- 1DNS服务器显示两个地址,dns服务器地址出现两个
- 2大数据开发学习笔记_大数据应用开发课堂笔记
- 3机器学习-KNN算法(鸢尾花分类实战)_鸢尾花knn算法
- 4虚拟机上的ubuntu本地跟gitlab或gitee远程仓库建立连接_虚拟机设置绑定gitee
- 5Gary Marcus:因果熵理论的荒诞和认知科学带给AI的11个启示 | 文末赠书
- 6[NLP] PyTorch 实现双向LSTM 情感分析
- 7企业内网通过itms-services(https)协议安装IOS应用_itms ssl
- 8图解二叉树遍历方法-前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历_先序遍历中序遍历后序遍历图解
- 9OSPF的工作流程_ns3 ospf
- 10基于GitLab搭建DevSecOps流水线_gitlab devsecops
数据结构与算法分析(排序,递归,链表)
赞
踩
1.C提供形如
#include <filename> 的语句,它读入文件filename并将其插到include语句处,include语句可以嵌套,换句话说,文件filename本身还可以包含include语句,但是显然一个文件在任何链接中不能包含它自己,编写一个程序,使它读入被include语句修饰的一个文件,并输出这个文件。
为什么递归调用要求不能包含它自己?因为那样会破坏递归要求有终点的约定,递归是重复调用,但不是无限调用,递归一定是有结束的,从形式上说,递归类似于无环的树结构,而如果文件链接包含的不是其它文件,而是自己,则会引入依赖环。
- #include<iostream>
- #include<string>
- #include<vector>
- #include<fstream>
- #include<algorithm>
- using namespace std;
-
- vector<string> files;
-
- void ProcessFile(const string& filename)
- {
- string line;
- ifstream in(filename);
- if (in.fail()) {
- cerr << "fail to open file " << filename << endl;
- return;
- }
- files.push_back(filename);
- while (getline(in, line)) {
- if (line.find("#include") != string::npos) {
- string::size_type beg = line.find_first_of("<\"");
- string::size_type end = line.find_last_of(">\"");
- string file = line.substr(beg + 1, end - beg - 1);
- if (find(files.begin(), files.end(), file) != files.end()) {
- cerr << "Existed file " << file << endl;
- continue;
- } else {
- ProcessFile(file);
- }
- } else {
- cout << line << endl;
- }
- }
- in.close();
- }
-
- int main()
- {
- ProcessFile("test.h");
- return 0;
- }
编译:
头文件内容

运行结果:

2.算法时间复杂度分析中几种典型的增长率函数。

3.快速排序的经典实现:
快速排序是一种基于分治思想的排序算法,该算法的主要步骤是选择一个基准值(pivot),将待排序序列划分为左右两个子序列,并对左右子序列递归进行排序,直到整个序列有序。
在快速排序过程中指针移动的方式通常是从数组连贯开始逐步移动并互相交换元素,而不是使用中间指针,这种交替移动指针的方式可以保证快速排序同时满足以下两个特性:
1.分治:算法每次选择一个基准值将序列划分为左右两个子序列,这样可以使得左子序列的所有元素都小于等于基准值,右子序列的所有元素都大于等于基准值,随后,继续对左右子序序列递归进行排序。
2.原地排序:该算法不需要借助额外的数据结构来实现排序,只需要在原数组中交换元素即可,这种方式可以节省空间并减少程序的运行时间。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quickSort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[j] > temp)
- j--;
- //将右边小于等于基准元素的数填入右边相应位置
- arr[i] = arr[j];
- //当左边的数小于等于基准数时,略过,继续向右查找
- //(重复的基准元素集合到左区间)
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的i对应的元素是大于等于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- i++;
- //将左边大于基准元素的数填入左边相应位置
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- }
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- arr[i] = temp;
- //此时的i即为基准元素的位置
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,begin,i-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,i+1,end);
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int num[12] = {23,45,17,11,13,89,72,26,3,17,11,13};
- int n = 12;
-
- quickSort(num,0,n-1);
- printf("排序后的数组为:\n");
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- printf("%d ", num[i]);
-
- printf("\n");
- return 0;
- }
测试结果:

快速排序为什么要从基准数的对面开始移动?
