的情况
解决办法:(如果你是学生的话就不要安装什么dll修复工具,很多都是收费的)
可能是电脑的MICROSOFT VISUAL C++ 2019 RUNTIME 损坏了 需要修复
由于我这里丢失了 所以没有 需要下载微软修复软件进行修复
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/16KZzWvV7PO9bxfOYuLQnkw?pwd=gayt
提取码:gayt
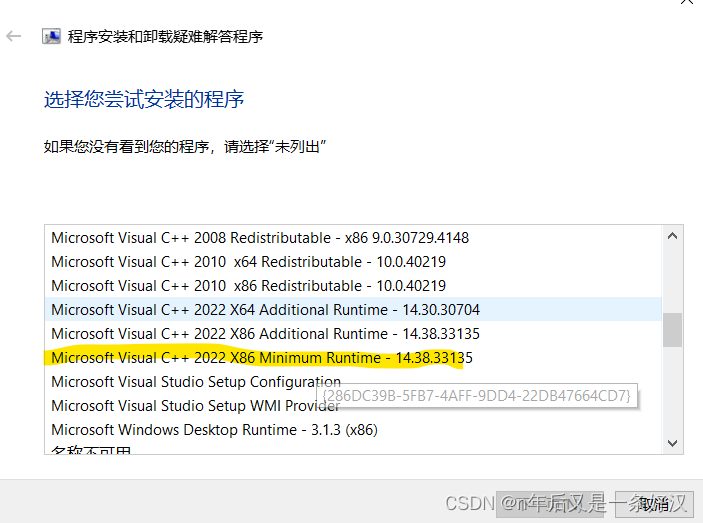
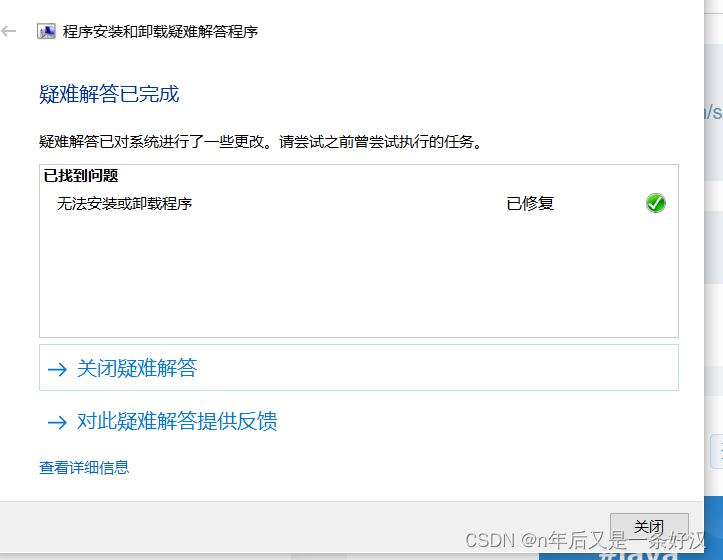
然后就可以找到有问题的组件进行修复就可以了,根据自己的问题选择
2.1 idea的配置
3. javaSE基础学习
3.1 git使用
可以将自己写的代码放到网上,将写的代码放上去,然后还可以进行修改,保存。别人也可以看到。这样你写的代码就都可以在上面看到了
1.下载git Git - 下载软件包 (git-scm.com)
2.双击安装,我习惯安装到空间足够大的盘符
3.配置git
3.1鼠标右键进入open git bash here
输入命令
- # 配置用户名
- git config --global user.name "huang" //(输入你自己的名字)
- # 配置邮箱
- git config --global user.email "qq号码@qq.com" //(注册账号时用的邮箱,输入你自己的)
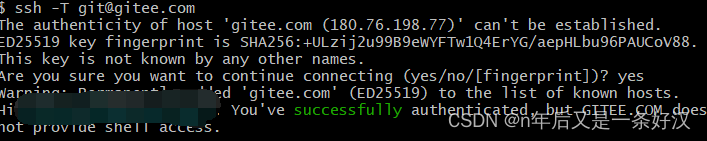
3.2配置ssh免密登录,就是每次登录不需要输入密码进行认证了
- # ssh免密登录
- ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "(qq号码)@qq.com" // 输入你自己的qq号码
- # 然后连续三次回车。 用户目录下会有 id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub
- # 查看密钥
- cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
- # 然后登录进入 gitee,在设置里面找到 SSH KEY 将id_rsa.pub 文件的密钥内容粘贴进去
- # 使用 ssh -T git@gitee.com 测试是否成功即可 注意第二个回车需要输入yes后在回车
- ssh -T git@gitee.com
4.然后我们去gitee去初始化一个仓库,用于存放我们开发的代码
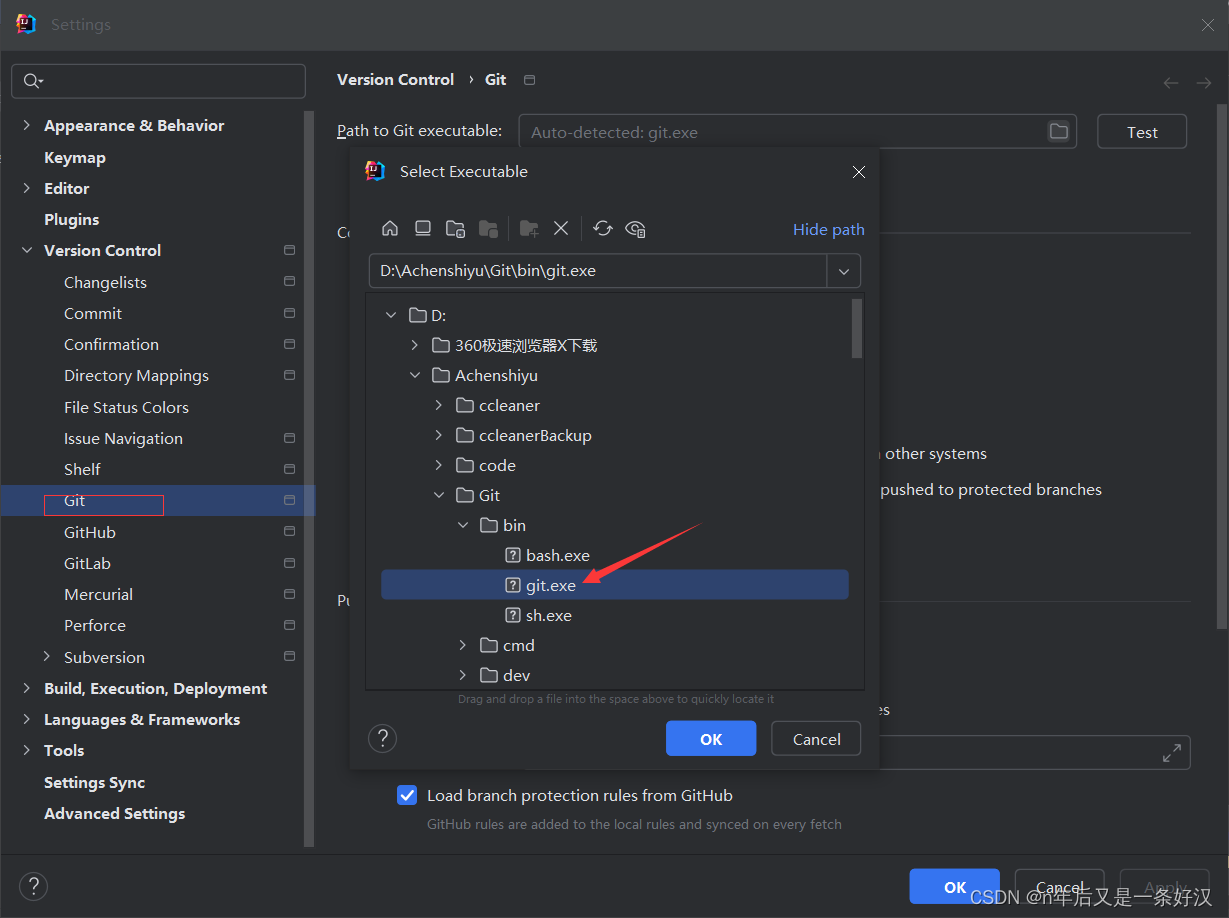
5.通过idea克隆到本地,idea配置git
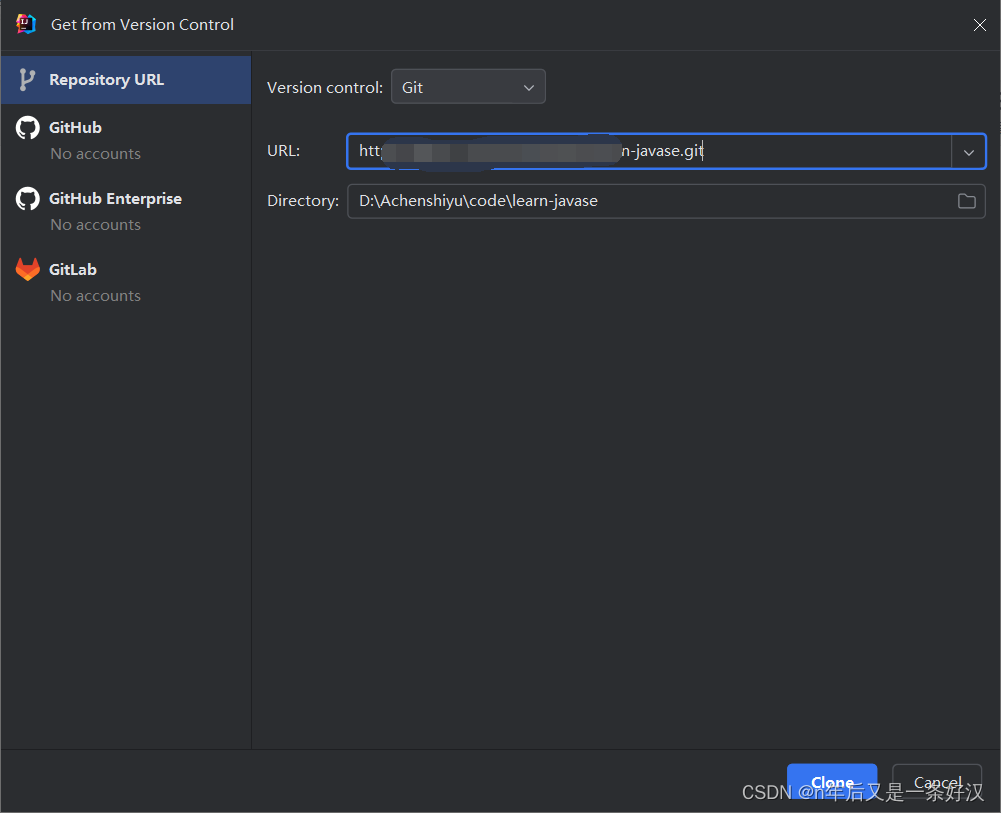
6.克隆gitee仓库
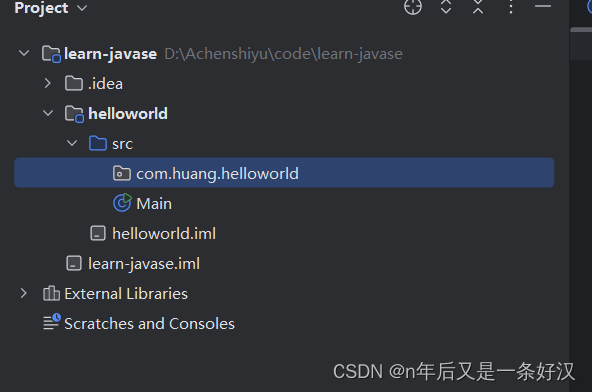
3.2 idea的HelloWorld
这部分较好理解,所以精简
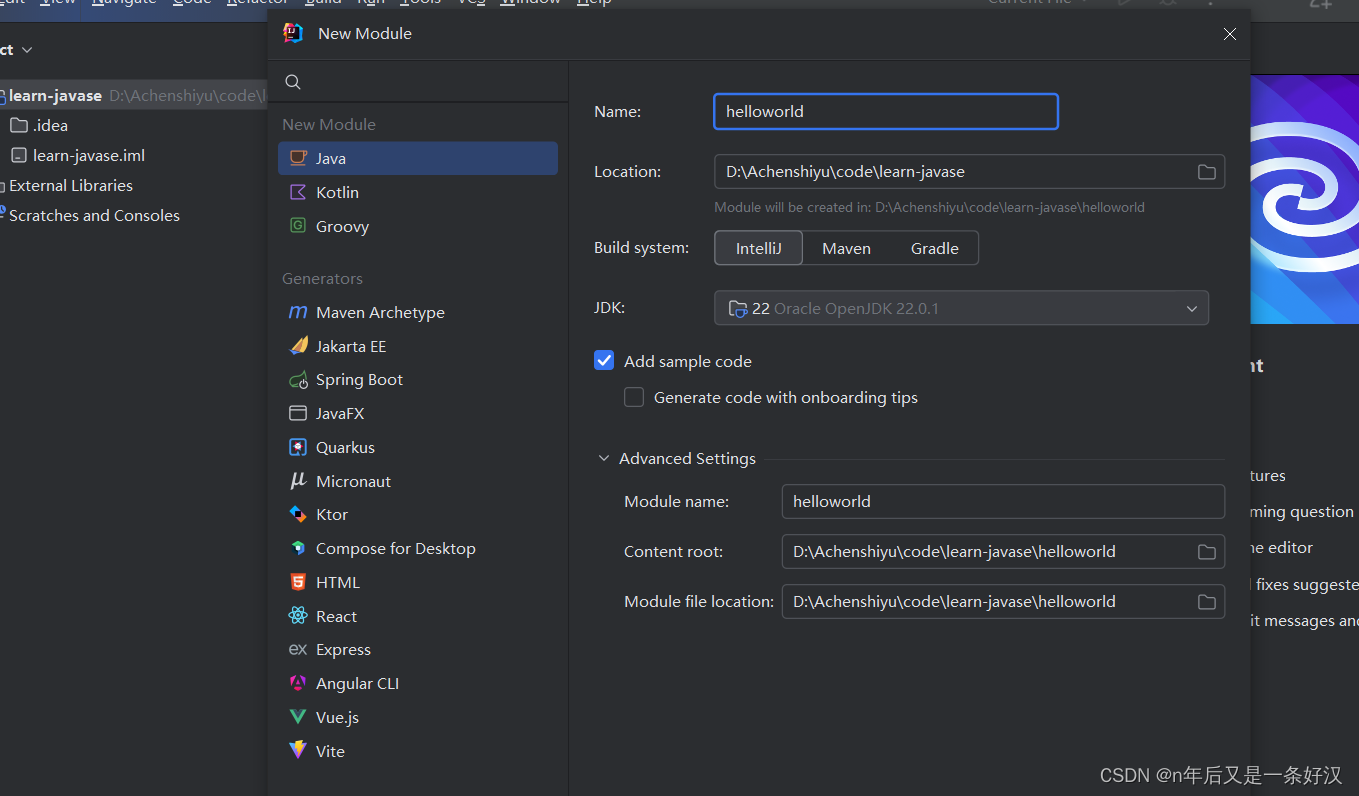
打开idea,然后创建工程,配置idea的jdk环境
首先创建工程和模块这些需要注意的是:创建顺序
- project工程(app)
- module模块(具体功能)
- package包(分类)
- class类(代码编写)
1.在idea中以及有一个空的工程learn-javase,至于这个工程具体是做什么的可以后面在这个工程里创建对应的模块
至于命名规则: 非强制性要求,可以随便命名,只不过这样命名容易理解
工程project表示做的这个工程是干什么的,比如学习javaSE的就可以这样命名:learn-javase
2.创建模块 在idea中file新建module 命名为helloworld
3.建包 在src中 命名为com.域名.功能名
比如,com.huang.helloworld
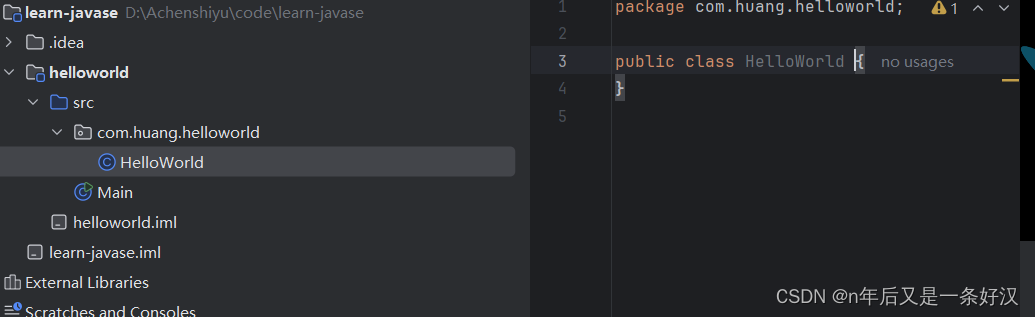
4.在包package里面建类 HelloWorld ,后面不需要加.java后缀了,因为idea自动加了。至于首字母为什么大写,规定。大驼峰命名法,并且类名要和文件名一致。
完整代码
右键在此代码页面然后运行即可
5. 提交到git
5.1 设置忽略不需要的提交的文件.gitignore
提交之前需要忽略的内容如下
- # 设置一些不需要提交的文件
- # **/ 表示父目录的任意目录下的名字为mvnw文件不会上传
- **/mvnw
- **/mvnw.cmd
- **/.gitignore
- **/.mvn
- **/target/
- .idea
这样gitee上就有了你写的所有代码了
3.3注释
- /**
- 学习目的:学习使用注释
- 1.什么是注释
- 写在程序中对程序进行解释说明的文字
- 2.java程序中书写注释的方式有几种,各有什么不同
- 单行注释://
- 多行注释:*/ /* */ /*
- 文档注释:*/ /** */ /*
- 3.注释有什么特点
- 不影响程序的执行,编译后的class文件中已经没有注释了
- 4.注释的快捷键是
- ctrl+/ 单行注释(对当前行进行注释)
- ctrl+shift+/ 多行注释(会将选中的内容进行注释)
- */
- public class annotation_01 {
- //这是一个main程序,是程序的主入口
- public static void main(String[] args){
- //输出语句,会将引号里面的内容在控制台打印输出
- System.out.println("学习注释的使用");
-
- //这是单行注释
-
- /*
- 这是多行注释
- */
-
- /**
- 这是文档注释
- */
- }
- }

