- 1Windows常见进程_ccmexec.exe是什么程序
- 22024年值得收藏的几款开源主机安全系统hids_2024 开源 主机安全
- 3Centos安装rabbitMQ_package erlang-r16b-03.18.el7.aarch64 requires erl
- 4Stable Diffusion 使用详解(2)---- 图生图原理,操作,参数
- 5人工智能大语言模型微调技术:SFT 、LoRA 、Freeze 监督微调方法_大模型 sft
- 6【ONLYOFFICE震撼8.1】ONLYOFFICE8.1版本桌面编辑器测评_onlyoffice提供哪些接口
- 7AI绘画专栏之statble diffusion SDXL 1.0 换脸roop easyphoto (24)_sd-webui-controlnet 支持xl
- 8国内开源RAG知识库ChatWiki MaxKb QAnyThing对比
- 9Parallels® Desktop 19 for Mac在 Mac 上运行 Windows,简单,强大,无缝。_pd19
- 10mysql 视图_如何用show table status查看视图
Spark Delta Lake
赞
踩
rm -r dp-203 -f
git clone https://github.com/MicrosoftLearning/dp-203-azure-data-engineer dp-203
cd dp-203/Allfiles/labs/07
./setup.ps1
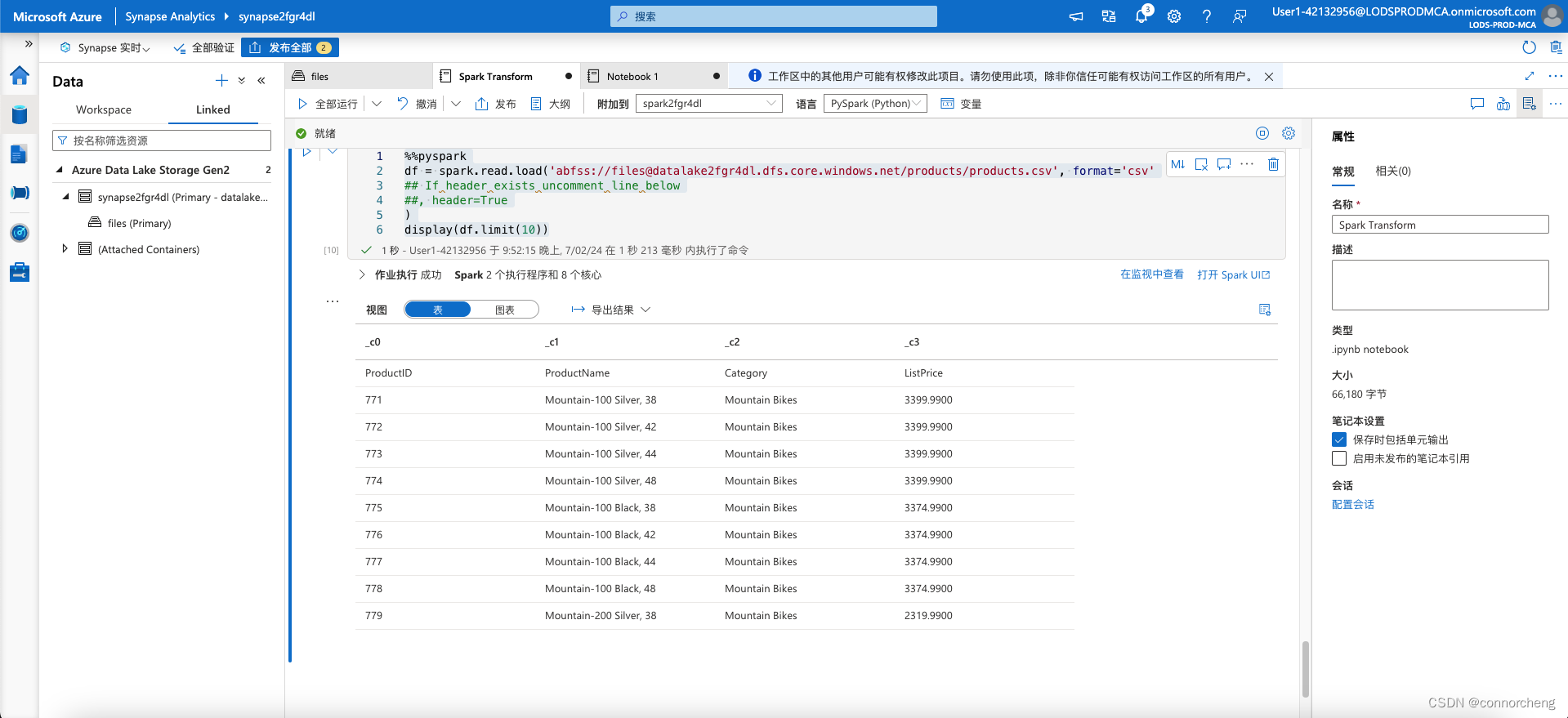
- %%pyspark
- df = spark.read.load('abfss://files@datalakexxxxxxx.dfs.core.windows.net/products/products.csv', format='csv'
- ## If header exists uncomment line below
- ##, header=True
- )
- display(df.limit(10))
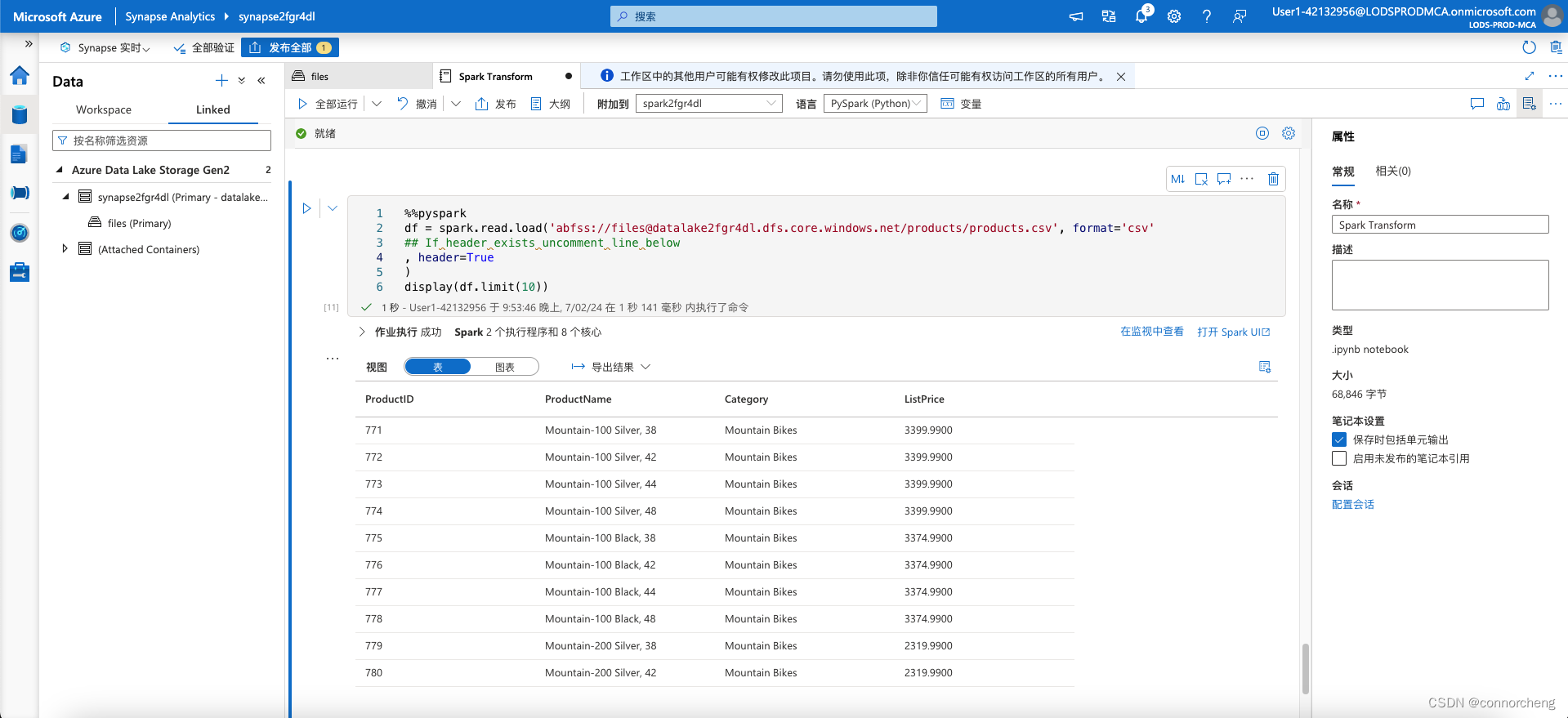
- %%pyspark