以自然序排序为例
如果选取最左边的数arr[left]作为基准数,那么先从右边开始可保证i,j在相遇时,相遇数是小于基准数的,交换之后temp所在位置的左边都小于temp。但先从左边开始,相遇数是大于基准数的,无法满足temp左边的数都小于它。所以进行扫描,要从基准数的对面开始。

可以思考一下这幅图和上面逻辑的相似之处
一个堆排序的C语言实现:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- static unsigned int input[] = {1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6, 9, 7, 8, 0};
- void heap_adjust(unsigned int *data, int parent, int length)
- {
- unsigned int temp = data[parent];
- unsigned int child = 2 * parent + 1;
-
- while(child < length)
- {
- if((child + 1 < length) && input[child] < input[child + 1])
- {
- child ++;
- }
-
- if(temp >= input[child])
- {
- break;
- }
-
- input[parent] = input[child];
-
- parent = child;
- child = 2 * child + 1;
- }
-
- input[parent] = temp;
- }
-
- static void dump(int time, unsigned int *buf)
- {
- int i;
-
- printf("\ntimes %d: ", time);
- for (i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- printf("%d ", buf[i]);
- }
- //printf("\n");
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
-
- for(i = (sizeof(input)/sizeof(input[0])) / 2; i >= 0; i --)
- {
- heap_adjust(input, i, sizeof(input)/sizeof(input[0]));
- }
-
- for(i = (sizeof(input)/sizeof(input[0])) -1; i > 0; i --)
- {
- int temp = input[i];
- input[i] = input[0];
- input[0] = temp;
-
- heap_adjust(input, 0, i);
- dump(10 - i, input);
- }
- printf("\n");
- return 0;
- }
- czl@czl-VirtualBox:~/paixu$ ./a.out
-
- times 1: 8 7 6 5 2 1 4 3 0 9
- times 2: 7 5 6 3 2 1 4 0 8 9
- times 3: 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 8 9
- times 4: 5 3 4 0 2 1 6 7 8 9
- times 5: 4 3 1 0 2 5 6 7 8 9
- times 6: 3 2 1 0 4 5 6 7 8 9
- times 7: 2 0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- times 8: 1 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- times 9: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- czl@czl-VirtualBox:~/paixu$
深度有限搜索递归算法
下面的代码会通过block数组将死胡同的路径标出来。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdbool.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- int n, m, p, q, min=99999999;
- int a[5][4], book[5][4], block[5][4];
- #define FAKE_BLOCK 2
-
- bool dfs(int prex, int prey, int x, int y, int step)
- {
- int next[4][2] = \
- {{0, 1}, //left
- {1, 0}, //down
- {0, -1}, //right
- {-1, 0}};//up
-
- int tx, ty, k;
-
- if(x == p && y == q)
- {
- printf("%s line %d, step %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, step);
- if(step < min)
- min = step;
-
- return true;
- }
-
- bool status = false;
- for(k = 0; k <= 3; k ++ )
- {
- tx = x + next[k][0];
- ty = y + next[k][1];
-
- if(tx < 0 || tx >= n || ty < 0 || ty >= m)
- continue;
-
- if(a[tx][ty] == 0 && book[tx][ty] == FAKE_BLOCK &&!(tx==prex && ty==prey))
- {
- status = true;
- continue;
- }
- else if(a[tx][ty] == 0 && book[tx][ty] == FAKE_BLOCK)
- {
- continue;
- }
-
- if(a[tx][ty] == 0 && book[tx][ty] == 0)
- {
- book[tx][ty] = FAKE_BLOCK;
-
- if (true == dfs(x, y, tx, ty, step + 1))
- {
- status = true;
- }
- else
- {
-
- }
-
- book[tx][ty] = 0;
- }
- }
-
- if(status == true)
- {
- printf("x=%d,y=%d.\n", x, y);
- }
- else
- {
- printf("[%d,%d]->[%d,%d] block.\n", prex, prey, x, y);