3.4字面量
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 1.字面量是什么
- 数据在程序中的书写格式
- 2.字符、字符串在程序中的书写格式有什么要求
- 字符必须用单引号围起来,有且只有一个字符
- 字符串必须用双引号围起来
- 3.几个常见的特殊值的书写格式是
- true false null /n /t
- */
- public class Literals_01 {
- public static void main(String[] args){
- //整数
- System.out.println(1);
- System.out.println(-1);
- //小数
- System.out.println(0.11);
- //字符
- System.out.println(' ');
- System.out.println('a');
- System.out.println('1');
- //补全当前字符串长度至8的整数倍,根据当前字符串长度补1~8个空格
- System.out.println('\t'+"石");
- //换行
- System.out.println('\n');
- System.out.println('荒');
-
- //字符串
- System.out.println("");
- System.out.println("你");
- System.out.println("你好呀");
- //布尔值
- System.out.println(true);
- System.out.println(false);
- //null
- String s = null;
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }

*关键字和标识符
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 什么是关键字
- 关键字就是java自己要用到的词,并且有特殊含义的一些词,我们就不能用来作为:类名,变量名,否则就会报错
- 什么是标识符
- 标识符就是名字
- 标识符的规则:由字母、数字、下划线、美元符等组成,且不能以数字开头,不能用关键字作为名字
- */
- public class KeywordAndIdentifierDemo {
- public static void main(String args[]){
- //关键字 就是java中自己要用到的词,并且有特殊含义的一些词
- //我们就不能作为:类名、变量名,否则会报错
- //int class = 10;
- int Class = 10;
- //标识符 就是名字,由字母、数字、下划线、美元符等组成,且不能以数字开头,
- //也不能用关键字作为名字
- // int 2a = 10;
- int _1 = 1;
- int $a = 3;
- // int static = 2;
- }
- }

3.5变量
1.变量的定义,用处、特点
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 1.变量是什么,完整的定义格式是什么样的
- 变量是用来存储一个数据的,本质是内存中的一块区域
- 数据类型 变量名称 = 数据
- 2.变量有什么用
- 可以用来记录要处理的数据,编写代码更灵活,管理代码更方便
- 3.变量有什么特点,基于这个特点有什么应用场景
- 变量里装的数据是可以被替换的。
- 比如:微信钱包里的余额,统计班级人数,统计公交车上下人数
- */
- public class VariableDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //定义一个变量记录一个数据
- int a = 22;
- double b = 32.3;
- System.out.println(a);
- System.out.println(b);
- }
- }


2.变量使用时的注意事项
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 使用变量时有哪些注意点
- 变量要先声明,才能使用
- 什么类型的变量,只能存储什么类型的数据
- 变量存在访问范围,同一个范围内,多个变量的名字不能一样
- 变量定义时可以不给赋初始值,但在使用时,变量里必须要有值
- */
- public class VariableDemo2 {
- public static void main(String args[]){
- //变量要先声明才能使用
- //System.out.println(a);
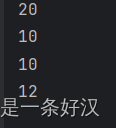
- int a = 20;
- System.out.println(a);
-
- //变量是什么类型,存储的数据就是什么类型
- /* int b;
- b = 20.3;*/
- int b;
- b = 10;
-
- //变量存在访问范围,同一个范围内,多个变量的名字不能一样
- //int a;
- {
- int c = 10;
- System.out.println(c);
- }
- int c = 10;
- System.out.println(c);
-
- //变量定义时可以不用赋初始值,但在使用时,变量里必须要有值
- int d;
- //System.out.println(d);
- d = 12;
- System.out.println(d);
- }
- }

3.6数据类型
1.ASCALL码
- /**
- 字符数据在计算机中是怎么存储的
- 字符存的是ASCAII码表中对应的数字的二进制形式
- 2进制、8进制、16进制的学习
- */
- public class VariableDemo3_ASCAII {
- public static void main(String args[]){
- //'a'-> 97
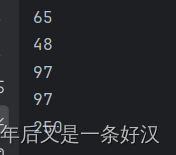
- System.out.println('a' + 0);
- //'A'-> 65
- System.out.println('A' + 0);
- //'0'-> 48
- System.out.println('0' + 0);
-
- //2进制 以0b或0B开头
- int a1 = 0b01100001;
- System.out.println(a1);
- //8进制 以0开头
- int a2 = 0141;
- System.out.println(a2);
- //16进制 以0X或0x开头
- int a3 = 0xFA;
- System.out.println(a3);
- }
- }