- df = spark.read.load('abfss://files@datalakexxxxxxx.dfs.core.windows.net/products/products.csv', format='csv'
- ## If header exists uncomment line below
- , header=True
- )
- display(df.limit(10))
- delta_table_path = "/delta/products-delta"
- df.write.format("delta").save(delta_table_path)
-
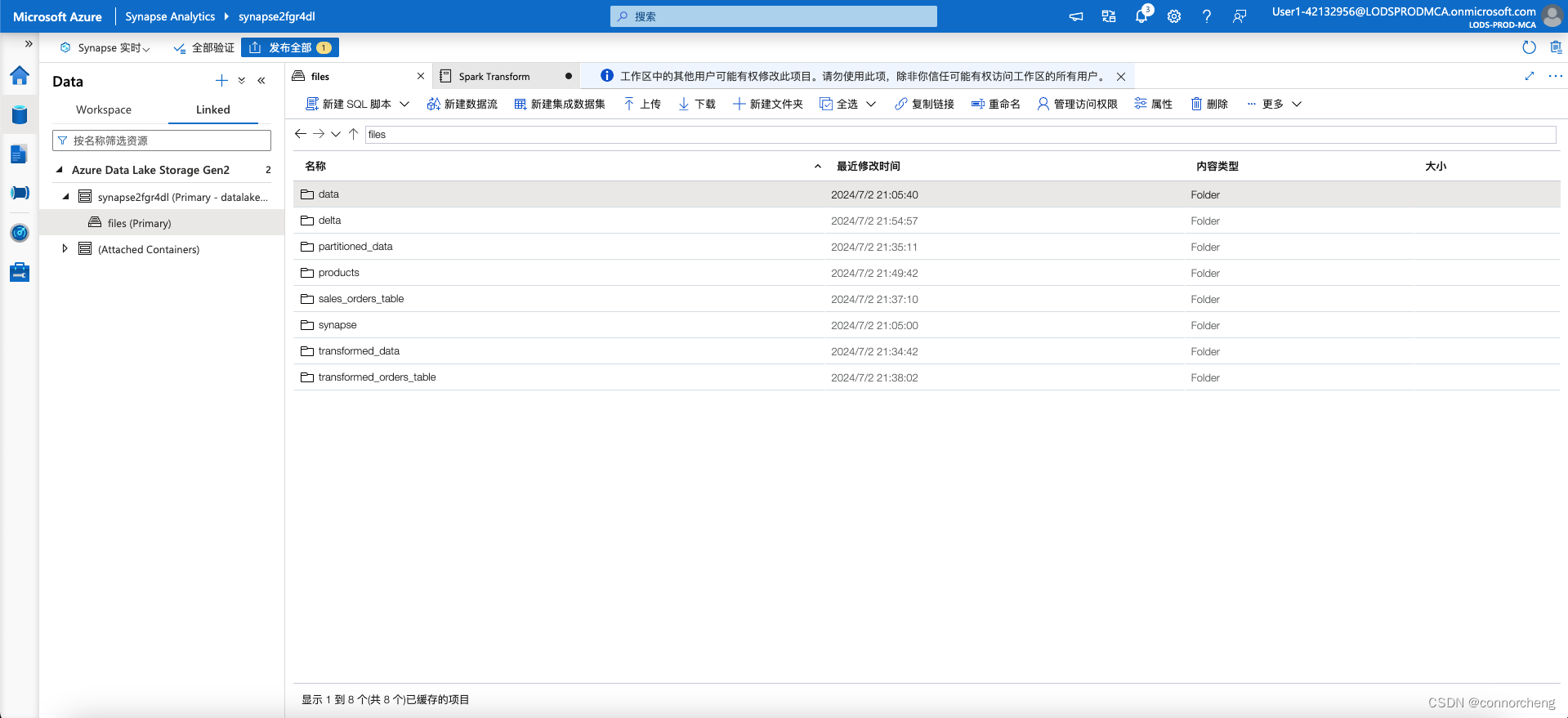
On the files tab, use the ↑ icon in the toolbar to return to the root of the files container, and note that a new folder named delta has been created. Open this folder and the products-delta table it contains, where you should see the parquet format file(s) containing the data.
- from delta.tables import *
- from pyspark.sql.functions import *
-
- # Create a deltaTable object
- deltaTable = DeltaTable.forPath(spark, delta_table_path)
-
- # Update the table (reduce price of product 771 by 10%)
- deltaTable.update(
- condition = "ProductID == 771",
- set = { "ListPrice": "ListPrice * 0.9" })
-
- # View the updated data as a dataframe
- deltaTable.toDF().show(10)
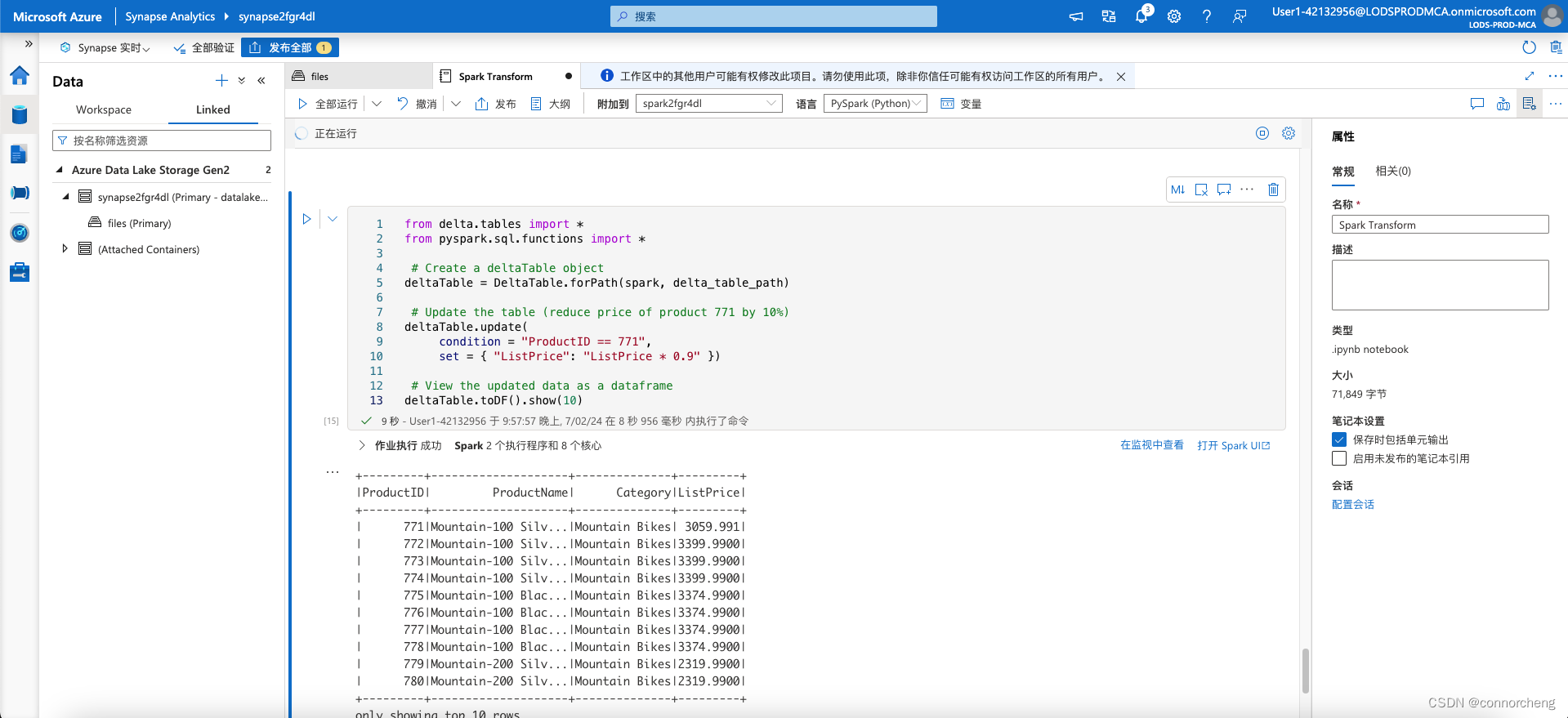