- block[x][y] = 1;
- }
-
- return status;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i, j, startx, starty;
-
- n = 5;
- m = 4;
-
- startx = 0;
- starty = 0;
-
- p = 3;
- q = 2;
-
- a[0][0] = 0; a[0][1] = 0; a[0][2] = 1; a[0][3] = 0;
- a[1][0] = 0; a[1][1] = 0; a[1][2] = 0; a[1][3] = 1;
- a[2][0] = 0; a[2][1] = 0; a[2][2] = 1; a[2][3] = 0;
- a[3][0] = 0; a[3][1] = 1; a[3][2] = 0; a[3][3] = 0;
- a[4][0] = 0; a[4][1] = 0; a[4][2] = 0; a[4][3] = 1;
-
- book[startx][starty] = FAKE_BLOCK;
-
- dfs(-1, -1, startx, starty, 0);
-
- printf("%d\n", min);
-
- printf("=========================================\n");
- for (i = 0; i < n; i ++)
- {
- for(j = 0; j < m; j ++)
- {
- printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- printf("=========================================\n");
-
- printf("=========================================\n");
- for (i = 0; i < n; i ++)
- {
- for(j = 0; j < m; j ++)
- {
- printf("%d ", book[i][j]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- printf("=========================================\n");
-
- printf("=========================================\n");
- for (i = 0; i < n; i ++)
- {
- for(j = 0; j < m; j ++)
- {
- printf("%d ", block[i][j]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
- printf("=========================================\n");
-
- return 0;
- }
运行结果:


以上代码可能还有些问题:
走法讲解:


使用栈实现的迷宫算法:
- //迷宫问题
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #define m 9
- #define n 9
- #define MAXSIZE 100
- //迷宫问题
-
- //定义移动位置 ,其中
- typedef struct{
- int x,y;
- }item;
- //定义一个数据类型为dataType,在栈里面存在此数据
- //主要作为迷宫移动位置的临时存放点,其中x为当前位置的横坐标,y为当前位置的纵坐标
- //d为 搜索的次数(方向)
- typedef struct{
- int x,y,d;
- }dataType;
-
- //定义一个栈
- typedef struct{
- dataType data[MAXSIZE];
- int top;
- }list,*pList;
-
-
- //创建栈
-
- pList initList(){
- pList p;
- p = (pList)malloc(sizeof(list));
- if(p){
- p->top = -1;
- }
-
- return p;
- }
-
- //判断栈是否为空
- int isEmpty(pList p){
- if(p->top==-1){
- return 1;//如果是空栈就返回1
- }else{
- return 0;
- }
- }
-
- //压栈
- int pushList(pList p,dataType data){
- if(p->top==MAXSIZE-1){//如果栈超出了大小,返回0
- return 0;
- }
- p->top++;
- p->data[p->top] = data;//压栈操作
- return 1;//压栈成功,返回1
- }
-
- //弹栈
- int popList(pList p,dataType *data){
- if(isEmpty(p)){
- return 0;//如果是空栈,就不弹,直接返回0
- }else{
- *data = p->data[p->top];
- p->top--;
- return 1;
- }
- }
-
- //销毁栈
- void destory(pList *p){
- if(*p){
- free(*p);
- }
- *p = NULL;
- return;
- }
-
- int mazePath(int maze[][n+2],item move[],int x0,int y0){//maze表示一个迷宫的数组,move表示当前探索,x0,y0表示初始位置
- pList p;//定义栈
- dataType temp;//定义临时位置
- int x,y,d,i,j;//x,y用来存放临时位置的角标,d表示临时的探索次数,i,j所在位置的迷宫角标
- p = initList();//创建栈
- if(!p){//如果创建失败
- printf("创建栈失败");
- return 0;
- }
-
- //初始化走过的位置
- temp.x = x0;
- temp.y = y0;
- temp.d = -1;
-
- //把迷宫入口压栈
- pushList(p,temp);
-
- //当栈里面不为空时
- while(!isEmpty(p)){
- popList(p,&temp);//弹栈
- x = temp.x;
- y = temp.y;
- d = temp.d+1;//给d+1,让其进行第一次探索
- while(d<4){//四次探索
- i = x+move[d].x;//原来的位置加上探索的位置
- j = y+move[d].y;
-
- //当某条路是通路的时候
- if(maze[i][j]==0){//表示此路可走
- //使用temp来保存路径
- temp.x = x;