2.基本数据类型
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 掌握基本数据类型
- 四大类八种
- 整型 byte short int long
- 浮点型 float double
- 字符型 char
- 布尔型 boolean
- */
- public class VariableDemo3_DataType {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //byte
- // byte b = 129;//超出范围
- byte b = 127;
-
- //short
- short s = 12333;
-
- //int
- int i = 2234;
-
- //long 任意数字默认是整数,在后面加个L/l就是long类型
- long L = 23999999999L;
-
- //浮点型 小数后要加f
- float f = 23.33f;
- double d = 34.22;
-
- //布尔型boolean
- boolean b1 = true;
- boolean b2 = false;
-
- //字符型
- char c1 = '你';
- char c2 = '他';
-
- //引用数据类型
- String str = "石昊";
- System.out.println(str);
- }
- }

![]()
3. 类型转换
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 为什么要进行类型转换
- 存在不同类型的变量赋值给其他类型的变量
- 什么是自动类型转换
- 类型范围小的变量可以直接赋值给类型范围大的变量
- */
- public class VariableDemo5_TypeConversion {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- byte c = 23;
- int a = c;
- System.out.println(c);
- System.out.println(a);
- }
- }
1. 表达式中的类型转换
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 什么是表达式的自动类型转换
- 小范围的类型会自动转换成大范围的类型进行运算
- 表达式的最终结果类型是由谁决定的
- 最终类型是由表达式中的最高类型决定的
- 表达式中有哪些类型转换是需要注意的
- byte short char 是直接转换成int类型参与运算的
- */
- public class VariableDemo6_TypeConversion {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //小范围的类型会自动转换为大范围的类型进行运算
- byte a = 10;
- int b = 20;
- int rs1 = a + b;
- System.out.println(rs1);
- System.out.println("-------------------------------");
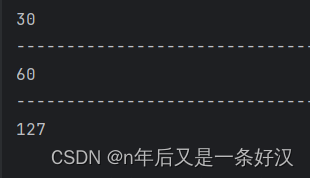
- //最终结果类型是由表达式中的最高类型决定的
- long d = 30;
- long rs2 = a + b + d;
- System.out.println(rs2);
- System.out.println("-------------------------------");
- //byte short char 是直接转换成int类型参与运算的
- byte a1 = 10;
- short a2 = 20;
- char a3 = 'a';
- int rs3 = a1 + a2 + a3;
- System.out.println(rs3);
-
- }
- }

2.强制类型转换
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 什么是强制类型转换
- 默认情况下,范围大的类型变量直接赋值给范围小的类型变量
- 可以强行将范围大的类型变量赋值给类型范围小的变量
- 强制类型转换中有什么注意的地方
- 可能出现数据丢失
- 小数强制类型转换成整数是直接截断小数保留整数
- */
- public class VariableDemo7_TypeConversion {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //范围大的类型变量赋值给范围小的
- int a = 20;
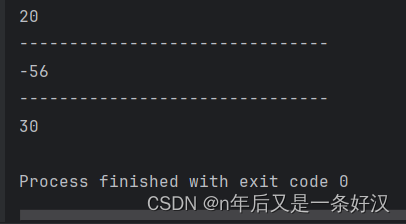
- byte b = (byte) a;
- System.out.println(b);//20
- System.out.println("-------------------------------");
- //可能出现数据丢失
- int c1 = 200;
- byte c2 = (byte) c1;
- System.out.println(c2);//-56
- System.out.println("-------------------------------");
-
- //小数强制转换成整数是直接截断小数保留整数
- double d = 30.22;
- int i = (int) d;
- System.out.println(i);//30
-
- }
- }

3.7运算符
1.算术运算符
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 算术运算符有哪些
- + - * / %
- /需要注意什么,为什么
- 如果两个整数做除法,其结果一定是整数,因为最高类型是整数
- +除了作基本数学运算,还有哪些功能
- 与字符串作+运算时会被当成连接符,其结果还是字符串
- 技巧:能算则算,不能算就在一起
- */
- public class OperatorDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int a = 5;
- int b = 2;
- System.out.println(a + b);//7
- System.out.println(a - b);//3
- System.out.println(a * b);//10
- System.out.println(a / b);//2
- //两个整数做除法时,其结果一定是整数,因为最高类型是整数
- System.out.println(1.0 * a / b);//2.5 如果非要是小数 ,则可以乘以1.0
- System.out.println(5.0 / 2);//2.5 可以用5.0
- System.out.println(a % b);//1
-
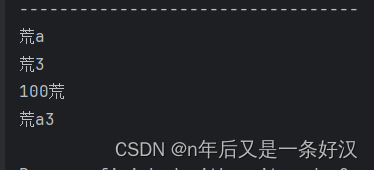
- System.out.println("----------------------------------");
- System.out.println("荒" + 'a');//荒a
- int a2 = 3;
- System.out.println("荒" + a2);//荒3
- System.out.println(a2 + 'a' + "荒");//100荒
- System.out.println("荒" + 'a' + a2);//荒a3
-
- }
- }

2.自增自减
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 自增、自减运算符是什么,有什么作用,需要注意什么
- ++ -- 对当前变量+1 -1;
- 只能操作变量,不能操作字面量
- 自增、自减运算符放在变量前后有什么区别吗
- 如果单独使用放前放后是没有区别的
- 非单独使用时,放在前面,先进行变量自增/自减,再使用变量
- 放在后面,先使用变量,在进行变量自增/自减
- */
- public class OperatorDemo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //++
- int a = 2;
- a++;
- ++a;
- System.out.println(a);//4
-
- //--
- int b = 2;
- b--;
- --b;
- System.out.println(b);//0
-
- //只能操作变量,不能操作字面量,否则会报错
- // System.out.println(2++);
-
- //非单独使用时
- //放在变量前,先自增/自减,在使用变量
- int a1 = 2;
- int b1 = ++a1;
- System.out.println(b1);//3
-
- //放在变量后,先使用变量,在自增/自减
- int i = 2;
- int j = i++;
- System.out.println(j);//2
- }
- }

3.赋值运算符
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 赋值运算符有哪些
- 基本赋值运算符:= (从右边往左边看)
- 扩展赋值运算符:+= -= *= /= %=
- 2.扩展赋值运算符的作用是什么,有什么特点
- +=可以实现数据的累加,把别人的数据加给自己
- 特点是扩展赋值运算符自带强制类型转换
- */
- public class OperatorDemo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //=
- int a = 2;
- System.out.println(a);
- //+=
- byte b = 5;
- byte c = 5;
- //b = (byte) (b + c);
- //b += c;//等价于 b = (byte) (b + c);
- //b -= c;//等价于 b = (byte) (b - c);
- //b *= c;//等价于 b = (byte) (b * c);
- //b /= c;//等价于 b = (byte) (b / c);
- b %= c; //等价于 b = (byte) (b % c);
- System.out.println(b);
-
- }
- }

4.逻辑运算符
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 1.逻辑运算符有哪些,有什么特点
- &:有一个为false,结果是false
- &&:有一个为false,结果是false,但前一个为false,后一个条件不执行
- |:有一个为true,结果是true
- ||:有一个为true,结果是true,但前一个为true,后一个条件不执行
- !:!false = true; !true = false;
- ^:相同是false,不同是true
- 实际开发中,常用的逻辑运算符还是:&& || !
- */
- public class OperatorDemo4 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //&:有一个为false,结果是false
- int a = 3;
- int b = 4;
- //System.out.println(a > b & ++a > 2);
- //System.out.println(a);
- // &&:有一个为false,结果是false,但前一个为false,后一个条件不执行
- System.out.println(a > b && ++a > 2);
- System.out.println(a);
- // |:有一个为true,结果是true
- //System.out.println(a < b | ++a > 2);
- //System.out.println(a);
- // ||:有一个为true,结果是true,但前一个为true,后一个条件不执行
- System.out.println(a < b || ++a > 2);
- System.out.println(a);
- // !:!false = true; !true = false;
- System.out.println(!false);
- System.out.println(!true);
- // ^:相同是false,不同是true
- System.out.println(false ^ false);
- System.out.println(true ^ true);
- System.out.println(true ^ false);
- System.out.println(false ^ true);
- }
- }

3.8第一个api的使用——Scanner 键盘录入
-
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 什么是api,什么是api文档
- api是application programming interface,应用程序编程接口,就是java已经写好的程序,可以直接用
- api文档是java提供的程序使用说明书
- 2.java程序中如何实现接收用户键盘录入的数据
- 使用java提供的Scanner来完成,步骤如下:
- 导包:import java.util.Scanner
- 抄代码得到扫描器对象:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- 抄代码等待接收用户输入的数据:int age = sc.nextInt();
- String name = sc.next();
- */
- public class Api_01_Scanner {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //java程序中如何实现接收用户键盘录入的数据
- // 使用java提供的Scanner来完成,步骤如下:
- // 导包:import java.util.Scanner
- // 抄代码得到扫描器对象:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- // 抄代码等待接收用户输入的数据:int age = sc.nextInt();
- System.out.println("请输入你的年龄:");
- int age = sc.nextInt();
- System.out.println("你的年龄是:" + age);
- // String name = sc.next();
- System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
- String name = sc.next();
- System.out.println(name + ",欢迎你");
- }
- }

3.9流程控制
1.顺序结构
2.分支结构
- /**
- 学习目标:
- if分支是什么,有哪些应用场景
- if分支是可以根据条件,选择执行某段程序 应用场景:发红包 绩效评级
- 2.if分支的写法有几种,各有什么特点
- if(条件表达式){
- 语句体;
- }
- if(条件表达式){
- 语句体1;
- } else{
- 语句体2;
- }
- if(条件表达式1){
- 语句体1;
- }else if(条件表达式2){
- 语句体2;
- }else if(条件表达式3){
- 语句体3;
- }
- ...
- else {
- 语句体n+1;
- }
- */
- public class IfDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //1.测量体温
- double bodyTemperature = 38.3;
- if(bodyTemperature >= 37){
- System.out.println("发烧了");
- }
-
- //2.发红包
- double money = 99.2;
- if(money > 80){
- System.out.println("发送成功");
- }else{
- System.out.println("余额不足^^");
- }
-
- //3.绩效评级
- int score = 83;
- if(score >= 0 && score < 60){
- System.out.println("评级为:D");
- }else if(score >= 60 && score < 80){
- System.out.println("评级为:C");
- }else if(score >= 80 && score < 90){
- System.out.println("评级为:B");
- }else if(score >= 90 && score <= 100){
- System.out.println("评级为:A");
- }else {
- System.out.println("输入的分数有误^^");
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 学习目标:
- 掌握switch分支的格式、执行流程
- 是通过比较值来决定执行那条分支
- 执行流程:
- 1.先执行表达式的值,在拿着这个值去与case后的值进行比较
- 2.与那个case后的值匹配为true就执行那个case块的代码,遇到break就跳出switch分支
- 3.如果全部case后的值与之匹配都是false,则执行default块的代码
- */
- public class SwitchDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String week = "周四";
- switch (week){
- case "周一" :
- System.out.println("全职法师");
- break;
- case "周二" :
- System.out.println("狐妖小红娘");
- break;
- case "周三" :
- System.out.println("镖人");
- break;
- case "周四" :
- System.out.println("不良人");
- break;
- case "周五" :
- System.out.println("完美世界");
- break;
- case "周六" :
- System.out.println("斗罗大陆");
- break;
- case "周日" :
- System.out.println("斗破苍穹");
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("输入错误");
- break;
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 学习目标:
- 使用switch的注意点
- */
- public class SwitchDemo32 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //表达式类型只能是byte short int char jdk5开始支持枚举,jdk7开始支持String,
- //不支持float double long
- //case给出的值不允许重复,且只能是字面量,不能是变量
- //正常使用switch的时候,不要忘记写break,否则会出现穿透现象
- //case穿透 丢失break导致
- String week = "周四";
- switch (week){
- case "周一" :
- System.out.println("全职法师");
- break;
- case "周二" :
- System.out.println("狐妖小红娘");
- break;
- case "周三" :
- System.out.println("镖人");
- break;
- case "周四" :
- System.out.println("不良人");
- //break;
- case "周五" :
- System.out.println("完美世界");
- break;
- case "周六" :
- System.out.println("斗罗大陆");
- break;
- case "周日" :
- System.out.println("斗破苍穹");
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("输入错误");
- break;
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 学习目标:
- switch穿透性能解决什么问题
- */
- public class SwitchDemo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //存在多个case分支的代码是一样时,可以把代码写到以一个case块
- //其他case块通过穿透性能穿透到该case块即可,这样可以简化代码
- String week = "周一";
- switch (week){
- case "周一" :
- case "周二" :
- case "周三" :
- case "周四" :
- System.out.println("全职法师");
- break;
- case "周五" :
- System.out.println("完美世界");
- break;
- case "周六" :
- System.out.println("斗罗大陆");
- break;
- case "周日" :
- System.out.println("斗破苍穹");
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("输入错误");
- break;
- }
- }
- }