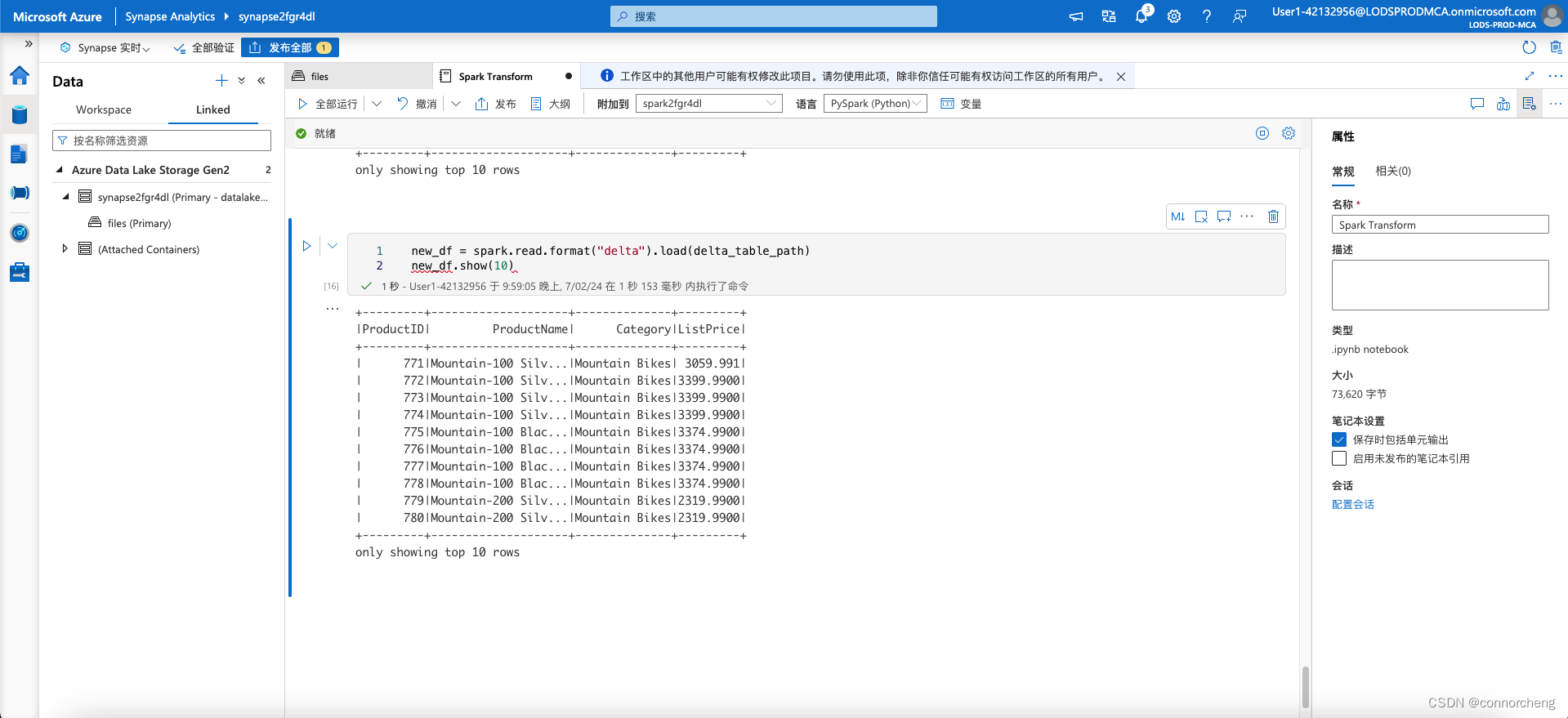
- new_df = spark.read.format("delta").load(delta_table_path)
- new_df.show(10)
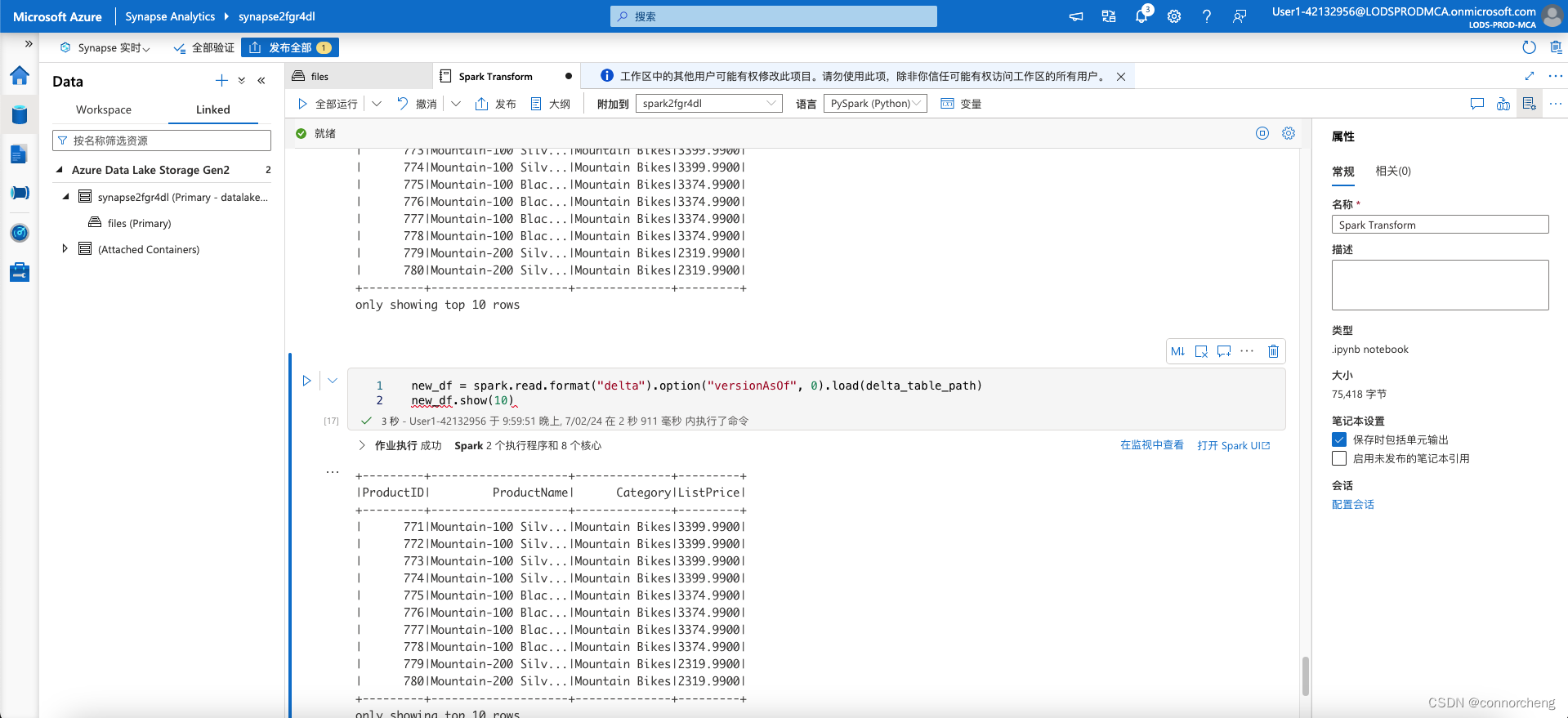
- new_df = spark.read.format("delta").option("versionAsOf", 0).load(delta_table_path)
- new_df.show(10)
deltaTable.history(10).show(20, False, True)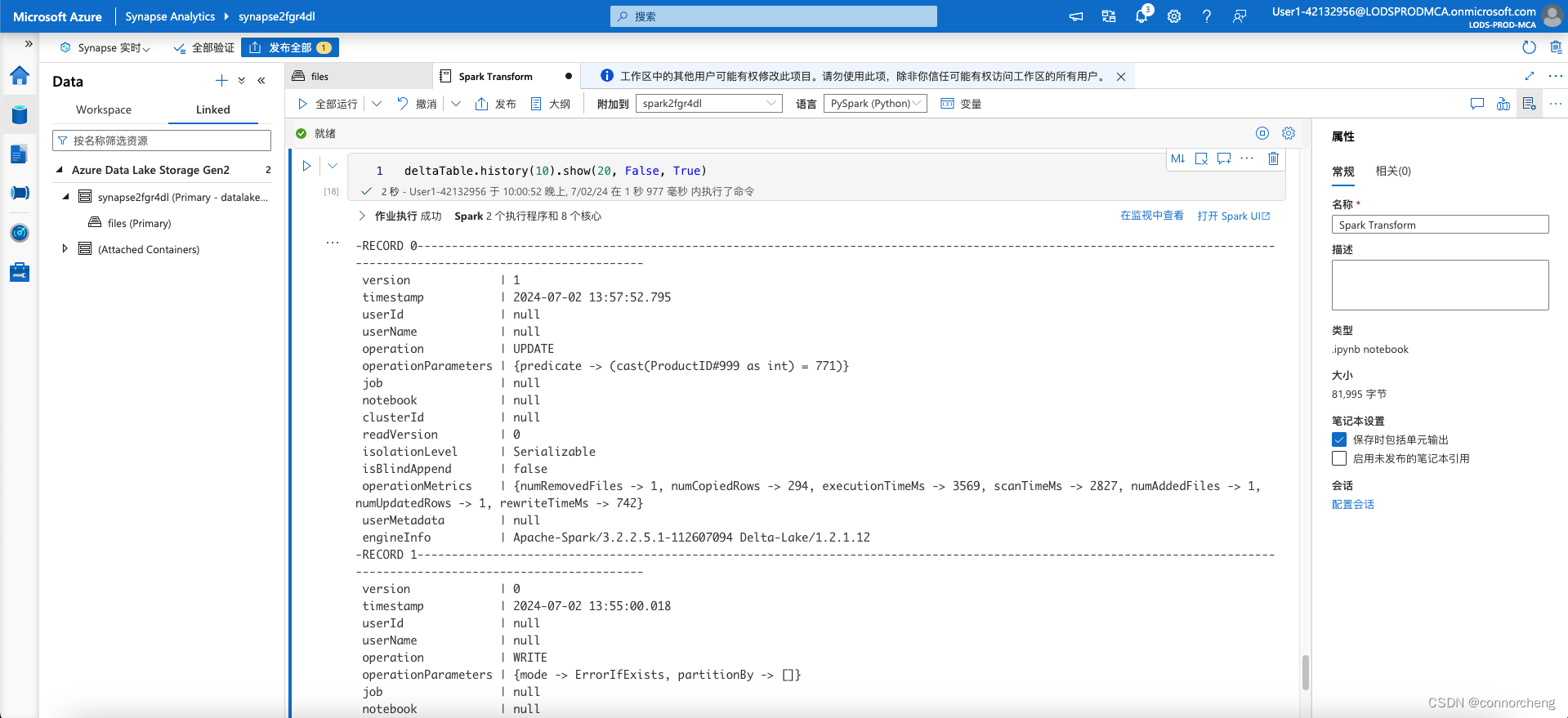
- spark.sql("CREATE DATABASE AdventureWorks")
- spark.sql("CREATE TABLE AdventureWorks.ProductsExternal USING DELTA LOCATION '{0}'".format(delta_table_path))
- spark.sql("DESCRIBE EXTENDED AdventureWorks.ProductsExternal").show(truncate=False)
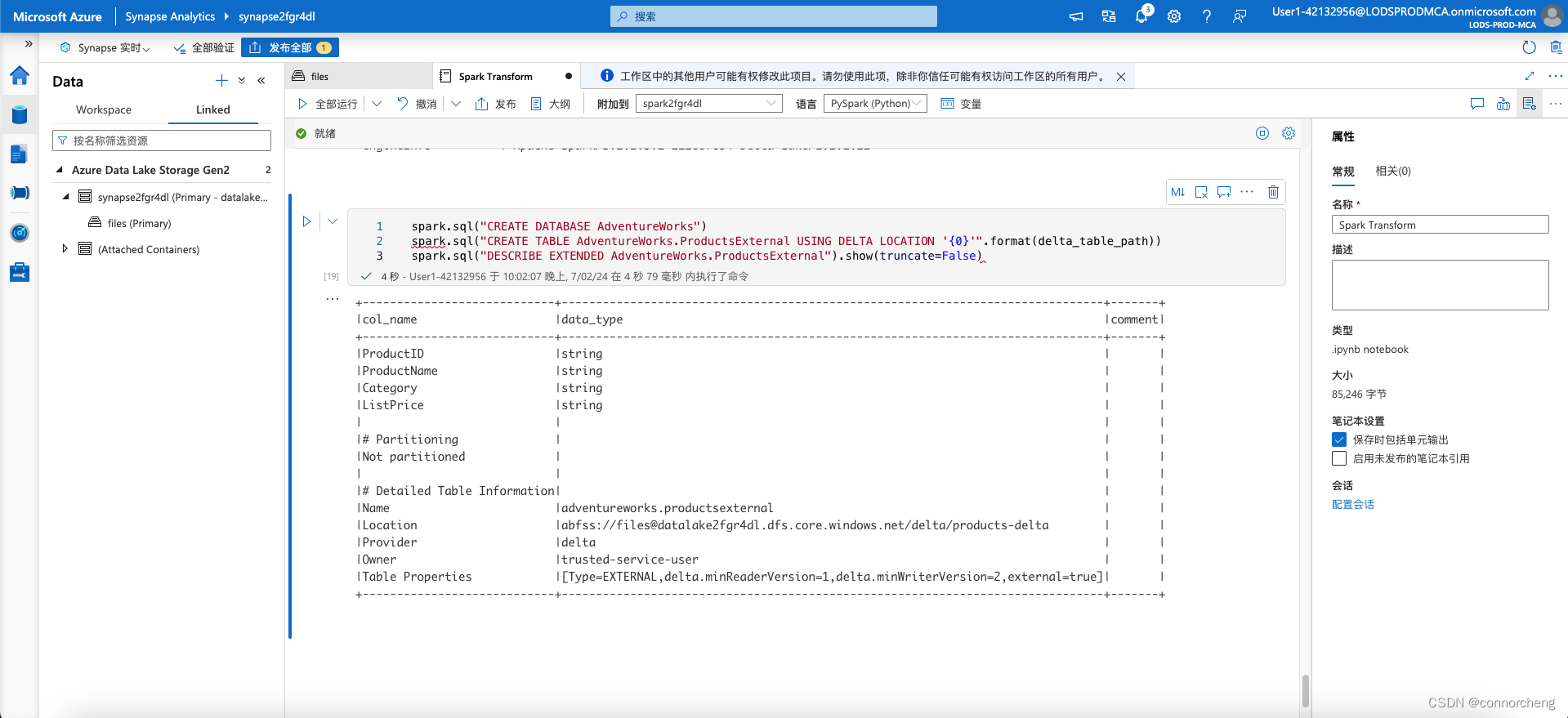
This code creates a new database named AdventureWorks and then creates an external tabled named ProductsExternalin that database based on the path to the parquet files you defined previously. It then displays a description of the table’s properties. Note that the Location property is the path you specified.
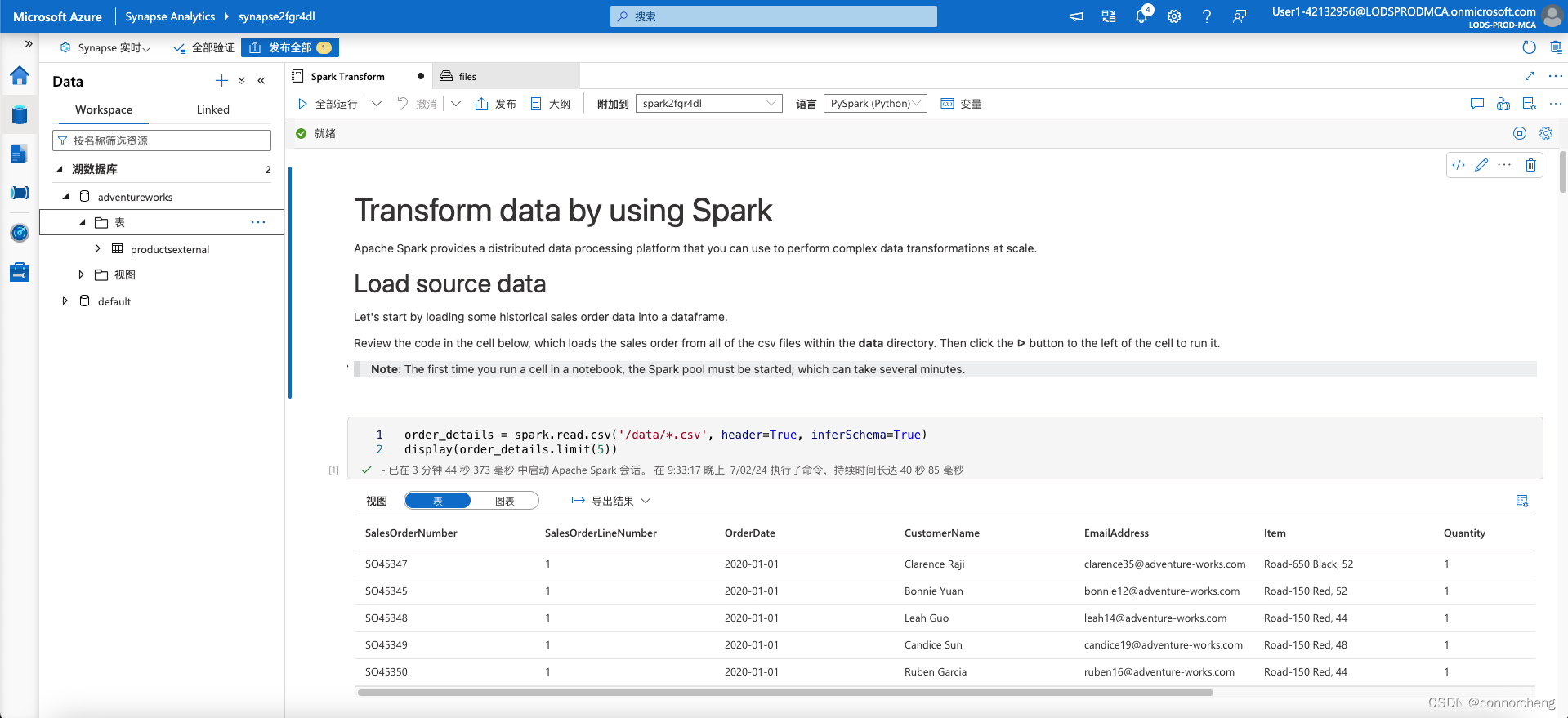
