- 1H5适配iOS顶部和底部安全区域
- 2Domino中的源代码管理工具_domino如何看nsf的代码行数
- 3产品经理常见面试题目——思维/场景问题_未来五年我认为会成为一个重要的方向,无论是从政策层面还是从融资方面,都显示web3
- 42020年11个Redis系列高频面试题,哪些你还不会?_redis高频面试题
- 5myST Login issue in STM32CubeIDE_stm32cube ide怎么登录不了
- 6Docker基础------安装docker,以及一些常用的docker命令,docker网络,自定义docker网络_docker方式部署环境,查询cps服务容器id并将docker容器内/home目录下的test.d
- 7普通字符再scanf中的应用_scanf普通字符
- 8Android性能优化之SharedPreference卡顿优化_sharepreference 优化
- 9Cocoa-01-Mac OS应用开发概述
- 10Spring Boot:@PostConstruct虽好,也要慎用_@postconstruct注解的好处与坏处
Java ExecutorService 示例
赞
踩
在本教程中,我们将了解Java 中的executorservice。我们已经知道 Java 与需要在线程中并发执行任务的多线程应用程序一起工作非常有效。
对于任何应用程序来说,同时执行大量线程都是具有挑战性的。因此,为了克服这个问题,Java 提供了 ExecutorService 接口,它是 Executors 框架的一个子接口。
在本文中,我们将了解如何创建 ExecutorService。并且,如何将要执行的任务提交给执行器服务,我们还讨论了如何查看这些任务的结果。
最后,我们将研究如何在需要时再次关闭 ExecutorService。
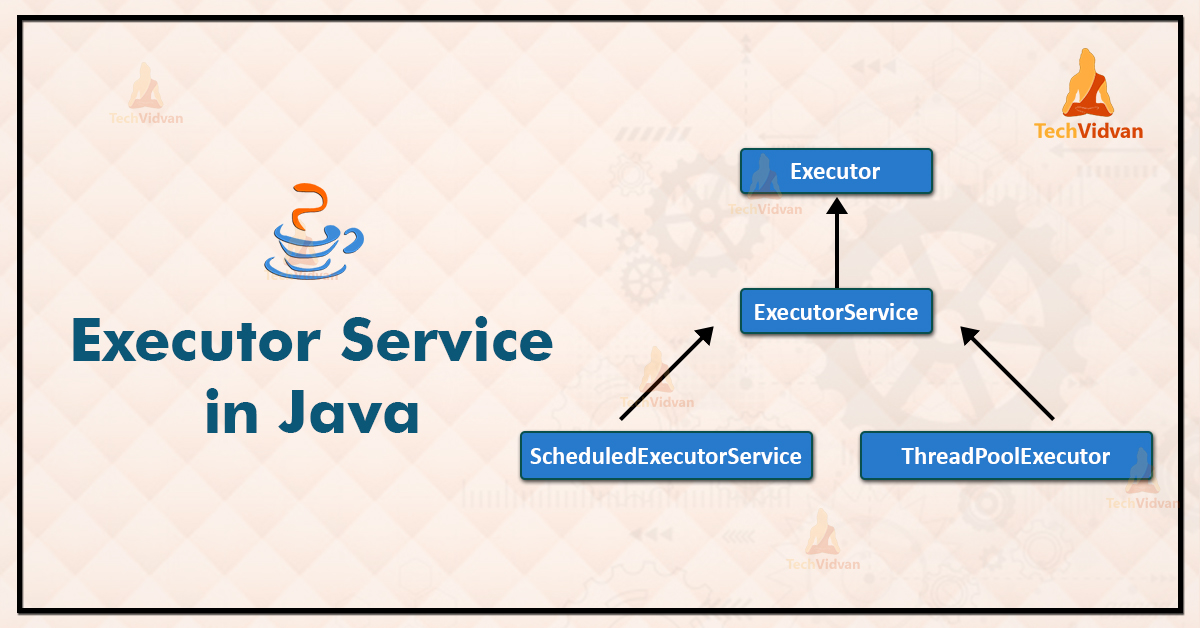
什么是执行器框架?