3.循环.
- /**
- 学习目标:
- 掌握for循环格式以及执行流程
- */
- public class ForDemo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
- System.out.println("荒");
- }
-
- System.out.println("-----------------");
- for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i+=2){
- System.out.println("荒");
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 学习目标:
- for循环的应用
- */
- public class ForDemo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //输出1-100之间的数
- for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
- System.out.println(i);
- }
-
- System.out.println("--------------------");
- //计算1到100之间的和
- int sum = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
- sum = sum + i;
- }
- System.out.println("和为:" + sum);
- System.out.println("--------------------");
- //计算1到100之间的奇数和
- int sum1 = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < 100; i += 2) {
- sum1 = sum1 + i;
- }
- System.out.println("奇数和为:" + sum1);
- System.out.println("--------------------");
- int sum2 = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
- if (i % 2 == 1) {
- sum2 = sum2 + i;
- }
- }
- System.out.println("奇数和为:" + sum2);
- }
- }

- /**
- 学习目标:
- while循环的格式,执行流程
- */
- public class WhileDemo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i = 1;
- while (i < 5){
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- i++;
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- 目标:
- 学习while的使用场景
- */
- public class WhileDemo4 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //珠穆朗玛峰高度为8848860mm,现在有一个纸张厚度为0.1mm,对纸张进行折叠
- //折叠多少次会超过它的高度
- double peakHeight = 8848860;
- double paperThickness = 0.1;
- int count = 0;
- while (paperThickness < peakHeight) {
- paperThickness = paperThickness * 2;
- count++;
- }
- System.out.println("纸张折叠次数为" + count);
- System.out.println("纸张此时厚度为" + paperThickness);
- }
- }

- /**
- 目标:
- 掌握dowhile循环的格式以及执行流程
- */
- public class DoWhileDemo5 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int i = 0;
- do{
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- i++;
- }while(i < 3);
-
- //for循环中,控制循环的变量只在循环中使用,while循环中控制
- //循环的变量在循环后还可以使用
- for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
- System.out.println("荒天帝2");
- }
- //System.out.println(j);
- int k = 0;
- while (k < 3) {
- System.out.println("荒天帝3");
- k++;
- }
- System.out.println(k);
- }
- }

- /**
- 目标:
- 了解循环嵌套的格式以及执行流程
- */
- public class LoopNestingDemo6 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- }
- System.out.println("--------------------");
- }
-
-
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
- System.out.print("*");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 目标:
- 了解死循环
- */
- public class EndlessLoopDemo7 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- /*for (; ;) {
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- }*/
-
- // while (true) {
- // System.out.println("荒天帝");
- // }
-
- do {
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- } while (true);
- }
- }

4.练习
- /**
- 目标:
- 生成随机数有几步
- 如何生成指定区间的随机数
- */
- public class Demo1_Random {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Random r = new Random();
- for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
- int number = r.nextInt(10);
- System.out.println(number);
- }
-
- System.out.println("------------------------");
- //生成9—20之间的随机数
- //9-20 -> -9 -> (0-11) + 9
- for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
- int number2 = r.nextInt(12) + 9;
- System.out.println(number2);
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- 目标:
- 学以致用,利用流程控制完成猜数字游戏
- */
- public class Demo2_Random {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //随机生成1-100之间的一个数字
- Random r = new Random();
- int luckNumber = r.nextInt(100) + 1;
-
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- //利用死循环猜数字
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请输入你猜的数字:");
- int guessNumber = sc.nextInt();
- //利用分支结构判断猜的数字与随机生成的数字是否一样
- if (guessNumber == luckNumber) {
- System.out.println("恭喜你,猜对了~");
- break;
- } else if (guessNumber > luckNumber) {
- System.out.println("你猜的数字过大");
- } else {
- System.out.println("你猜的数字过小");
- }
- }
- }
- }

3.10数组
1.数组定义
- /**
- 目标:
- 掌握数组的定义
- */
- public class Demo1_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ages = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
- int ages2[] = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4};
- int[] ages3 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
-
- double[] scores = {88.2, 89.2, 99.3, 80};
- }
- }
- /**
- 目标:
- 掌握静态初始化数组,访问数组 修改数组
- */
- public class Demo2_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ages = {29, 20, 34, 30};
- System.out.println(ages[0]);
- System.out.println(ages[1]);
- System.out.println(ages[2]);
- System.out.println(ages[3]);
- ages[0] = 20;
- System.out.println(ages[0]);
- System.out.println(ages[1]);
- System.out.println(ages[2]);
- System.out.println(ages[3]);
-
- System.out.println(ages.length);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道什么是遍历,会遍历
- */
- public class Demo3_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ages = {10, 20, 30, 40};
- for (int i = 0; i < ages.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(ages[i]);
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 数组遍历-求和
- */
- public class Demo4_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40};
- int sum = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- sum = sum + arr[i];
- }
- System.out.println("总和为:" + sum);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 掌握动态初始化数组
- */
- public class Demo5_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] ages = new int[3];
- for (int i = 0; i < ages.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(ages[i]);
- }
-
- ages[0] = 1;
- ages[1] = 1;
- ages[2] = 1;
-
- for (int i = 0; i < ages.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(ages[i]);
- }
-
- //默认值
- //byte short int char long默认值为0
- byte[] arr = new byte[10];
- System.out.println(arr[0]);
- System.out.println(arr[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
- short[] arr1 = new short[10];
- System.out.println(arr1[0]);
- System.out.println(arr1[9]);
- System.out.println("-------------------");
- char[] arr2 = new char[10];
- System.out.println((int) arr2[0]);
- System.out.println((int) arr2[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
- long[] arr3 = new long[10];
- System.out.println(arr3[0]);
- System.out.println(arr3[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
-
- //float double类型的默认值为0.0
- float[] arr4 = new float[10];
- System.out.println(arr4[0]);
- System.out.println(arr4[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
- double[] arr5 = new double[10];
- System.out.println(arr5[0]);
- System.out.println(arr5[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
- //String类型为null
- String[] arr6 = new String[10];
- System.out.println(arr6[0]);
- System.out.println(arr6[9]);
- System.out.println("------------------");
- }
- }

-
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 完成评委打分案例
- */
- public class Demo6_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //定义一个动态数组用于后面存储6个评委的打分
- double[] scores = new double[6];
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- //遍历数组,将评委的分数存储到数组
- for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("请输入第" + ( i + 1 ) + "个评委的打分:");
- double score = sc.nextDouble();
- scores[i] = score;
- }
- //定义变量用于求和
- double sum = 0;
- //遍历数组求和
- for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
- sum = sum + scores[i];
- }
- //求平均分
- sum = sum / scores.length;
- System.out.println("最终分数为:" + sum);
- }
- }

2.数组内存
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道变量和数组在计算机中的执行过程,java程序在计算机中的执行过程
- */
- public class Demo1_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //变量里的数据是在栈内存里存放的
- int a = 10;
- System.out.println(a);
- // arr在栈内存中 arr变量存放的是数组地址值
- // 数组元素在堆内存中
- int[] arr = {20, 39, 40, 48};
- System.out.println(arr);
- System.out.println(arr[0]);
-
- arr[0] = 1;
-
-
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道多个数组变量指向同一个数组对象的原因
- */
- public class Demo2_Array {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = {20, 10, 30, 40};
- int[] arr2 = arr;
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(arr[i]);
- }
- System.out.println("------------------");
- for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(arr2[i]);
- }
-
- arr2[1] = 1;
- System.out.println(arr[1]);
- }
- }

3.练习
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 求数组中的最大值
- */
- public class Demo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //把数据拿到程序中,用数组装起来
- int[] arr = {1, 3, 6, 9, 4, 1, 8, 2, 5, 7};
- //定义变量用来记录最大值,初始值默认存储的是数组中的第一个元素作为参照
- int max = arr[0];
- //从第二个元素开始遍历
- for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
- //如果当前元素大于变量max存储的数据,则替换变量max存储的值为该元素
- if (arr[i] > max) {
- max = arr[i];
- }
- }
- System.out.println("最大值为:" + max);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 数组反转
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //定义数组存储数据
- int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- //通过遍历数组来交换
- //定义i指向前一个位置,j指向后一个位置,然后两两交换值,i<j时才交换
- for (int i = 0, j = arr.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- //定义临时变量,记录后一个位置的值
- int temp = arr[j];
- //把前一个位置的值赋值给后一个位置
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- //把临时变量记录的后一个位置的值赋值给前一个位置
- arr[i] = temp;
- }
-
- //遍历数组
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
- }
- }
- }

- import java.util.Random;
- import java.util.Scanner;
-
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 实现数组打乱
- */
- public class Demo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //定义动态数组存放数据
- int[] arr = new int[5];
- //遍历数组记录数据
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个数据");
- int num = sc.nextInt();
- arr[i] = num;
- }
-
- //遍历数组打乱数据
- Random r = new Random();
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- //定义随机索引 用来和当前元素交换值
- int index = r.nextInt(arr.length);
- //定义临时变量记录随机索引的值
- int temp = arr[index];
- //将当前元素的值赋值给随机索引处的元素
- arr[index] = arr[i];
- //将temp中记录的随机索引的元素的值赋值给当前元素
- arr[i] = temp;
- }
-
- //遍历数组即可
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
- }
- }
- }

3.11方法
1.方法定义
修饰符: 方法可以有访问修饰符,例如 public、private、protected 或默认(包内可见)。
返回类型: 方法可以返回一个值,指定返回值的数据类型,如果方法不返回任何值,可以使用 void。
方法名: 方法名是方法的标识符,用于在程序中调用方法。
参数列表: 方法可以接受零个或多个参数,参数用于向方法传递数据。
方法体: 方法体包含实际执行的代码块,实现方法的功能。
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 学习方法的使用
- 方法(Method):一组执行特定任务的代码块。它可以在类中定义一次,然后在本方法、其他方法中被多次调用。
- 作用:提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
- */
- public class Demo1_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int rs = sum(10, 20);
- System.out.println("和是:" + rs);
- }
-
- public static int sum(int a, int b){
- int c = a + b;
- return c;
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 根据需求设计合适的方法
- */
- public class Demo2_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- print(3);
- System.out.println("------------");
- print(4);
- }
- public static void print(int n){
- for (int i = 1; i <= n ; i++) {
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道方法使用时的常见问题
- */
- public class Demo3_Method {
- public static int sum(int a, int b){
- int c = a + b;
- //如果方法的返回值类型写了具体类型,方法内部则必须使用return返回对应类型的数据
- return c;
- //return下面的语句,不能编写代码,属于无效的代码,执行不到
- //System.out.println("荒天帝");
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //但一个方法不能定义在另一个方法里面
- /* public static void print(){
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- }*/
-
- //方法不调用就不会执行,调用方法时传给方法的数据,必须严格匹配方法的参数情况
- int sum = sum(10, 20);
-
- //调用有返回值的方法,有三种方式,1.可以定义变量接收结果
- int sum1 = sum(28,38);
- //2.直接输出调用
- System.out.println(sum(10,38));
- //3.直接调用
- sum(12,38);
-
- //调用无返回值的方法,只有一种方式:直接调用
- print();
- }
- //方法在类中的位置放前放后无所谓
- public static void print(){
- System.out.println("荒天帝");
- //方法的返回值类型写void(无返回声明时),方法内不能使用return返回数据,
- //return 3;
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 方法案例
- */
- public class Demo4_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(sum(100));
-
- judge(21);
- judge(10);
- }
- public static int sum(int n){
- int sum = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n ; i++) {
- sum += i;
- }
- return sum;
- }
-
- public static void judge(int num){
- if (num % 2 == 0) {
- System.out.println(num + "是偶数");
- } else {
- System.out.println(num + "是奇数");
- }
- }
- }