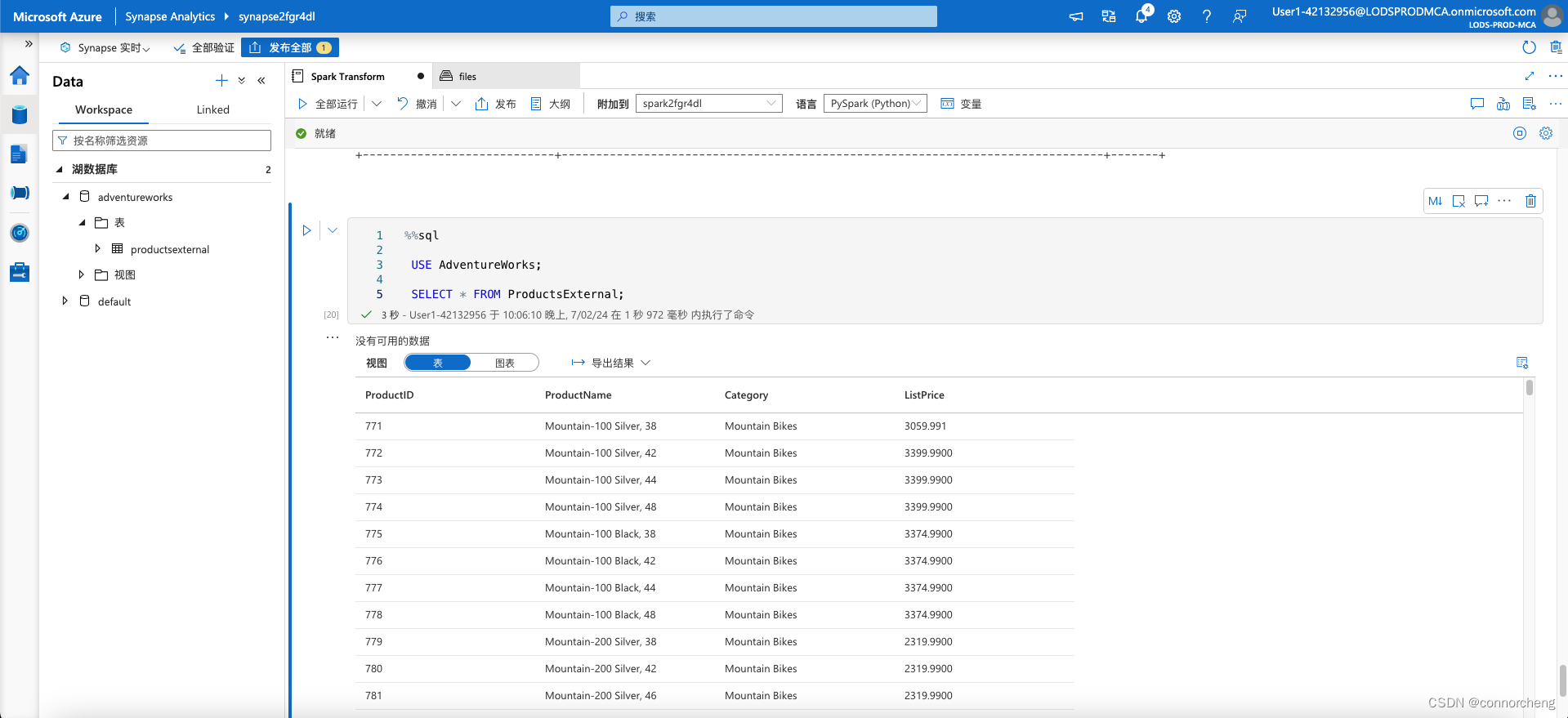
- %%sql
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- SELECT * FROM ProductsExternal;
- df.write.format("delta").saveAsTable("AdventureWorks.ProductsManaged")
- spark.sql("DESCRIBE EXTENDED AdventureWorks.ProductsManaged").show(truncate=False)
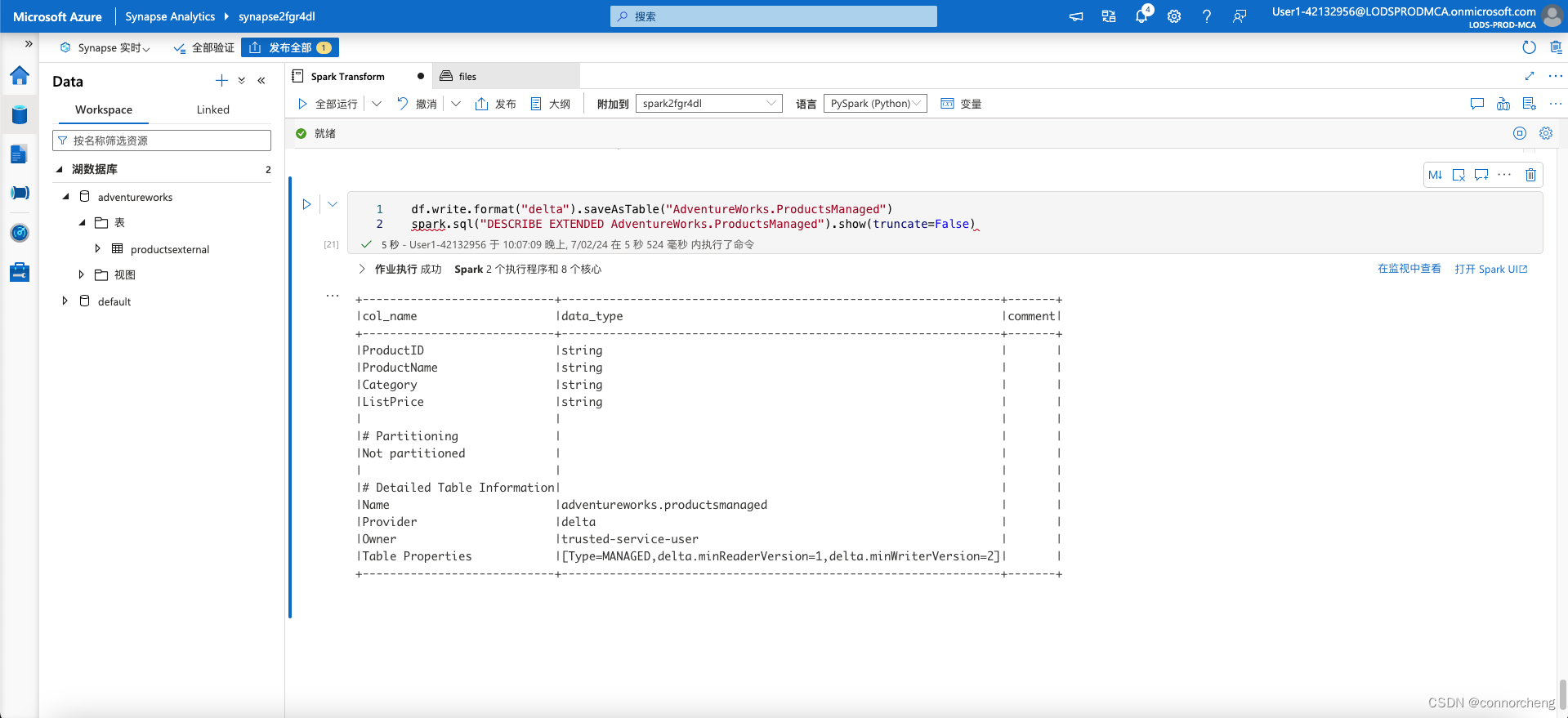
This code creates a managed tabled named ProductsManaged based on the DataFrame you originally loaded from the products.csv file (before you updated the price of product 771). You do not specify a path for the parquet files used by the table - this is managed for you in the Hive metastore, and shown in the Location property in the table description (in the files/synapse/workspaces/synapsexxxxxxx/warehouse path).
- %%sql
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- SELECT * FROM ProductsManaged;
- %%sql
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- SHOW TABLES;
- %%sql
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS ProductsExternal;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS ProductsManaged;