我们更容易同时创建和执行一两个线程。但是当线程数量增加到相当多的时候,就变得很困难了。许多多线程应用程序有数百个线程同时运行。
因此,需要将线程的创建与应用程序中的线程管理分开。
Java ExecutorService 接口位于 java.util.concurrent 包中。该接口代表了一种异步执行机制,可以在后台并发执行多个任务。
ExecutorService 执行的任务
执行程序服务框架有助于在应用程序中创建和管理线程。执行器框架执行以下任务。
1、线程创建: Executor服务提供了很多线程创建的方法。这有助于并发运行应用程序。
2. 线程管理: Executor 服务也有助于管理线程生命周期。在提交任务执行之前,我们不必担心线程是处于活动状态、忙碌状态还是死状态。
3. 任务提交与执行: Executor 框架还提供了在线程池中提交任务的方法。它还提供了决定线程是否执行的权力。
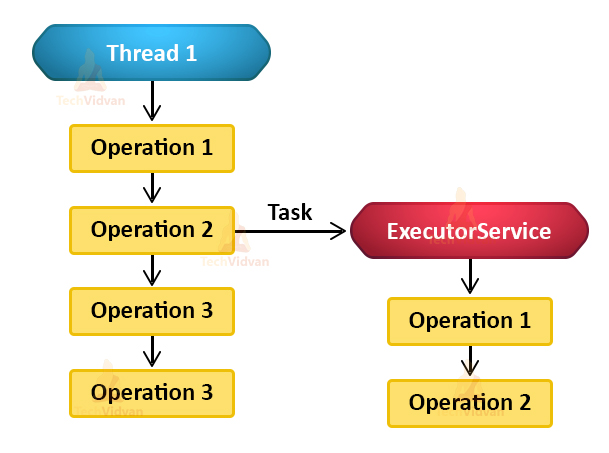
任务委托
下图表示将任务委托给 Java ExecutorService 进行异步执行的线程:
创建 ExecutorService
ExecutorService 是 Java 中的一个接口。此接口的实现可以异步方式执行 Runnable 或 Callable 类。我们必须注意,以同步方式调用 Runnable 接口的 run() 方法是调用一个方法。
我们可以通过以下方式创建 ExecutorService 接口的实例:
1. Executors类
Executors 类是一个实用程序类,它提供工厂方法来创建 Executor 服务接口的实现。
- //Executes only one thread
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
-
- //Internal management of thread pool of 2 threads
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
-
- //Internally managed thread pool of 10 threads to run scheduled tasks
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
2. 构造函数
下面的语句创建了一个线程池执行器。我们使用最小线程数为 10 的构造函数创建它。最大线程数为 100。保持活动时间为 5 毫秒。而且,有一个阻塞队列来监视将来的任务。
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
- import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
- import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
- import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
- ExecutorService exService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 100, 5L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue < Runnable > ());
Java ExecutorService 示例
Java中的ExecutorService是executor框架的一个子接口。它提供了某些功能来管理应用程序的线程生命周期。还有一个 submit() 方法可以接受可运行和可调用对象。
在下面的示例中,我们将创建一个单线程的 ExecutorService,然后提交要在线程内执行的任务。
- import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
- import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
- public class Example {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- System.out.println("Inside: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- System.out.println("Creating ExecutorService");
- ExecutorService executorservice = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
- System.out.println("Creating a Runnable");
- Runnable runnable = () - >{
- System.out.println("Inside: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
- };
- System.out.println("Submitting the task specified by the runnable to the executorservice");
- executorservice.submit(runnable);
- }
- }
输出:
- Inside: main
- Creating ExecutorService
- Creating a Runnable
- Submitting the task specified by the runnable to the executorservice
- Inside: pool-1-thread-1
注意:运行上述程序时,程序永远不会退出。您需要明确关闭它,因为执行程序服务一直在侦听新任务。
Java ExecutorService 实现
ExecutorService 与线程池非常相似。java.util.concurrent包中ExecutorService的实现是线程池实现。java.util.concurrent 包中有以下 ExecutorService 的实现:
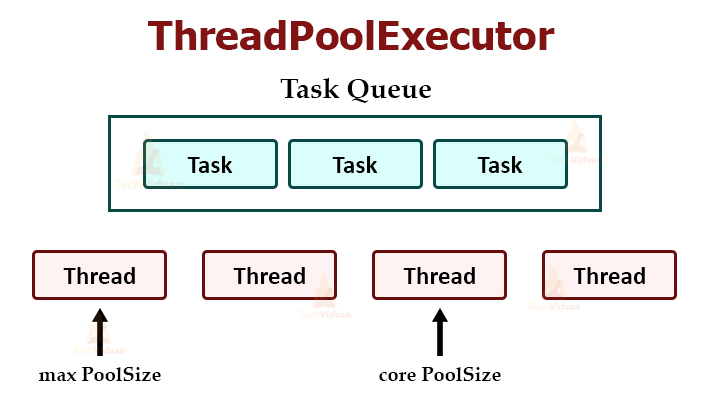
1.线程池执行器
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用其内部池线程之一执行指定的任务。
创建一个线程池执行器
- int corethreadPoolSize = 10;
- int maxPoolSize = 15;
- long keepAliveTime = 6000;
- ExecutorService es = new threadPoolExecutor(corethreadPoolSize, maxPoolSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue < Runnable > ());
2. ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是一个 ExecutorService,它可以调度任务在延迟后运行或在每次执行之间以固定的时间间隔重复执行。
创建 ScheduledthreadPoolExecutor
- ScheduledExecutorService scheduledexecutorservice = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
- ScheduledFuture scheduledfuture = scheduledExecutorService.schedule(new Callable() {
- public Object call() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("executed");
- return "called";
- }
- },
- 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Java 中的 ExecutorService 使用
以下是将要执行的任务委托给 ExecutorService 的不同方法:
- execute(Runnable)
- submit(Runnable)
- submit(Callable)
- invokeAny(…)
- invokeAll(…)
1.在java中执行Runnable
Java 的 ExecutorService execute(Runnable) 方法接受一个 Runnable 对象并异步执行它。
下面是使用 ExecutorService 执行 Runnable 的示例:
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
- executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- System.out.println("asynchronous task");
- }
- });
- executorService.shutdown();
2.在java中提交Runnable
submit(Runnable) 方法采用 Runnable 实现并返回一个 Future 对象。我们可以使用这个 Future 对象来检查 Runnable 是否已完成执行。
这是一个 Java ExecutorService submit() 示例:
- Future future = executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- System.out.println(" asynchronous task ");
- }
- });
- future.get();
3. 在 Java 中提交 Callable
Java submit(Callable) 方法类似于 submit(Runnable) 方法,除了它采用 Callable 对象而不是 Runnable。我们可以使用 submit(Callable) 方法返回的 Java Future 对象获取 Callable 的结果。
这是一个 ExecutorService Callable 示例:
- Future future = executorService.submit(new Callable() {
- public Object call() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("Asynchronous callable");
- return "Callable Result";
- }
- });
- System.out.println("future.get() = "
- future.get());
输出:
Asynchroous callable
future.get = Callable Result
4.java中的invokeAny()
invokeAny() 方法采用 Callable 对象的集合或子接口。此方法返回 Callable 对象之一的结果。无法保证我们将获得哪些 Callable 结果。
例如:
- public class ExecutorServiceExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException,
- InterruptedException {
- ExecutorService es = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
- Set < Callable < String >> callable = new HashSet < Callable < String >> ();
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 1";
- }
- });
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 2";
- }
- });
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 3";
- }
- });