2.方法形参
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道java的参数传递机制
- */
- public class Demo1_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int a = 30;
- change(a);
- System.out.println("mian:" + a);
- }
-
- public static void change(int a) {
- System.out.println("方法1:" + a);
- a = 29;
- System.out.println("方法2:" + a);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标
- * 引用数据类型的参数传递
- */
- public class Demo2_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
- change(arr);
- System.out.println("main方法:" + arr[1]);
- }
-
- public static void change(int[] arr) {
- System.out.println("方法1:" + arr[1]);
- arr[1] = 100;
- System.out.println("方法2:" + arr[1]);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 打印数组内容
- */
- public class Demo3_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- printArray(arr);
-
- int[] arr2 = null;
- printArray(arr2);
-
- int[] arr3 = {};
- printArray(arr3);
- }
-
- public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
- //判断数组是否合法 ,如果为null直接打印null
- if (arr == null) {
- System.out.println("null");
- return;
- }
-
- System.out.print("[");
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- // if (i == arr.length - 1) {
- // System.out.print(arr[i]);
- // } else {
- // System.out.print(arr[i] + ", ");
- // }
- System.out.print(i == arr.length - 1 ? arr[i] : arr[i] + ", ");
- }
-
- System.out.println("]");
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 判断两个数组里面的内容是否一样
- */
- public class Demo4_Method {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3};
- int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3};
- System.out.println(equals(arr1, arr2));
- }
-
- public static boolean equals(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
- //如果两个都为null
- if (arr1 == null && arr2 == null) {
- return true;
- }
- //其中有一个为null
- if (arr1 == null || arr2 == null) {
- return false;
- }
- //长度不一样不相等
- if (arr1.length != arr2.length) {
- return false;
- }
- //元素内容不一样不相等
- for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
- if (arr1[i] != arr2[i]) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- //其他情况相等
- return true;
- }
- }

3.方法重载
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道方法重载是什么
- */
- public class Demo1_Overload {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- test();
- test(1.1);
-
- }
- //方法重载只跟方法和形参列表相关
- //方法名相同,形参列表不同:形参个数、类型、顺序不同
- public static void test(){
- System.out.println("1");
- }
- public static void test(double a){
- System.out.println(a);
- }
- int test(int a){
- return a;
- }
- void test(int a, double b){
- System.out.println(a + b);
- }
- void test(double b, int a){
- System.out.println(a + b);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 方法重载练习
- */
- public class Demo2_Overload {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- fire();
- fire("米国");
- fire("米国",999);
- }
- public static void fire(){
- //System.out.println("向岛国发送了一枚武器");
- fire("岛国");
- }
-
- public static void fire(String country){
- //System.out.println("向" + country + "发送了一枚武器");
- fire(country,1);
- }
-
- public static void fire(String country, int num){
- System.out.println("向" + country + "发送了" + num + "枚武器");
- }
- }

4.return
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 知道无返回值的方法中,怎么跳出并结束当前所在的方法
- */
- public class Demo1_Return {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- division(2,0);
- }
-
- public static void division(int a, int b){
- if(b == 0){
- System.out.println("除数不能为0");
- return;//跳出并结束当前所在方法的执行
- }
- int c = a / b;
- System.out.println(c);
- }
- }

3.12案例练习
1.购买飞机票
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 完成购买飞机票案例
- */
- public class Demo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- double price = calculate(1000, 8, "头等舱");
- System.out.println(price);
- }
- public static double calculate(double price, int month, String seat){
- if(month >= 5 && month <= 10){
- //旺季
- switch (seat){
- case "头等舱":
- price *= 0.9;
- break;
- case "经济舱":
- price *= 0.85;
- break;
- }
- }else {
- //淡季
- switch (seat){
- case "头等舱":
- price *= 0.7;
- break;
- case "经济舱":
- price *= 0.65;
- break;
- }
- }
- return price;
- }
- }

2.生成随机验证码
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 完成生成随机验证码的案例
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(createCode(4));
- }
- public static String createCode(int n){
- //for循环 生成几位随机数
- Random r = new Random();
- String code = "";
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
- //随机0:数字 1:大写字母 2:小写字母
- int num = r.nextInt(3);
- switch (num){
- case 0:
- code += r.nextInt(10);
- break;
- case 1:
- //大写字母 65 65+25 0-25
- char c = (char) (r.nextInt(26) + 65);
- code += c;
- break;
- case 2:
- //小写字母 97 97+25 0-25
- char c1 = (char) (r.nextInt(26) + 97);
- code += c1;
- break;
- }
- }
- return code;
- }
- }

3.评委打分
- /**
- * 目标
- * 完成评委打分案例
- */
- public class Demo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(getScore(6));
- }
- public static double getScore(int number){
- //定义动态数组存放评委分数
- int[] scores = new int[number];
- //for循环遍历 录入评委分数
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("请输入第" + (i + 1) + "个评委的分数:");
- int score = sc.nextInt();
- scores[i] = score;
- }
- //记录总和
- int sum = 0;
- //记录最大值
- int max = scores[0];
- //记录最小值
- int min = scores[0];
-
- //遍历求值
- for (int i = 0; i < scores.length; i++) {
- int score = scores[i];
- //总和
- sum += score;
- //最大值
- if(score > max){
- max = score;
- }
- //最小值
- if(score < min){
- min = score;
- }
- }
- return 1.0 * (sum - max - min) / (number - 2);
- }
- }

4.数字加密
- /**
- * 目标
- * 完成数字加密案例
- */
- public class Demo4 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println(encrypt(8346));
- }
-
- public static String encrypt(int number){
- //拆分数字
- int[] numbers = split(number);
- //遍历数组进行加密
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
- numbers[i] = (numbers[i] + 5) % 10;
- }
- //数组反转
- reverse(numbers);
- //拼接数字
- String encrypt = "";
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
- encrypt += numbers[i];
- }
- return encrypt;
- }
-
- public static void reverse(int[] numbers) {
- for (int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
- //定义临时变量存放后一个位置的值
- int temp = numbers[j];
- //将前一个位置的值赋值给后一个位置
- numbers[j] = numbers[i];
- //将temp中记录的后一个位置的值赋值给前一个位置
- numbers[i] = temp;
- }
- }
-
- public static int[] split(int number) {
- //定义动态初始化数组存放拆分的数字
- int[] numbers = new int[4];
- numbers[0] = number / 1000;
- numbers[1] = (number / 100) % 10;
- numbers[2] = (number / 10) % 10;
- numbers[3] = number % 10;
- return numbers;
- }
- }

5.数组拷贝
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 完成数组拷贝
- */
- public class Demo5 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] arr = {11, 22, 33};
- int[] copy = copy(arr);
- print(copy);
- }
-
- public static void print(int[] copy) {
- System.out.print("[");
- for (int i = 0; i < copy.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(i == copy.length - 1 ? copy[i] : copy[i] + ", ");
- }
- System.out.println("]");
- }
-
- public static int[] copy(int[] arr) {
- //定义新数组
- int[] arr1 = new int[arr.length];
- //将原数组的值赋值给新数组
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- arr1[i] = arr[i];
- }
- return arr1;
- }
- }

6.抢红包
- /**
- * 目标
- * 抢红包
- */
- public class Demo6 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] moneys = {20, 30, 10, 999, 666};
- money1(moneys);
- }
-
- public static void money(int[] moneys) {
- //遍历数组
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- Random r = new Random();
- for (int i = 0; i < moneys.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("请输入随机内容进行抽奖~");
- sc.next();
- //进行抽奖
- //获得一个随机索引,如果不为0则中奖,然后将这个索引对应的
- //元素值改为0
- while (true) {
- int index = r.nextInt(moneys.length);
- if (moneys[index] != 0) {
- System.out.println("恭喜你抽中了" + moneys[index] + "红包");
- moneys[index] = 0;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static void money1(int[] moneys) {
- //遍历数组 将数组中的红包进行打乱
- //将当前元素与随机索引位置的元素进行交换
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- Random r = new Random();
- for (int i = 0; i < moneys.length; i++) {
- int index = r.nextInt(moneys.length);
- //定义临时变量记录随机索引处的值
- int temp = moneys[index];
- //将当前元素的值赋值给随机索引对应的元素
- moneys[index] = moneys[i];
- //将temp里面存储的随机索引对应的元素值赋值给当前元素
- moneys[i] = temp;
- }
-
- //进行抽奖
- for (int i = 0; i < moneys.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("请输入随机内容进行抽奖~");
- sc.next();
- System.out.println("恭喜你抽中了" + moneys[i] + "红包");
- }
- }
- }

7.找素数
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 找素数
- */
- public class Demo7 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("共有" + search2(100, 200));
-
- int count = 0;
- for (int i = 100; i <= 200; i++) {
- if(check(i)){
- count++;
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
- System.out.println("共有" + count);
-
- }
-
- public static int search1(int start, int end) {
- int count = 0;
-
- for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
- //信号位
- boolean flag = true;
- //从2遍历到该数据的一半进行判断
- for (int j = 2; j <= i / 2; j++) {
- if (i % j == 0) {
- flag = false;
- break;
- }
- }
- //根据flag判断是否为素数
- if (flag) {
- count++;
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- public static int search2(int start, int end) {
- int count = 0;
- out:
- for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
- //从2遍历到该数据的一半进行判断
- for (int j = 2; j <= i / 2; j++) {
- if (i % j == 0) {
- continue out;
- }
- }
- //为素数
- count++;
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- return count;
- }
-
- public static boolean check(int data) {
- //从2遍历到该数据的一半进行判断
- for (int j = 2; j <= data / 2; j++) {
- if (data % j == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- //为素数
- return true;
- }
- }

8.打印乘法表
- /**
- * 打印乘法表 三角形
- */
- public class Demo8 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
- for (int j = 1; j <= i ; j++) {
- System.out.print(j + "X" + i + "=" + (j * i) + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- // 行数 个数 空格数
- // * 1 1 2
- // *** 2 3 1
- //***** 3 5 0
- int n = 10;
- for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
- //打印空格数
- for (int j = 1; j <= n - i; j++) {
- System.out.print(" ");
- }
- //打印*
- for (int j = 1; j <= 2*i - 1; j++) {
- System.out.print(j % 2 == 0 ? " " : "*");
- }
- System.out.println();
- }
- }
- }