- Return to the files tab and view the files/delta/products-delta folder. Note that the data files still exist in this location. Dropping the external table has removed the table from the metastore, but left the data files intact.
- View the files/synapse/workspaces/synapsexxxxxxx/warehouse folder, and note that there is no folder for the ProductsManaged table data. Dropping a managed table removes the table from the metastore and also deletes the table’s data files.
- %%sql
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- CREATE TABLE Products
- USING DELTA
- LOCATION '/delta/products-delta';
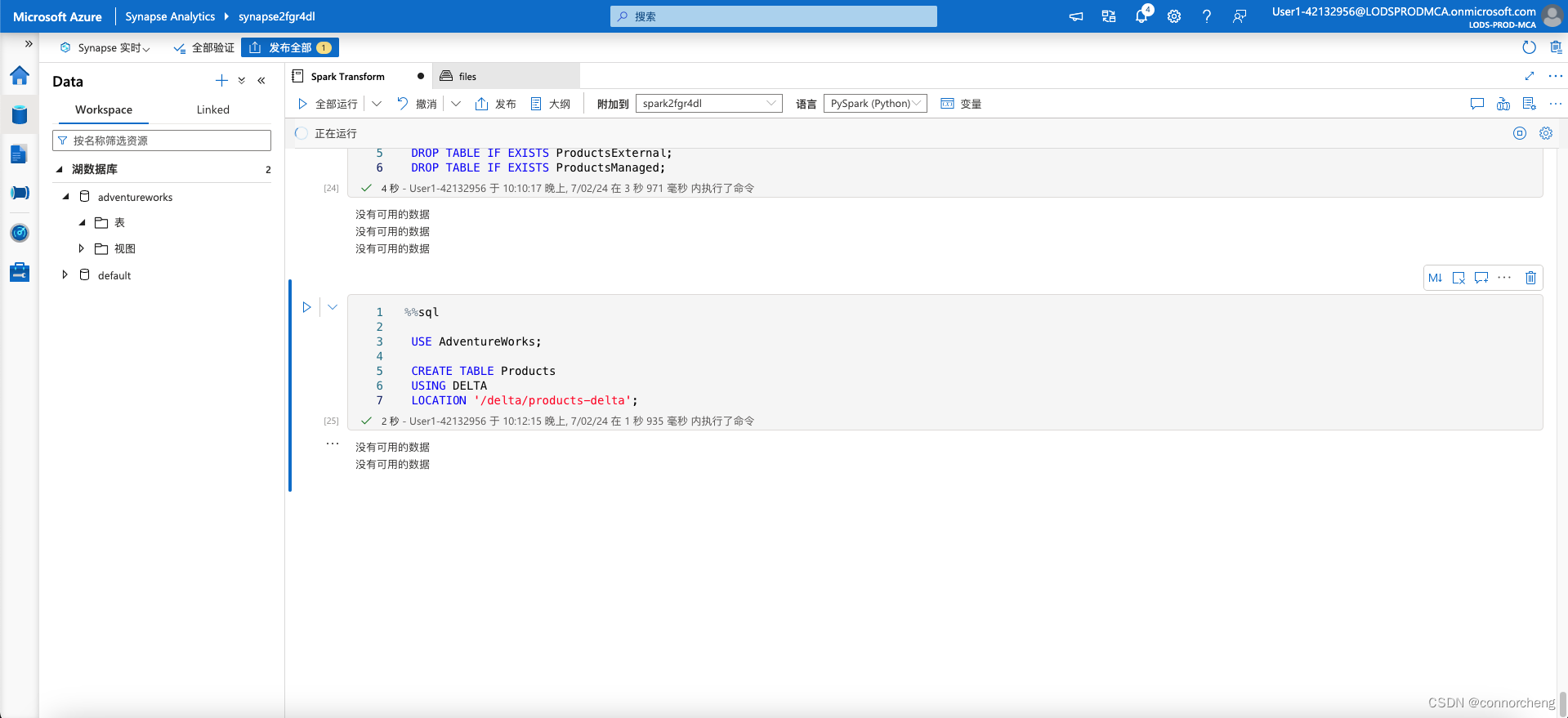
- %%sql
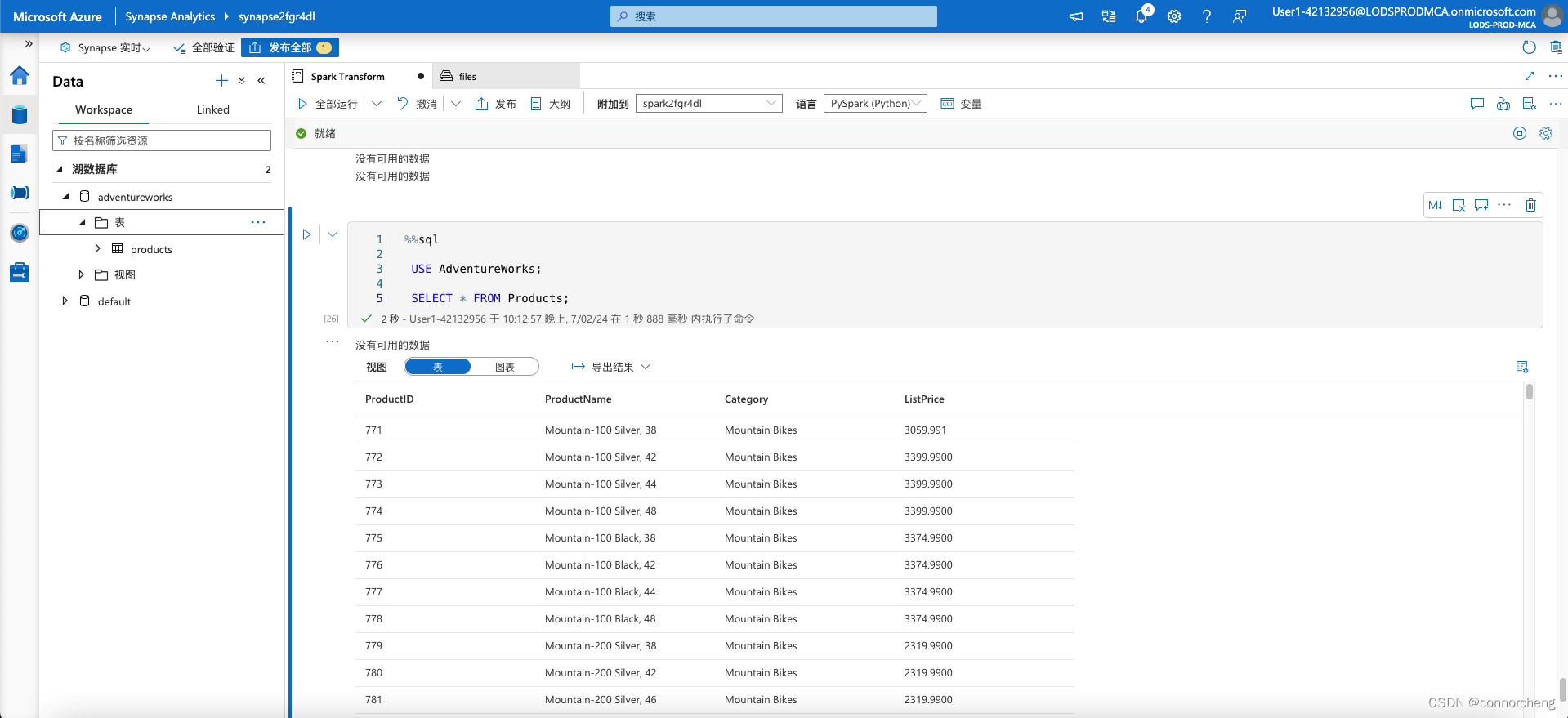
-
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- SELECT * FROM Products;
- from notebookutils import mssparkutils
- from pyspark.sql.types import *
- from pyspark.sql.functions import *
-
- # Create a folder
- inputPath = '/data/'
- mssparkutils.fs.mkdirs(inputPath)