- temp.y = y;
- temp.d = d;
- //将路径压栈
- pushList(p,temp);
- //x、y来保存当前新的路径
- x = i;
- y = j;
- maze[x][y] = -1;//把走过的路径的值设为-1
-
- if(x==m && y==n){//判断是否走到头,如果走到头
- while(!isEmpty(p)){//如果栈不为空
- popList(p,&temp);//弹栈
- printf("(%d,%d,%d),<-",temp.x,temp.y,temp.d);//打印路径
- }
- printf("origin\n");
- //程序结束,销毁栈
- destory(&p);
- return 1;
- }else{//如果能走通,但是却没有走完迷宫,把d置为0
- d = 0;
- }
- } else{//如果路不通,换个方向在进行探索
- d++;
- }
- }
-
- }
- //如果最后都没找到,说明迷宫没有通路
- destory(&p);
- return 0;
-
- }
-
- void main(){
- item move[4];//定义一个控制探索路径的移动数组
- //定义迷宫数组
- int maze[11][11]={
- {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
- {1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,1},
- {1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1},
- {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,1},
- {1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1},
- {1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,1},
- {1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1},
- {1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1},
- {1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1},
- {1,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1},
- {1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
- };
-
- //定义第一次移动 ,方向为北
- move[0].x = 0;
- move[0].y = 1;
-
- //定义第二次移动,方向为南
- move[1].x = 0;
- move[1].y = -1;
-
- //规定第三次移动,方向为东
- move[2].x = 1;
- move[2].y = 0;
-
- //规定第三次移动,方向为西
- move[3].x = -1;
- move[3].y = 0;
-
- mazePath(maze,move,1,1);
- }
运行:

冒泡排序:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int a[10];
-
- int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- a[i] = 10-i;
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- printf("a[%d] = %d.\n", i, a[i]);
- }
-
- printf("=======================================================\n");
- int j;
-
- for (j = 9; j > 0; j --)
- {
- for(i = 0; i < j; i ++)
- {
- if(a[i] > a[i+1])
- {
- int tmp;
- tmp = a[i + 1];
- a[i+1] = a[i];
- a[i] = tmp;
- }
- }
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- printf("a[%d] = %d.\n", i, a[i]);
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
时间复杂度和空间复杂度分析:
对于N个数据,外循环N-1次,内循环次数依赖于外循环的记数,一共为N-1+N-2+...+1 = N(N-1)/2
次,如果最差情况下,每次都会执行交换,包含三次赋值,则复杂度为 3N(N-1)/2,所以,冒泡排序:
最优的时间复杂度为:O( n^2 ) ;
最差的时间复杂度为:O( n^2 );
平均的时间复杂度为:O( n^2 );
有的说 O(n),下面会分析这种情况,修改程序,当检测到当前循环不需要交换的时候,说明都是正序,这个时候直接跳出循环:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int a[10];
- int flag = 1;
-
- int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- /*a[i] = 10-i;*/
- a[i] = i;
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- printf("a[%d] = %d.\n", i, a[i]);
- }
-
- printf("=======================================================\n");
- int j;
-
- for (j = 9; j > 0; j --)
- {
- flag = 1;
- for(i = 0; i < j; i ++)
- {
- if(a[i] > a[i+1])
- {
- int tmp;
- tmp = a[i + 1];
- a[i+1] = a[i];
- a[i] = tmp;
- flag = 0;
- }
- }
- if(flag) break;
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
- {
- printf("a[%d] = %d.\n", i, a[i]);
- }
-
- return 0;
- }

空间复杂度好说了,也就是TMP占用的空间,理想情况不需要交换,空间复杂度为0,最差的时候也仅仅是需要1个TMP的空间,也即是O(1).