- String result = es.invokeAny(callable);
- System.out.println("result = " + result);
- executorService.shutdown();
- }
- }

输出:
5. Java 中的 invokeAll()
invokeAll() 方法调用我们在集合中作为参数传递给它的所有 Callable 对象。这个方法返回一个 Future 对象的列表,通过它我们可以获得每个 Callable 的执行结果。
例如:
- public class ExecutorServiceExample {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException,
- ExecutionException {
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
- Set < Callable < String >> callable = new HashSet < Callable < String >> ();
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 1";
- }
- });
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 2";
- }
- });
- callable.add(new Callable < String > () {
- public String call() throws Exception {
- return "Task 3";
- }
- });
- java.util.List < Future < String >> futures = executorService.invokeAll(callable);
-
- for (Future < String > future: futures) {
- System.out.println("future.get = " + future.get());
- }
- executorService.shutdown();
-
- }
- }

输出:
future.get = Task 3
future.get = Task 2
Java 中的 ExecutorService 关闭
当我们使用 Java ExecutorService 进行竞争时,我们应该关闭它,这样线程就不会继续运行。在某些情况下,通过 main() 方法启动应用程序并且主线程退出我们的应用程序。
在这种情况下,如果应用程序中有活动的 ExecutorService,应用程序将继续运行。ExecutorService 中存在的这些活动线程可防止 JVM 关闭。
让我们讨论关闭 Executor 服务的方法:
1. Java中的shutdown()
我们调用shutdown() 方法来终止ExecutorService 中的线程。这不会立即关闭 ExecutorService,但它将不再接受新任务。
一旦所有线程完成其当前任务,ExecutorService 就会关闭。在我们调用 shutdown() 之前,所有提交给 ExecutorService 的任务都会被执行。
以下是执行 Java ExecutorService 关闭的示例:
executorService.shutdown();
2. Java 中的 shutdownNow()
如果我们需要立即关闭 ExecutorService,我们可以调用 shutdownNow() 方法。此方法将尝试立即停止所有正在执行的任务,并跳过所有已提交但未处理的任务。
但是,将无法保证执行的任务。它们可能会停止,也可能会一直执行到最后。
例如:
executorService.shutdownNow();3. Java 中的 awaitTermination()
ExecutorService awaitTermination() 方法会阻止调用它的线程,直到 ExecutorService 完全关闭,或者直到发生给定的超时。通常在调用 shutdown() 或 shutdownNow() 之后调用 awaitTermination() 方法。
下面是调用 ExecutorService awaitTermination() 方法的示例:
executorService.awaitTermination();Java 中的 Runnable 与 Callable 接口
Runnable 接口几乎类似于 Callable 接口。Runnable 和 Callable 接口都表示一个线程或一个 ExecutorService 可以并发执行的任务。两个接口中都有一个方法。
Runnable 和 Callable 接口之间有一个小区别。当我们看到接口声明时,两个接口之间的区别就很明显了。
下面是 Runnable 接口的声明:
- public interface Runnable {
- public void run();
- }
这是 Callable 接口的声明:
- public interface Callable {
- public Object call() throws Exception;
- }
Runnable 的 run() 方法和 Callable 的 call() 方法的主要区别在于 call() 可以抛出异常,而 run() 不能抛出异常,除了未经检查的异常——RuntimeException 的子类。
call() 和 run() 之间的另一个区别是 call() 方法可以从方法调用返回一个对象。
在 Java 中取消任务
我们也可以取消一个提交给 Java 的 ExecutorService 的 Runnable 或 Callable 任务。我们可以通过调用 Future 的 cancel() 方法来取消任务。只有在任务尚未开始执行时才可以取消任务。
例如:
Future.cancel();结论
最后我们看到 ExecutorService 有助于最小化复杂的代码。它还有助于通过内部利用线程池来管理资源。程序员应该小心避免一些常见的错误。
例如,在完成不再需要的任务和服务后,始终关闭执行器服务。否则,JVM 永远不会终止,通常。在本教程中,我们涵盖了 Java 中 Executor 服务的每一个概念。