-
- # Create a stream that reads data from the folder, using a JSON schema
- jsonSchema = StructType([
- StructField("device", StringType(), False),
- StructField("status", StringType(), False)
- ])
- iotstream = spark.readStream.schema(jsonSchema).option("maxFilesPerTrigger", 1).json(inputPath)
-
- # Write some event data to the folder
- device_data = '''{"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev2","status":"error"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"error"}
- {"device":"Dev2","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev2","status":"error"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}'''
- mssparkutils.fs.put(inputPath + "data.txt", device_data, True)
- print("Source stream created...")

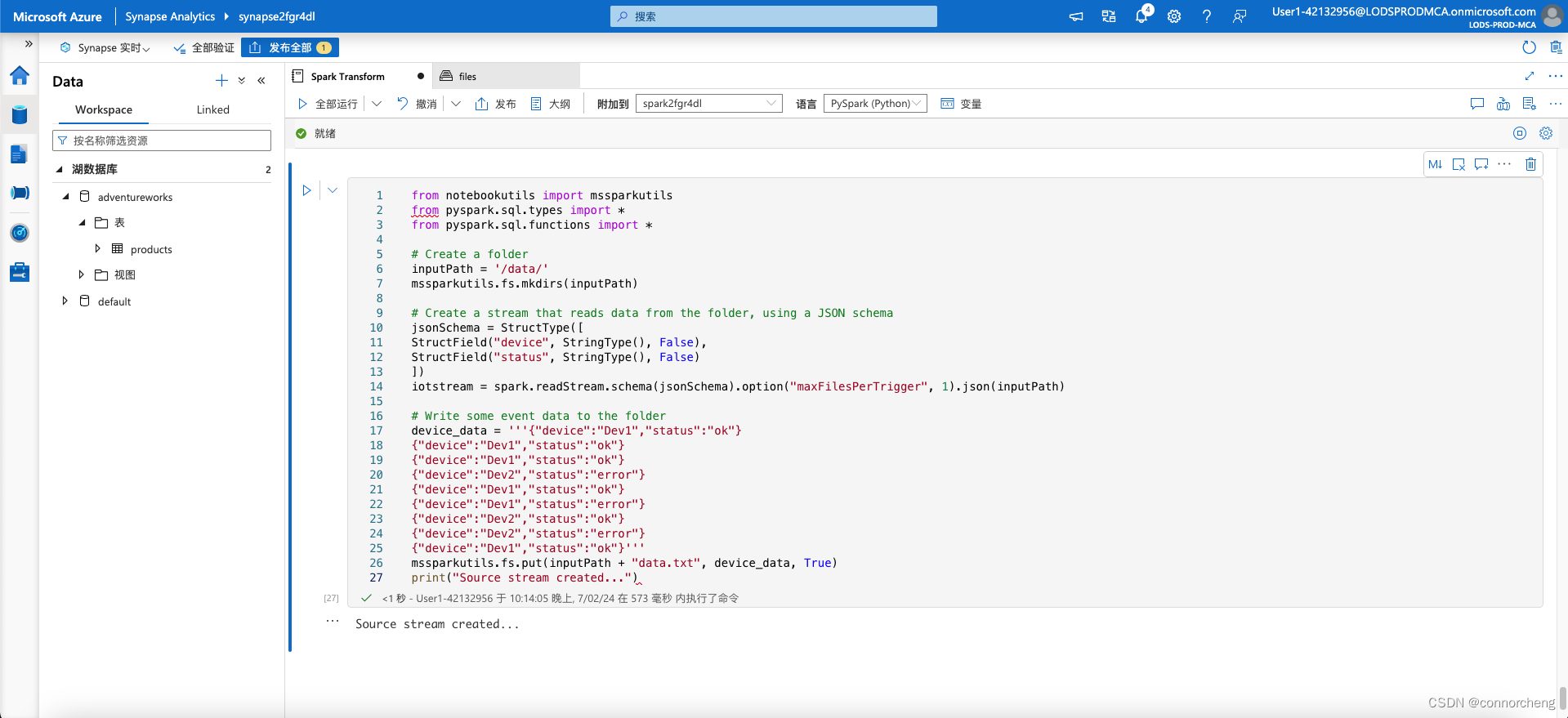
Ensure the message Source stream created… is printed. The code you just ran has created a streaming data source based on a folder to which some data has been saved, representing readings from hypothetical IoT devices.