关于循环条件的两种情况:
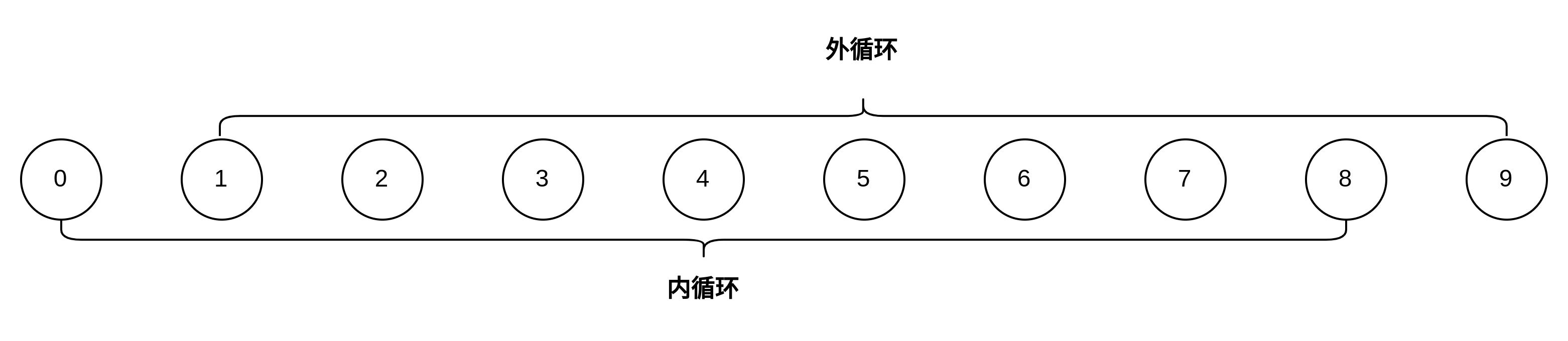
冒泡排序的变种奇偶排序
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- void swap(int *array, int j, int k)
- {
- int temp = array[j];
- array[j] = array[k];
- array[k] = temp;
- }
-
- void scan(int *array, int j)
- {
- while(j < 9)
- {
- if(array[j] > array[j + 1])
- {
- swap(array, j, j + 1);
- }
-
- j += 2;
- }
-
- return;
- }
-
- void print_array(int *array, int count)
- {
- int i;
-
- for(i = 0; i < count; i ++)
- printf(" %d ", array[i]);
-
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- int array[10] = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0};
-
- print_array(array, 10);
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i += 2)
- {
- int j = 0;
-
- scan(array, j);
- print_array(array, 10);
-
- j = 1;
-
- scan(array, j);
- print_array(array, 10);
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
run:
- ~/czl$ ./a.out
- 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
- 8 9 6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1
- 8 6 9 4 7 2 5 0 3 1
- 6 8 4 9 2 7 0 5 1 3
- 6 4 8 2 9 0 7 1 5 3
- 4 6 2 8 0 9 1 7 3 5
- 4 2 6 0 8 1 9 3 7 5
- 2 4 0 6 1 8 3 9 5 7
- 2 0 4 1 6 3 8 5 9 7
- 0 2 1 4 3 6 5 8 7 9
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- ~/czl$
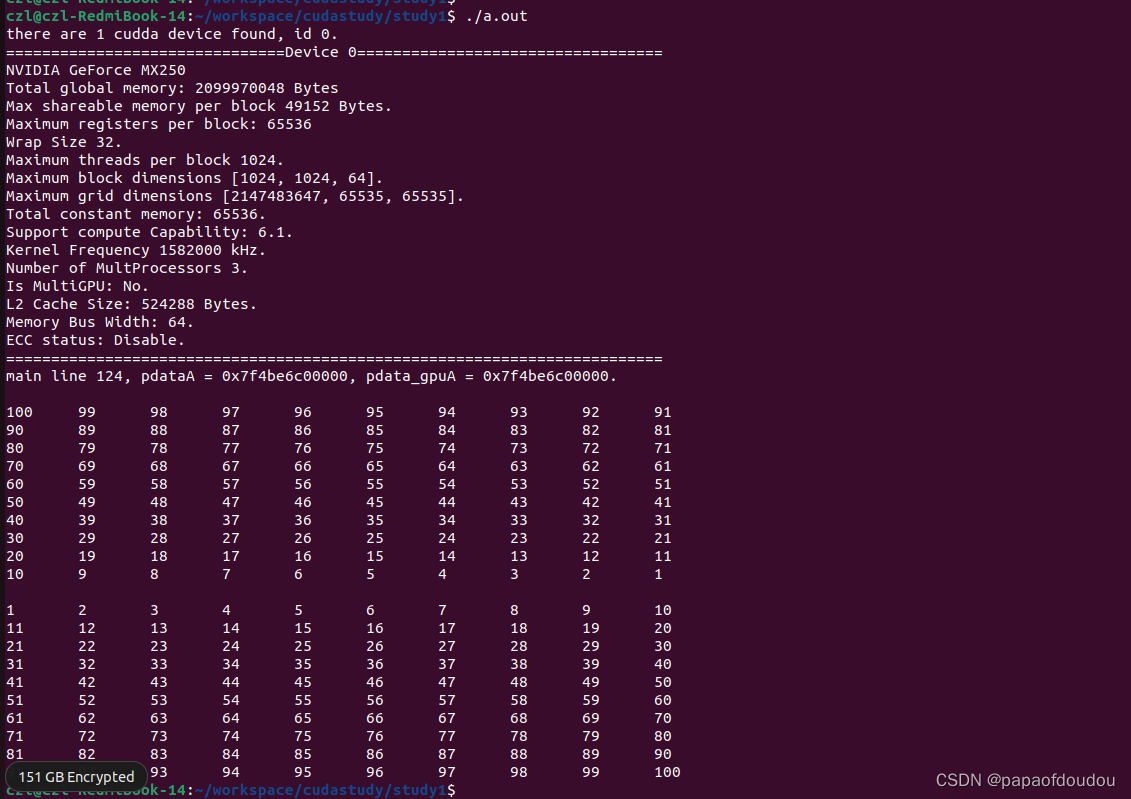
奇偶排序的GPU实现版本:
- #include <cuda_runtime.h>
- #include <device_launch_parameters.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <time.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
-
- #define MATRIX_M 16
- #define MATRIX_N 16
-
- void init_cuda(void)
- {
- int count, dev;
- int i;
- cudaDeviceProp prop;
-
- cudaGetDeviceCount(&count);
- if(count == 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "there is no cuda device.\n");
- return;
- } else {
- cudaGetDevice(&dev);
- fprintf(stdout,"there are %d cudda device found, id %d.\n", count, dev);