9.双色球
- import java.util.Random;
- import java.util.Scanner;
-
- /**
- * 目标:
- * 实现双色球
- */
- public class Demo9 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int[] userNumbers = userSelectNumbers();
- System.out.println("您投注的号码为:");
- print(userNumbers);
- int[] luckyNumbers = createNumbers();
- System.out.println("中奖号码为:");
- print(luckyNumbers);
- judge(userNumbers,luckyNumbers);
- }
-
- //打印数组
- public static void print(int[] numbers) {
- System.out.print("[");
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
- System.out.print(i == numbers.length - 1 ? numbers[i] : numbers[i] + ", ");
- }
- System.out.println("]");
- }
-
- //用户选号
- public static int[] userSelectNumbers() {
- //定义动态初始化数组 6个红色球号码,1个蓝色号码
- int[] numbers = new int[7];
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length - 1; i++) {
- //用户输入6个蓝色号码
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请您输入第" + (i + 1) + "个蓝色号码");
- int number = sc.nextInt();
- //判断输入的号码是否合法 1-33 不重复
- if (number < 1 || number > 33) {
- System.out.println("对不起,您输入的号码不在范围内,请重新输入");
- } else {
- //重复
- if (exist(numbers, number)) {
- System.out.println("对不起,您输入的号码重复,请重新输入");
- } else {
- //合法
- numbers[i] = number;
- //跳出循环
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //生成蓝色号码 1-16
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请输入最后一个蓝色号码");
- int number = sc.nextInt();
- if (number < 1 || number > 16) {
- System.out.println("对不起,您输入的蓝色号码不在范围内,请重新输入");
- } else {
- //合法
- numbers[6] = number;
- //结束循环
- break;
- }
- }
- return numbers;
- }
-
- //判断号码是否重复
- public static boolean exist(int[] numbers, int number) {
- //遍历数组 如果遍历到0,说明号码已经比对完,没有重复,直接返回false
- // [1,2,3,4,0,0] 5
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
- if (numbers[i] == 0) {
- return false;
- }
- //相等则表示重复了
- if (numbers[i] == number) {
- return true;
- }
- }
- //如果循环结束都没有 找出重复号码表示没有重复
- return false;
- }
-
- //随机一组中奖号码
- public static int[] createNumbers() {
- //定义动态数组存放中将号码
- int[] numbers = new int[7];
- Random r = new Random();
- //6个红色号码
- for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length - 1; i++) {
- while (true) {
- //生成随机号码 1-33 -> (0-32) + 1
- int number = r.nextInt(33) + 1;
- //号码不重复
- if (!exist(numbers, number)) {
- numbers[i] = number;
- break;//将不重复的号码赋值给当前位置,结束死循环
- }
- }
- }
- //1个蓝色号码 1-16 ->(0-15)+1
- int number = r.nextInt(16) + 1;
- numbers[6] = number;
- return numbers;
- }
-
- //判断中奖情况
- public static void judge(int[] userNumbers, int[] luckyNumbers) {
- //记录红球、蓝球中奖数量
- int redCount = 0;
- int blueCount = 0;
-
- //比对红球中奖数量
- for (int i = 0; i < userNumbers.length - 1; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < luckyNumbers.length - 1; j++) {
- if (userNumbers[i] == luckyNumbers[i]) {
- redCount++;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- //比对蓝球中奖数量
- blueCount = userNumbers[6] == luckyNumbers[6] ? 1 : 0;
- System.out.println("红球命中数量为:" + redCount);
- System.out.println("蓝球命中数量为:" + blueCount);
- //判断中奖情况
- if (redCount == 6 && blueCount == 1) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖1000万");
- } else if (redCount == 6 && blueCount == 0) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖500万");
- } else if (redCount == 5 && blueCount == 1) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖3000元");
- } else if (redCount == 5 && blueCount == 0 || redCount == 4 && blueCount == 1) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖200元");
- } else if (redCount == 4 && blueCount == 0 || redCount == 3 && blueCount == 1) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖10元");
- } else if (redCount < 3 && blueCount == 1) {
- System.out.println("恭喜您,中奖5元");
- } else {
- System.out.println("谢谢参与~~~");
- }
- }
- }

3.13oop学习
1.面向对象基础
-
- public class Student {
- String name;
- double chinese;
- double english;
- double score;
-
- public void pass(double score){
- if(this.score > score){
- System.out.println("恭喜您,考试通过");
- }else{
- System.out.println("不及格");
- }
- }
-
- public void totalScore() {
- System.out.println(name + "总成绩为:" + (chinese + english));
- }
-
- public void averageScore() {
- System.out.println(name + "平均成绩为:" + (chinese + english) / 2);
- }
- }
- //一个代码文件中,可以写多个class类,但只能有一个用public修饰,
- //且public修饰的类名必须成为代码文件名
- class Person {
-
- }
-
- /*public class Car {
- }*/

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 面向对象快速入门
- */
- public class Demo1_Object {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student1 = new Student();
- student1.name = "播妞";
- student1.chinese = 88;
- student1.english = 89;
- student1.totalScore();
- student1.averageScore();
- Student student2 = new Student();
-
- student2.name = "播仔";
- student2.chinese = 80;
- student2.english = 90;
- student2.totalScore();
- student2.averageScore();
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 掌握类和对象的注意点
- */
- public class Demo2_Object {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //成员变量存在默认值,不用赋初值
- Student s1 = new Student();
- System.out.println(s1.name);
- System.out.println(s1.english);
-
-
- //对象与对象之间的数据不会相互影响,但多个变量指向同一个对象的时候
- //就会相互影响了
- Student s2 = new Student();
- s1.name = "张三";
- s2.name = "李四";
- System.out.println(s1.name);
- System.out.println(s2.name);
-
- //如果某个对象没有一个变量引用它,则该对象无法被操作了,该对象
- //会成为垃圾对象
- s1 = null;
- //System.out.println(s1.name);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标
- * 了解this关键字 :用来拿到当前对象 那个对象调用方法,this就指向那个对象
- */
- public class Demo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Student student = new Student();
- student.score = 90;
- student.pass(80);
- }
- }
2.构造器
1.构造器是什么
public 类名(){}
2.在哪里调用,常用他来干嘛
对象创建时,我们可以指定对象去调用那个构造器执行
构造器常用于完成对象初始化
3.构造器在使用时,有哪些注意点
类在设计时,如果不屑构造器,java会为类自动生成一个无参构造器
一旦定义了有参构造器,java就不会帮我们的类生成无参构造器了,此时就建议自己写一个无参构造器出来了
- public class Student {
- private String name;
- private int age;
-
- public void setAge(int age){
- if(age >= 0 && age <= 100){
- this.age = age;
- }else {
- System.out.println("您输入的年龄不合法");
- }
- }
-
- public int getAge(){
- return age;
- }
-
- public Student(){
- System.out.println("无参构造器执行了");
- }
-
- public Student(String name, int age){
- System.out.println("有参构造器执行了");
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- }

- public class Teacher {
- private String name;
- private int age;
-
- public Teacher() {
- }
-
- public Teacher(String name, int age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
-
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
-
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
-
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
-
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- }

- public class TeacherOperator {
- Teacher teacher;
-
- public TeacherOperator(Teacher teacher) {
- this.teacher = teacher;
- }
-
- public void printAge(){
- System.out.println(teacher.getAge());
- }
- }
- /**
- * 目标
- * 掌握构造器以及封装
- */
- public class Demo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //如果没有写构造器,java会为类自动生成一个无参构造器的
- Student student = new Student();
- /*student.name = "荒天帝";
- student.age = 18;*/
-
- Student s1 = new Student("张三", 20);
- /*System.out.println(s1.name);
- System.out.println(s1.age);*/
-
- Student s2 = new Student();
- s2.setAge(-23);
- System.out.println(s2.getAge());
- }
- }

3.封装
1.什么是封装
就是用类设计对象处理某一个事物的数据时,应该把要处理的数据,以及处理这些数据的方法,设计到一个对象中去
2.封装的设计规范是什么样的
合理隐藏,合理暴露
3.代码层面如何控制对象的成员公开或隐藏
public 公开
private 隐藏
- /**
- * 目标
- * javabean学习
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Teacher t1 = new Teacher();
- t1.setAge(77);
- TeacherOperator to = new TeacherOperator(t1);
- to.printAge();
- }
- }
- public class Movie {
- private int id;
- private String name;
- private double prince;
- private double score;
- private String actor;
- private String director;
- private String info;
-
- public Movie() {
- }
-
- public Movie(int id, String name, double prince, double score, String actor, String director, String info) {
- this.id = id;
- this.name = name;
- this.prince = prince;
- this.score = score;
- this.actor = actor;
- this.director = director;
- this.info = info;
- }
-
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
-
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
-
- public double getPrince() {
- return prince;
- }
-
- public void setPrince(double prince) {
- this.prince = prince;
- }
-
- public double getScore() {
- return score;
- }
-
- public void setScore(double score) {
- this.score = score;
- }
-
- public String getActor() {
- return actor;
- }
-
- public void setActor(String actor) {
- this.actor = actor;
- }
-
- public String getDirector() {
- return director;
- }
-
- public void setDirector(String director) {
- this.director = director;
- }
-
- public String getInfo() {
- return info;
- }
-
- public void setInfo(String info) {
- this.info = info;
- }
-
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
-
- public void setId(int id) {
- this.id = id;
- }
- }

- public class MovieOperator {
- private Movie[] movies;
-
- public MovieOperator(Movie[] movies){
- this.movies = movies;
- }
-
- //打印全部电影信息
- public void printAllMovies(){
- for (int i = 0; i < movies.length; i++) {
- Movie m = movies[i];
- System.out.println("电影编号是:" + m.getId());
- System.out.println("电影名是:" + m.getName());
- System.out.println("电影价格是:" + m.getPrince());
- System.out.println("电影主演是:" + m.getActor());
- System.out.println("电影导演是:" + m.getDirector());
- System.out.println("电影评分是:" + m.getScore());
- System.out.println("电影其他信息是:" + m.getInfo());
- System.out.println("-------------------");
- }
- }
-
- //根据id查询电影信息
- public void selectMovieById(int id){
- for (int i = 0; i < movies.length; i++) {
- Movie m = movies[i];
- if(m.getId() == id){
- System.out.println("你查询的电影信息如下:");
- System.out.println("电影编号是:" + m.getId());
- System.out.println("电影名是:" + m.getName());
- System.out.println("电影价格是:" + m.getPrince());
- System.out.println("电影主演是:" + m.getActor());
- System.out.println("电影导演是:" + m.getDirector());
- System.out.println("电影评分是:" + m.getScore());
- System.out.println("电影其他信息是:" + m.getInfo());
- }
- }
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标
- * 面向对象练习 展示电影信息
- */
- public class Demo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Movie[] movies = new Movie[4];
- movies[0] = new Movie(1, "全职法师", 23, 10, "莫凡", "未知", "100人想看");
- movies[1] = new Movie(2, "完美世界", 23, 10, "莫凡", "未知", "100人想看");
- movies[2] = new Movie(3, "镖人", 23, 10, "莫凡", "未知", "100人想看");
- movies[3] = new Movie(4, "狐妖小红娘", 23, 10, "莫凡", "未知", "100人想看");
- //电影操作对象
- MovieOperator mo = new MovieOperator(movies);
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("欢迎来到电影系统-----------------");
- System.out.println("请选择操作");
- System.out.println("1:查询所有电影信息");
- System.out.println("2:根据id查询电影信息");
- int select = sc.nextInt();
- switch (select) {
- case 1:
- mo.printAllMovies();
- break;
- case 2:
- System.out.println("请输入id:");
- int id = sc.nextInt();
- mo.selectMovieById(id);
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("没有此选项");
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }