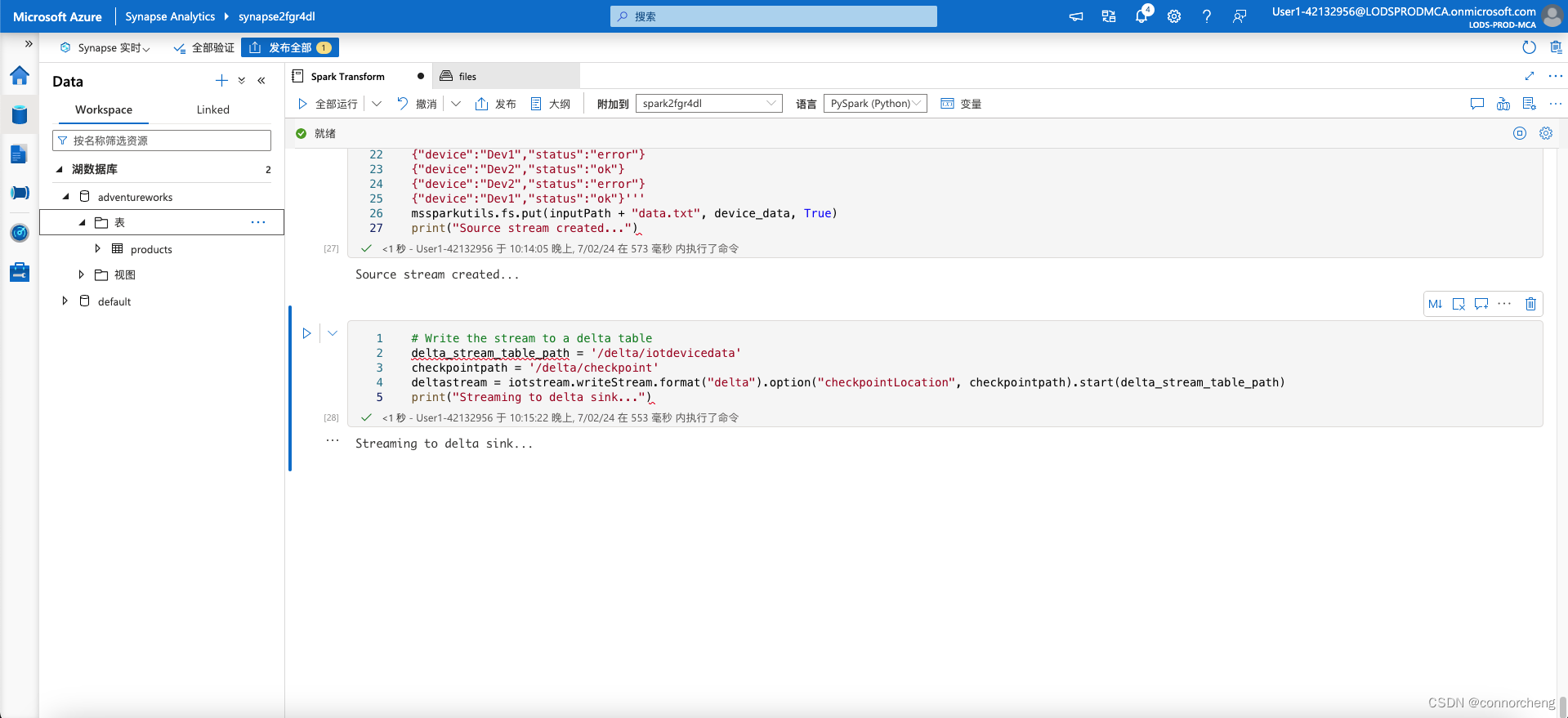
- # Write the stream to a delta table
- delta_stream_table_path = '/delta/iotdevicedata'
- checkpointpath = '/delta/checkpoint'
- deltastream = iotstream.writeStream.format("delta").option("checkpointLocation", checkpointpath).start(delta_stream_table_path)
- print("Streaming to delta sink...")
- # Read the data in delta format into a dataframe
- df = spark.read.format("delta").load(delta_stream_table_path)
- display(df)
- # create a catalog table based on the streaming sink
- spark.sql("CREATE TABLE IotDeviceData USING DELTA LOCATION '{0}'".format(delta_stream_table_path))
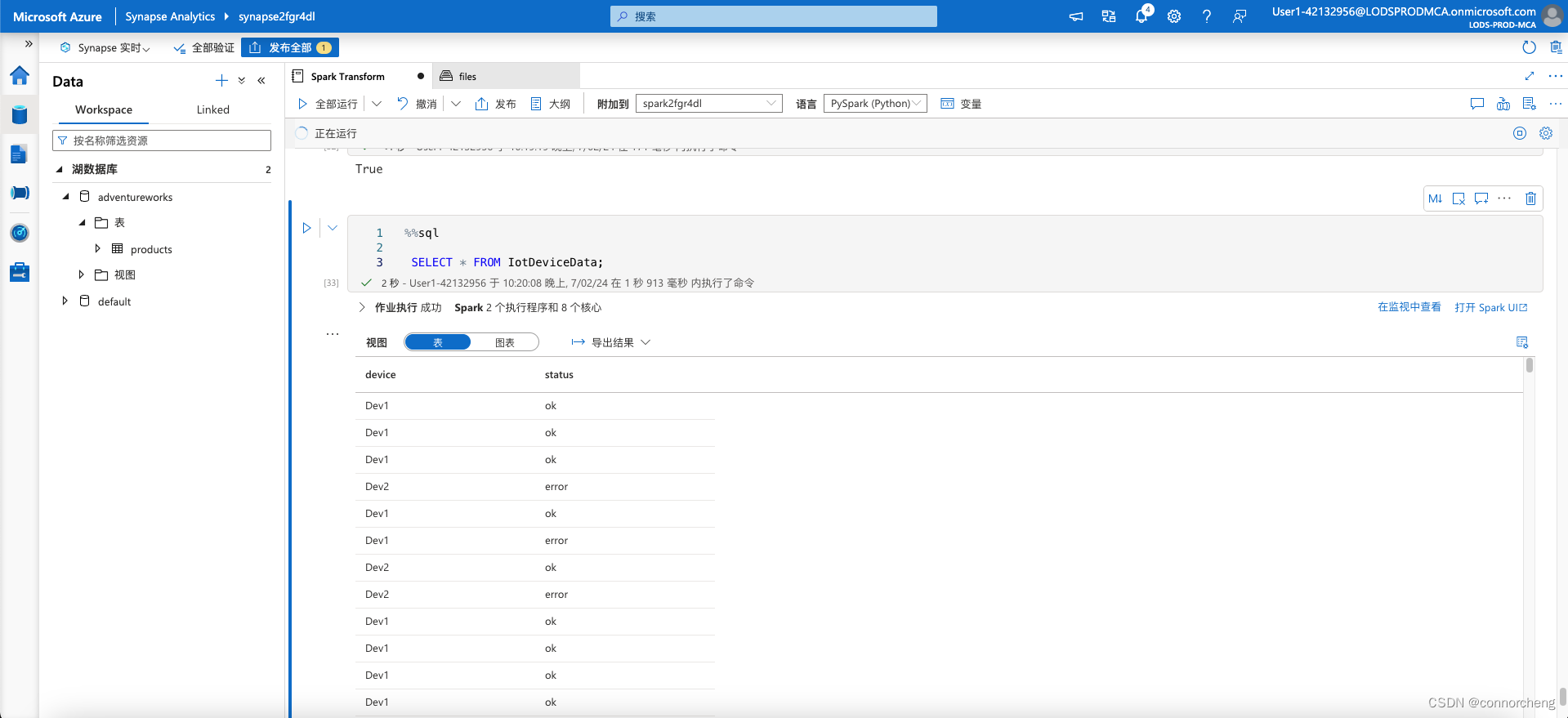
- %%sql
-
- SELECT * FROM IotDeviceData;
- # Add more data to the source stream