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
- printf("===============================Device %d==================================\n", i);
- if(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, i) == cudaSuccess) {
- printf("%s\n", prop.name);
- printf("Total global memory: %ld Bytes\n", prop.totalGlobalMem);
- printf("Max shareable memory per block %ld Bytes.\n", prop.sharedMemPerBlock);
- printf("Maximum registers per block: %d\n", prop.regsPerBlock);
- printf("Wrap Size %d.\n", prop.warpSize);
- printf("Maximum threads per block %d.\n", prop.maxThreadsPerBlock);
- printf("Maximum block dimensions [%d, %d, %d].\n", prop.maxThreadsDim[0], prop.maxThreadsDim[1], prop.maxThreadsDim[2]);
- printf("Maximum grid dimensions [%d, %d, %d].\n", prop.maxGridSize[0], prop.maxGridSize[1], prop.maxGridSize[2]);
- printf("Total constant memory: %ld.\n", prop.totalConstMem);
- printf("Support compute Capability: %d.%d.\n", prop.major, prop.minor);
- printf("Kernel Frequency %d kHz.\n", prop.clockRate);
- printf("Number of MultProcessors %d.\n", prop.multiProcessorCount);
- printf("Is MultiGPU: %s.\n", prop.isMultiGpuBoard ? "Yes" : "No");
- printf("L2 Cache Size: %d Bytes.\n", prop.l2CacheSize);
- printf("Memory Bus Width: %d.\n", prop.memoryBusWidth);
- printf("ECC status: %s.\n", prop.ECCEnabled? "Enable" : "Disable");
- }
- printf("=========================================================================\n");
- }
-
- cudaSetDevice(1);
- }
-
- void init_array(int *data, int n)
- {
- int i = 0;
-
- for(i = 0; i < n; i ++){
- data[i] = n - i;
- }
- }
-
- void print_array(int *data, int n)
- {
- int i;
-
- for(i = 0; i < n; i ++){
- if(i % 10 == 0) printf("\n");
- printf("%d\t", data[i]);
- }
-
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- #define N 100
- __global__ static void sort_array(int *array)
- {
- int tid = threadIdx.x;
- int a;
- int i = 0;