4.成员变量
- /**
- * 目标
- * 区别局部变量和成员变量
- */
- public class A03_variable {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //类中的位置不同,成员变量在类中,方法外,局部变量常见于方法内
- int a = 10;
- //初始值不同:成员变量有默认值不需要初始化,局部变量没有默认值,使用前要赋值
-
- //内存位置不同:成员变量在堆内存中,局部变量在栈内存中
- //作用域不同:成员变量:整个对象,局部变量:在所属的大括号内
- //生命周期不同:成员变量:与对象共生死,局部变量:方法调用而生,方法结束而亡
- }
- }
3.14 api
1. String
- /* 目标
- * 常用api-String
- */
- public class Demo1_String {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "荒天帝";
- System.out.println(s);
- String s1 = new String("荒天帝");
- System.out.println(s1);
- char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
- byte[] bytes = {65,66,67};
- String s2 = new String(chs);
- System.out.println(s2);
- String s3 = new String(bytes);
- System.out.println(s3);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标
- * String提供的操作字符串数据的常用方法
- */
- public class Demo2_String {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //public int length();获取字符串的长度返回,就是字符个数
- String s = "今天,天气真好";
- System.out.println(s.length());
- //public char charAt(int index)获取某个索引位置处的字符返回
- String s1 = "今天,一定也要坚持到最后";
- System.out.println(s1.charAt(7));
- //public char[] toCharArray();将当前字符串转换成字符数组返回
- String s2 = "坚持,坚持,再坚持";
- char[] chars = s2.toCharArray();
- for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(chars[i]);
- }
- //public boolean equals(Object anObject)判断当前字符串与另外一个字符串
- //的内容是否一样,一样返回true
- String s3 = new String("荒天帝");;
- String s4 = new String("炎帝");
- String s5 = new String("炎帝");
- System.out.println(s4 == s5);
- System.out.println(s4.equals(s5));
- System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
-
- //public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
- //判断当前字符串与另外一个字符串的内容是否一样(忽略大小写)
- String s6 = "12abC";
- String s7 = "12Abc";
- System.out.println(s6.equals(s7));
- System.out.println(s6.equalsIgnoreCase(s7));
-
- //public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
- //根据开始和结束索引进行截取,得到新的字符串(包前不包后)
- String str1 = "我不能选择那最好的,是那最好的选择了我";
- String substring = str1.substring(10, 19);
- System.out.println(substring);
- //public String substring(int beginIndex)
- //从传入的索引处截取,截取到末尾,得到新的字符串返回
- String str2 = "人不是生来就给打败的,你可以毁灭我,但就是打不败我";
- String substring1 = str2.substring(18);
- System.out.println(substring1);
-
- //public String replace(CharSequence target,CharSequence replacement)
- //使用新值将字符串中的旧值替换,得到新的字符串
- String str3 = "你就是个垃圾,连垃圾都不如";
- String newStr3 = str3.replace("垃圾", "**");
- System.out.println(newStr3);
- //public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
- //判断字符串中是否包含了某个字符串
- String str4 = "要在这个世界上取得胜利,就必须贯彻始终:至逝世都不能撒手。";
- System.out.println(str4.contains("胜利"));
-
- //public boolean startsWith(String prefix)
- //判断字符串是否以某个字符串内容开头,开头返回true
- String str5 = "凡事都要有统一和决断,因此成功不站在自信的一方,而站在有计划的一方。";
- boolean flag = str5.startsWith("凡事");
- System.out.println(flag);
-
- //public String[] split(String regex)
- //把字符串按照某个字符串内容分割,并返回字符串数组回来
- String str6 = "如果说时间是最宝贵的东西,那么浪费时间就是最大的挥霍。";
- String[] split = str6.split(",");
- for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(split[i]);
- }
-
- }
- }

1.1练习
- import java.util.Scanner;
- /**
- 目标:
- 完成用户登录
- 需求:系统的正确登录名好密码是:qingtian/123456,请在控制台开发一个登录界面
- 接收用户输入的登录名和密码,判断用户是否登录成功,登录成功后展示:“欢迎进入系统!”
- 即可停止程序,(注意:要求最多给用户三次登录机会)
- */
- public class Demo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //获得一个扫描器用于获得用户键盘录入的数据
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- //4.使用循环控制登录界面最多显示3次
- for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
- //1.开发登录界面提示用户通过键盘输入用户名和密码
- System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
- //等待接收用户输入的用户名
- String username = sc.next();
- System.out.println("请输入密码:");
- //等待接收用户输入的密码
- String password = sc.next();
-
- //3.根据登录方法返回的认证结果判断用户是否登录成功
- boolean rs = check(username, password);
- if (rs) {
- //登录成功
- System.out.println("欢迎进入系统!");
- break;//登录成功后结束for循环
- }else {
- //登录失败
- System.out.println("您输入的用户名或密码错误~~");
- }
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * 2.设计一个登录方法,对用户的登录名和密码进行正确性认证
- * @param username
- * @param password
- * @return
- */
- public static boolean check(String username, String password){
- //记录正确的用户名和密码
- String rightUsername = "qingtian";
- String rigthPassword = "123456";
- //判断用户输入的用户名和密码是否正确
- /* if(rightUsername.equals(username) && rigthPassword.equals(password)){
- return true;
- }
- return false;*/
- //简化代码
- return rightUsername.equals(username) && rigthPassword.equals(password);
- }
- }

- import java.util.Random;
-
- /**
- 目标
- 使用String开发验证码
- 需求:实现随机产生验证码,验证码的每位可能是数字、大写字母、小写字母
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //4.主程序中,调用该方法即可得到随机验证码了
- System.out.println(createCode(4));
- System.out.println(createCode(6));
- }
-
- /**
- * 1.设计一个方法,该方法接收一个整型变量,最终要返回对应位数的随机验证码
- * @param n
- * @return
- */
- public static String createCode(int n) {
- //2.方法内定义两个变量:一个用来记录生成的验证码,
- // 一个用来记住要用到的全部字符
- String code = "";
- String data = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789";
-
- //3.定义for循环控制生成多少位随机字符,每次得到一个字符范围内的随机索引
- //根据索引提取该字符,把字符交给code变量连接起来,循环结束后
- //在循环外返回code即可
-
- //获得一个随机数对象,用于获取随机索引
- Random r = new Random();
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- //调用Random里面的方法生成随机索引
- //参数包前不包后
- //调用String里面length()方法,获取字符串的长度返回(就是字符个数)
- int index = r.nextInt(data.length());
- //根据索引在data中提取该字符
- //调用String里面的charAt(int index)方法,获取某个索引位置处的字符返回
- //把字符交给code变量连接起来
- code += data.charAt(index);//等价于 code = code + data.charAt(index)
- }
- //将生成的随机验证码返回
- return code;
- }
- }

2.ArrayList
- import java.util.ArrayList;
-
- /**
- 目标
- ArrayList提供的常用方法
- */
- public class Demo1 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
-
- //public boolean add(E e)
- //将指定的元素添加到此集合的末尾
- list.add("荒天帝石昊");
- list.add("纳兰家纳兰嫣然");
- list.add("萧家萧炎");
-
- //public void add(int index, E element)
- // 在此集合的指定位置插入指定的元素
- list.add(1,"萧家萧炎");
- System.out.println(list);
- //public E get(int index)
- //返回指定索引处的元素
- System.out.println(list.get(1));
-
- //public int size()
- //返回集合中元素的个数
- System.out.println(list.size());
-
- //public E remove(int index)
- // 删除指定索引处的元素,返回被删除的元素
- list.remove(0);
- System.out.println(list);
-
- //public boolean remove(Object o)
- // 删除指定的元素,返回删除是否成功
- System.out.println(list.remove("萧家萧炎"));
- System.out.println(list);
-
- //public E set(int index, E element)
- //修改指定索引处的元素,返回被修改的元素
- System.out.println(list.set(0, "云岚山云韵"));
- System.out.println(list);
-
- }
- }

- import java.util.ArrayList;
-
- /**
- 目标:
- 掌握从容器中找出某些数据并成功删除的技巧
- 需求:现在购物车中存储了如下商品:java入门,宁夏枸杞,黑枸杞
- 人字拖,特级枸杞,枸杞子。现在用户不想买枸杞了,选择了批量删除
- 请完成该需求
- */
- public class Demo2 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- //1.后台使用ArrayList集合表示购物车,存储这些商品名
- ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
- list.add("java入门");
- list.add("宁夏枸杞");
- list.add("黑枸杞");
- list.add("人字拖");
- list.add("特级枸杞");
- list.add("枸杞子");
- //2.遍历集合中的每一个数据,只要这个数据包含了“枸杞”
- //就删除它
-
- /*//public int size():返回集合中元素的个数
- for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
- //public E get(int index)
- //返回指定索引处的元素
- String e = list.get(i);
- //包含“枸杞” 就删除
- //public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
- //判断字符串中是否包含了某个字符串
- if (e.contains("枸杞")) {
- //public boolean remove(Object o)
- //删除指定的元素,返回删除是否成功
- list.remove(e);
- //索引值i-1
- i--;
- }
- }*/
- //倒着遍历
- for (int i = list.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
- //public E get(int index)
- //返回指定索引处的元素
- String e = list.get(i);
- //包含“枸杞” 就删除
- //public boolean contains(CharSequence s)
- //判断字符串中是否包含了某个字符串
- if (e.contains("枸杞")) {
- //public boolean remove(Object o)
- //删除指定的元素,返回删除是否成功
- list.remove(e);
- }
- }
- //3.输出集合看是否已经成功删除了全部枸杞数据了
- System.out.println(list);
- }
- }

- /**
- * 目标:
- * 模仿外卖系统中的商家系统
- * 需求:完成菜品的上架以及菜品信息浏览功能
- */
- public class Demo3 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- FoodOperator fo = new FoodOperator();
- fo.start();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 菜品实体类
- * 用来封装数据
- */
- public class Food {
- private String name;
- private double price;
- private String desc;
-
- public Food() {
- }
-
- public Food(String name, double price, String desc) {
- this.name = name;
- this.price = price;
- this.desc = desc;
- }
-
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
-
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
-
- public double getPrice() {
- return price;
- }
-
- public void setPrice(double price) {
- this.price = price;
- }
-
- public String getDesc() {
- return desc;
- }
-
- public void setDesc(String desc) {
- this.desc = desc;
- }
- }

- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Scanner;
-
- /**
- * 菜品操作实体类
- * 数据的业务处理
- */
- public class FoodOperator {
- //用于存放商品
- private ArrayList<Food> foodList = new ArrayList<>();
-
- //上架商品
- public void add(){
- //创建菜品对象 用来保存菜品数据
- Food f = new Food();
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入菜品名字:");
- String name = sc.next();
- f.setName(name);
- System.out.println("请输入价格:");
- double price = sc.nextDouble();
- f.setPrice(price);
- System.out.println("请输入描述:");
- String desc = sc.next();
- f.setDesc(desc);
- //将菜品对象添加到集合中
- foodList.add(f);
- System.out.println("商品上架成功");
- }
-
- //展示菜品信息
- public void get(){
- if (foodList.size() == 0) {
- System.out.println("没有菜品,请先上架!!");
- return;
- }
- System.out.println("商品信息如下:");
- for (int i = 0; i < foodList.size(); i++) {
- Food f = foodList.get(i);
- System.out.println(f.getName());
- System.out.println(f.getPrice());
- System.out.println(f.getDesc());
- System.out.println("-------------");
- }
- }
-
- public void start(){
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("欢迎来到系统~~");
- System.out.println("1.上架商品");
- System.out.println("2.展示商品");
- System.out.println("3.退出系统");
- System.out.println("请输入您的选择");
- String option = sc.next();
-
- switch (option) {
- case "1":
- add();
- break;
- case "2":
- get();
- break;
- case "3":
- return;
- default:
- System.out.println("没有此选项,请重新选择!");
- break;
- }
- }
-
-
- }
- }