- more_data = '''{"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"error"}
- {"device":"Dev2","status":"error"}
- {"device":"Dev1","status":"ok"}'''
-
- mssparkutils.fs.put(inputPath + "more-data.txt", more_data, True)
- %%sql
-
- SELECT * FROM IotDeviceData;
deltastream.stop()
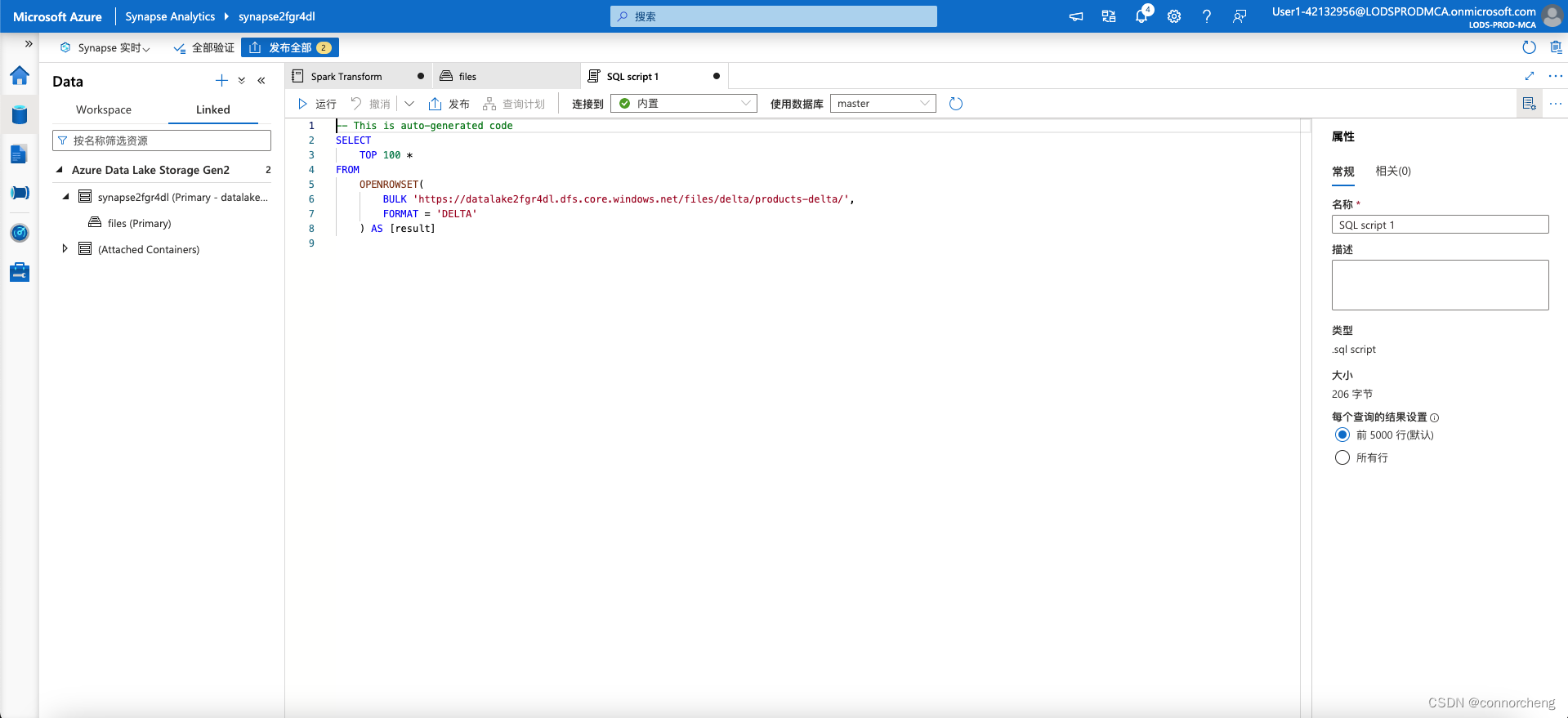
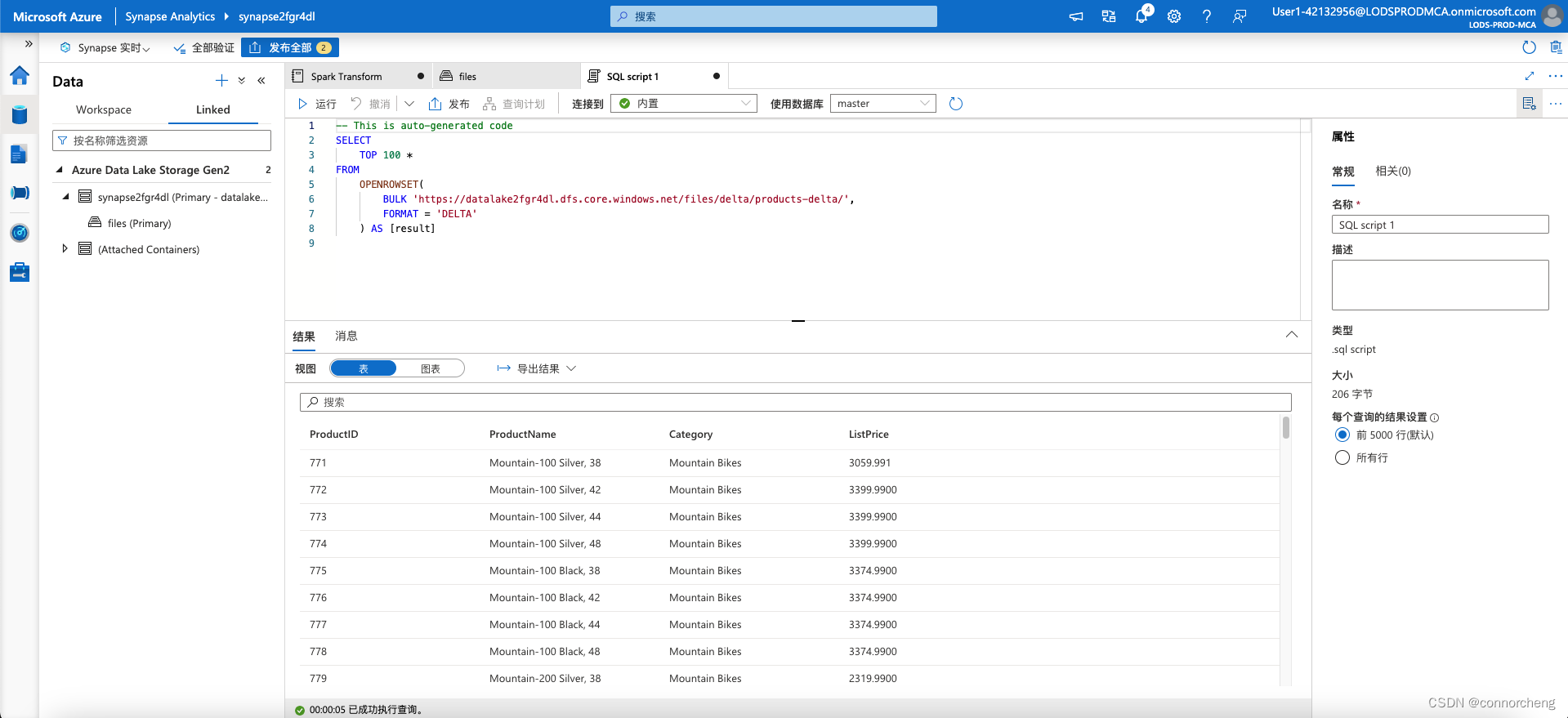
- -- This is auto-generated code
- SELECT
- TOP 100 *
- FROM
- OPENROWSET(
- BULK 'https://datalakexxxxxxx.dfs.core.windows.net/files/delta/products-delta/',
- FORMAT = 'DELTA'
- ) AS [result]
- USE AdventureWorks;
-
- SELECT * FROM Products;
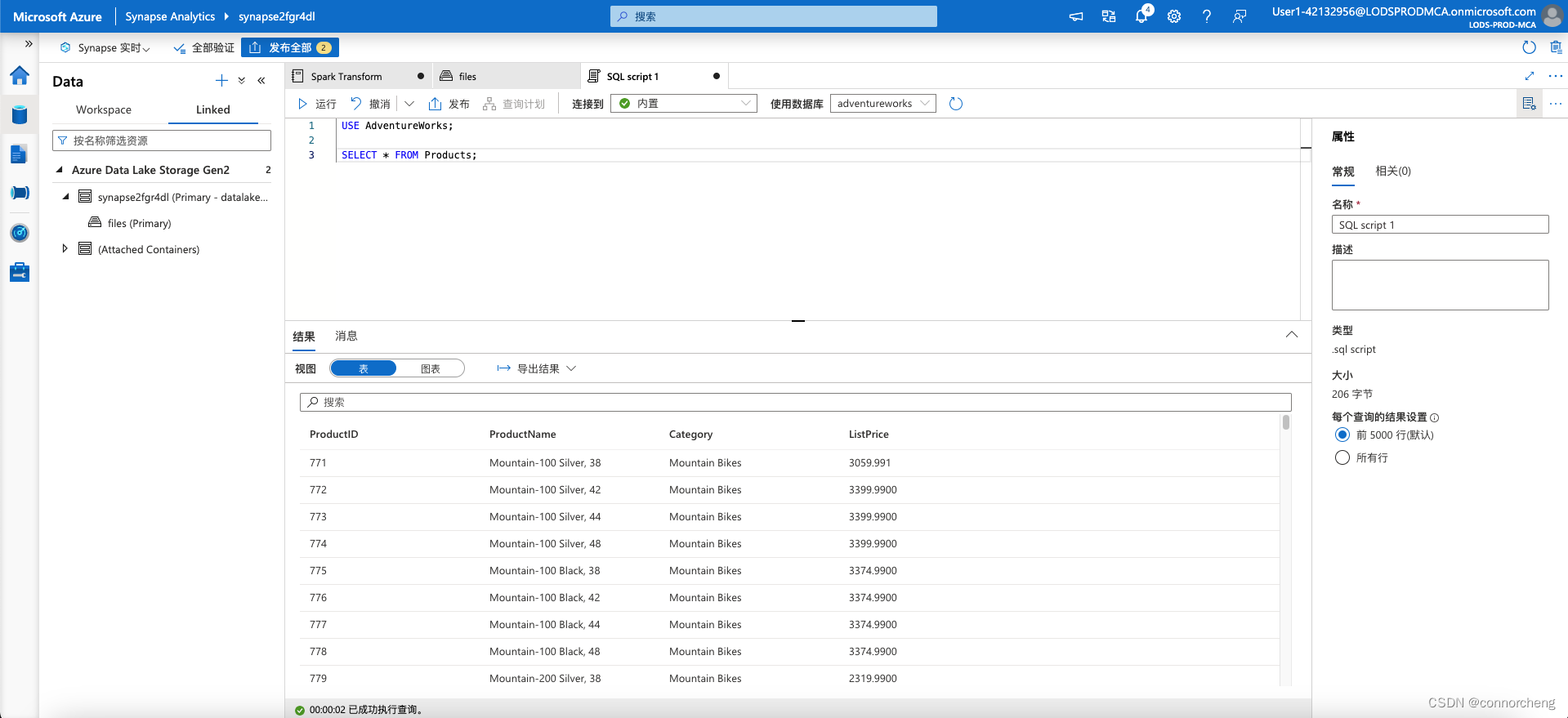
Run the code and observe that you can also use the serverless SQL pool to query Delta Lake data in catalog tables that are defined the Spark metastore.