-
- for(i = 0; i < N/2; i ++){
- if((2 * tid + 1) < N) {
- if(array[2*tid] > array[2*tid + 1]) {
- a = array[2 * tid];
- array[2 * tid] = array[2 * tid + 1];
- array[2 * tid +1] = a;
- }
- }
-
- __syncthreads();
-
- if((2 * tid + 2) < N) {
- if(array[2 * tid + 1] > array[2 * tid + 2]) {
- a = array[2 * tid + 1];
- array[2 * tid +1] = array[2 * tid + 2];
- array[2 * tid + 2] = a;
- }
- }
-
- __syncthreads();
- }
-
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int *pdataA;
- int *pdata_gpuA;
-
- init_cuda();
-
- cudaMallocHost((void**)&pdataA, N * sizeof(int));
-
- if(pdataA == NULL) {
- fprintf(stderr, "fatal error, malloc host buffer failure.\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- cudaHostGetDevicePointer((void**)&pdata_gpuA, (void*)pdataA, 0);
- if(pdata_gpuA == NULL) {
- fprintf(stderr, "fatal error, get device ptr failure.\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- printf("%s line %d, pdataA = %p, pdata_gpuA = %p.\n", __func__, __LINE__, pdataA, pdata_gpuA);
-
- if(pdataA != pdata_gpuA) {
- printf("%s line %d, not uma address space.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- }
-
- init_array(pdataA, N);
- print_array(pdataA,N);
-
- dim3 blocksize(N/2, 1, 1);
- dim3 gridsize(1, 1, 1);
-
- sort_array<<< gridsize, blocksize >>>(pdata_gpuA);
- cudaDeviceSynchronize();
-
- print_array(pdataA,N);
-
- cudaFree(pdataA);
- return 0;
- }
二分排序
一把撸成的二分排序。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
- int *binary_sort(int *array, int n)
- {
- int *p = malloc(n * sizeof(int));
- if(p == NULL)
- {
- printf("%s line %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- return NULL;
- }
-
- memset(p, 0x00, sizeof(int)*n);
-
- if (n == 1)
- {
- p[0] = array[0];
- return p;
- }
-
- int n1,n2;
-
- if(n % 2 == 0)
- {
- n1 = n2 = n/2;
- }
- else
- {
- n1 = n/2;
- n2 = n1 + 1;
- }
-
- if((n1 + n2) != n)
- {