3.案列
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ATM atm = new ATM();
- atm.start();
- }
- }
- public class Account {
- private String cardId;//卡号
- private String username;//用户名
- private char gender;
- private String password;
- private double money;//余额
- private double limit;//每次取现额度
-
- public String getCardId() {
- return cardId;
- }
-
- public void setCardId(String cardId) {
- this.cardId = cardId;
- }
-
- public String getUsername() {
- return username + (gender == '男' ? "先生" : "女士");
- }
-
- public void setUsername(String username) {
- this.username = username;
- }
-
- public char getGender() {
- return gender;
- }
-
- public void setGender(char gender) {
- this.gender = gender;
- }
-
- public String getPassword() {
- return password;
- }
-
- public void setPassword(String password) {
- this.password = password;
- }
-
- public double getMoney() {
- return money;
- }
-
- public void setMoney(double money) {
- this.money = money;
- }
-
- public double getLimit() {
- return limit;
- }
-
- public void setLimit(double limit) {
- this.limit = limit;
- }
- }

- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Random;
- import java.util.Scanner;
-
- public class ATM {
- private ArrayList<Account> accounts = new ArrayList<>();
- private Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- private Account loginAcc;
- {
- Account acc = new Account();
- acc.setUsername("荒天帝");
- acc.setPassword("123456");
- acc.setGender('男');
- acc.setCardId("12345678");
- acc.setLimit(1000);
- accounts.add(acc);
- }
-
- public void start() {
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("=========欢迎来到ATM系统==========");
- System.out.println("1.账户登录");
- System.out.println("2.账户开户");
- System.out.println("请选择~~");
- int choose = sc.nextInt();
- switch (choose) {
- case 1:
- //登录
- login();
- break;
- case 2:
- //开户
- createAccount();
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("没有此选项!");
- }
- }
- }
-
- /** 展示用户登录成功后的操作界面 */
- private void showUserCommand(){
- while (true) {
- System.out.println(loginAcc.getUsername() + "您可以进行以下操作:===========");
- System.out.println("1、查询账户");
- System.out.println("2、存款");
- System.out.println("3、取款");
- System.out.println("4、转账");
- System.out.println("5、修改密码");
- System.out.println("6、退出");
- System.out.println("7、注销当前账户");
- System.out.println("请输入您的选择");
- int command = sc.nextInt();
- switch(command){
- case 1:
- //查询账户
- showLoginAccount();
- break;
- case 2:
- //存款
- depositMoney();
- break;
- case 3:
- //取款
- withdrawMoney();
- break;
- case 4:
- //转账
- transferMoney();
- break;
- case 5:
- //修改密码
- updatePassword();
- return;
- case 6:
- //退出
- System.out.println(loginAcc.getUsername() + "您退出系统成功");
- return;
- case 7:
- //注销当前账户
- if (deletAccount()) {
- return;//返回欢迎界面
- }
- break;
- default:
- System.out.println("没有此选项,请确认~");
- }
- }
- }
- /** 修改密码操作 */
- private void updatePassword() {
- System.out.println("==修改密码操作==");
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请输入当前密码:");
- String password = sc.next();
- //判断登录密码是否正确
- if(loginAcc.getPassword().equals(password)){
- while (true) {
- //正确则可以开始修改密码了
- //请输入新的密码
- System.out.println("请输入新的密码:");
- String newPassword = sc.next();
- System.out.println("请再次输入密码");
- String confirmPassword = sc.next();
- //判断两次输入的密码是否一致
- if(confirmPassword.equals(newPassword)){
- //一样就可以更新账户密码了
- loginAcc.setPassword(confirmPassword);
- System.out.println("恭喜您,修改密码成功~~");
- return;
- }else{
- //不一样
- System.out.println("您输入的两次密码不一致~~");
- }
- }
-
- }else{
- System.out.println("您输入的登录密码不正确~~");
- }
- }
- }
-
- private boolean deletAccount() {
- System.out.println("==销户操作==");
- //确认用户是否要销户
- System.out.println("您真的要销户吗?y/n");
- String command = sc.next();
- switch (command){
- case "y":
- //确认销户
- //判断当前账户是否还有余额
- if(loginAcc.getMoney() > 0){
- //还有余额则不能销户
- System.out.println("您当前的账户还有余额,不能销户~~");
- return false;
- }else{
- //表明可以销户了
- accounts.remove(loginAcc);
- System.out.println("您的账户销户成功~~");
- return true;
- }
- default:
- System.out.println("好的,您的账户保留");
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- /** 转账 */
- private void transferMoney() {
- System.out.println("==转账操作==");
- //判断当前系统是否有其他账户
- if(accounts.size() < 2){
- System.out.println("当前系统只有您一个账户,不能转账~~");
- return;
- }
- //判断自己账户是否有钱
- if(loginAcc.getMoney() == 0){
- System.out.println("当前余额为0,不能转账~");
- return;
- }
- while (true) {
- //输入转账卡号
- System.out.println("请输入对方卡号:");
- String cardId = sc.next();
- // 判断当前卡号在系统是否存在
- Account acc = getAccountByCardId(cardId);
- if(acc == null){
- System.out.println("您输入的卡号不存在");
- }else{
- while (true) {
- //说明卡号存在,请输入转账金额
- System.out.println("请输入转账金额");
- double money = sc.nextDouble();
- //判断转账金额是否超过账户金额
- if(loginAcc.getMoney() < money){
- System.out.println("转账失败,您的余额为:" + loginAcc.getMoney());
- }else{
- //说明可以进行转账,认证对方姓氏
- String name = "*" + acc.getUsername().substring(1);
- System.out.println("请输入【" + name + "】的姓氏");
- String preName = sc.next();
- //判断是否认证成功
- if(!acc.getUsername().startsWith(preName)){
- //认证失败
- System.out.println("认证失败");
- }else {
- //说明认证成功,开始转账
- loginAcc.setMoney(loginAcc.getMoney() - money);
- acc.setMoney(acc.getMoney() + money);
- System.out.println("转账成功~~");
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- /** 取款 */
- private void withdrawMoney() {
- System.out.println("==取款操作==");
- //先判断账户的余额是否大于等于100
- if(loginAcc.getMoney() < 100){
- //如果小于100,则表示余额不足
- System.out.println("余额不足,不能取款,您当前的余额是:" + loginAcc.getMoney());
- return;//跳出并结束当前取款操作
- }
- while (true) {
- //说明余额充足可以取款
- System.out.println("请输入您取款的数目:");
- double money = sc.nextDouble();
- //判断取款金额是否足够
- if(loginAcc.getMoney() < money){
- //不足够
- System.out.println("余额不足,您当前的余额为:" + loginAcc.getMoney());
- }else{
- //余额足够 判断是否取款金额是否超过取款限额
- if(loginAcc.getLimit() < money){
- System.out.println("您当前取款金额超过每次限额,您每次最多可取:" + loginAcc.getLimit());
- }else{
- //取款成功,更新当前的账户余额
- loginAcc.setMoney(loginAcc.getMoney() - money);
- System.out.println("恭喜您取款" + money + "成功,您当前的余额为:" + loginAcc.getMoney() );
- break;
- }
-
- }
- }
- }
-
- /** 存款 */
- private void depositMoney() {
- System.out.println("==存款操作==");
- System.out.println("请输入您要存款的数目:");
- double money = sc.nextDouble();
- //存款成功,更新账户余额
- loginAcc.setMoney(loginAcc.getMoney() + money);
- System.out.println("恭喜您,存款:" + money + "成功,您当前的余额是:" + loginAcc.getMoney());
- }
-
- /** 查询账户 */
- private void showLoginAccount(){
- System.out.println(loginAcc.getUsername() + "您的账户信息如下:==============");
- System.out.println("用户名:" + loginAcc.getUsername());
- System.out.println("卡号:" + loginAcc.getCardId());
- System.out.println("性别:" + loginAcc.getGender());
- System.out.println("余额:" + loginAcc.getMoney());
- System.out.println("取现额度:" + loginAcc.getLimit());
- }
-
- /** 完成用户登录操作 */
- private void login(){
- System.out.println("======用户登录=======");
- //判断当前系统中是否存在账户
- if(accounts.size() == 0){
- //当前系统没有账户,直接结束登录操作
- System.out.println("当前系统还没有账户哟~,请先开户后,再来登录哟~");
- return;//跳出登录方法
- }
- while (true) {
- //如果当前系统存在账户,提示用户输入卡号
- System.out.println("请输入您的卡号:");
- String cardId = sc.next();
- //根据卡号去账户集合中查询账户对象
- Account acc = getAccountByCardId(cardId);
- //如果没有找到账户对象,说明登录卡号不存在,提示继续输入卡号
- if(acc == null){
- System.out.println("您输入的卡号不存在,请确认~");
- }else{
- while (true) {
- //如果找到了账户对象,说明卡号存在,继续输入密码
- System.out.println("请您输入密码:");
- String pwd = sc.next();
- //如果密码不正确,提示继续输入密码
- if(!acc.getPassword().equals(pwd)){
- System.out.println("您输入的密码不正确,请确认~");
- }else{
- loginAcc = acc;
- //如果密码正确,说明登录成功,并给出相应的提示
- System.out.println("欢迎" + acc.getUsername() + ",登录成功,您的卡号是:" + acc.getCardId());
- //......
- showUserCommand();
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- private void createAccount() {
- //创建账户对象封装数据
- System.out.println("===========开户操作==============");
- Account account = new Account();
- System.out.println("请输入账户名:");
- String name = sc.next();
- account.setUsername(name);
-
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请输入性别:");
- char gender = sc.next().charAt(0);
- if (gender == '男' || gender == '女') {
- account.setGender(gender);
- break;
- } else {
- System.out.println("性别只能是男或女");
- }
- }
-
- while (true) {
- System.out.println("请输入密码:");
- String password = sc.next();
- System.out.println("请输入确认密码:");
- String confirmPassword = sc.next();
- if (password.equals(confirmPassword)) {
- account.setPassword(confirmPassword);
- break;
- } else {
- System.out.println("两次输入的密码不一样");
- }
- }
-
- System.out.println("请输入每次取现限制额度");
- double limit = sc.nextDouble();
- account.setLimit(limit);
-
- //系统生成卡号
- String cardId = createCardId();
- account.setCardId(cardId);
- accounts.add(account);
- System.out.println("恭喜你," + account.getUsername() + "开户成功,您的卡号是:" + account.getCardId());
- }
-
- /**
- * 定义方法,用来生成不重复的卡号
- */
- private String createCardId() {
- Random r = new Random();
- while (true) {
- //定义变量记录卡号
- String cardId = "";
- //循环生成卡号
- for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
- int number = r.nextInt(10);//随机生成0-9
- cardId += number;
- }
- //判断卡号是否重复
- if (getAccountByCardId(cardId) == null) {
- //没有重复
- return cardId;
- }
- }
- }
-
- /**
- * 定义方法根据id查询账户
- *
- * @param cardId
- * @return
- */
- private Account getAccountByCardId(String cardId) {
- //遍历账户集合
- for (int i = 0; i < accounts.size(); i++) {
- Account acc = accounts.get(i);
- //根据id判断是否查询到账户
- if (acc.getCardId().equals(cardId)) {
- //id相等,查询成功
- return acc;
- }
- }
- //查无此账户
- return null;
- }
- }