- printf("fatal error.\n");
- return NULL;
- }
-
- int *pre = binary_sort(array, n1);
- int *pos = binary_sort(array + n1, n2);
-
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- int s = 0;
-
- int tmp;
- for(s = 0; s < n; s ++)
- {
- if(i < n1 && j < n2)
- {
- if( pre[i] <= pos[j] )
- {
- tmp = pre[i];
- i ++;
- }
- else
- {
- tmp = pos[j];
- j ++;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(i >= n1)
- {
- tmp = pos[j]; j ++;
- }
- else
- {
- tmp = pre[i]; i ++;
- }
- }
-
- p[s] = tmp;
- }
-
- free(pre);
- free(pos);
- pre = pos = NULL;
-
- return p;
- }
-
- #define NUM 800
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- int array[NUM];
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUM; i ++)
- {
- array[i] = NUM-i;
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUM; i ++)
- {
- printf("array[%d] = %d.\n", i, array[i]);
- }
-
- int *p = binary_sort(array, NUM);
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUM; i ++)
- {
- printf("p[%d] = %d.\n", i, p[i]);
- }
-
- free(p);
-
- return 0;
- }

归并排序复杂度分析:
所以,复杂度为
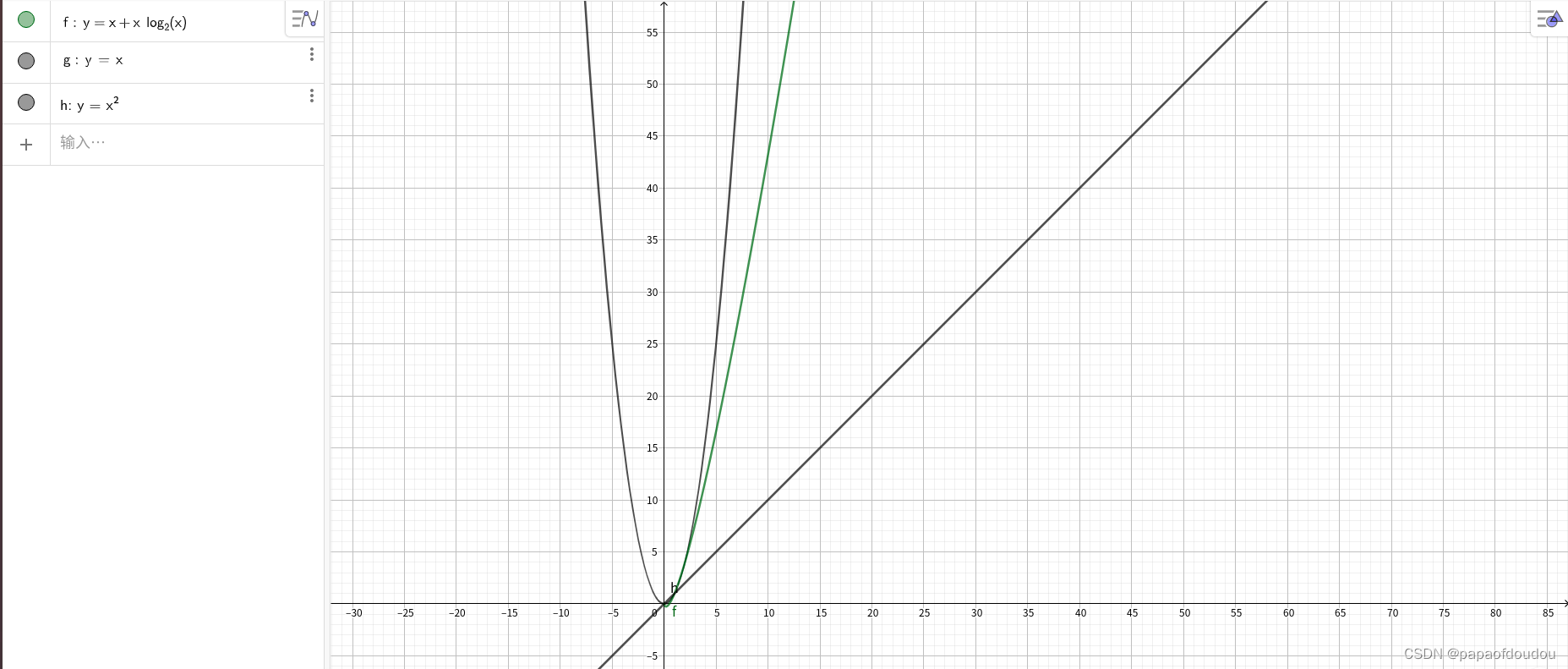
全排列程序:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- #define NUMS 10
-
- static int num[NUMS];
- static int flag[NUMS];
- static int res[NUMS];
- static int depth = 0;
- static long total = 0;
-
- void total_pailie(void)
- {
- int i;
-
- if(depth == NUMS)
- {
- int j = 0;
- for (j = 0; j < NUMS ;j ++)
- {
- printf("%d ", res[j]);
- }
- total ++;
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUMS; i ++)
- {
- if(flag[i] == 1) continue;
-
- flag[i] = 1;
- res[depth] = num[i];
- depth ++;
- total_pailie();
- depth --;
- flag[i] = 0;
- }
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUMS; i ++)
- {
- num[i] = i;
- flag[i] = 0;
- res[i] = 0;
- }
-
- total_pailie();
-
- printf("%s line %d, total %ld.\n", __func__, __LINE__, total);
- return 0;
- }
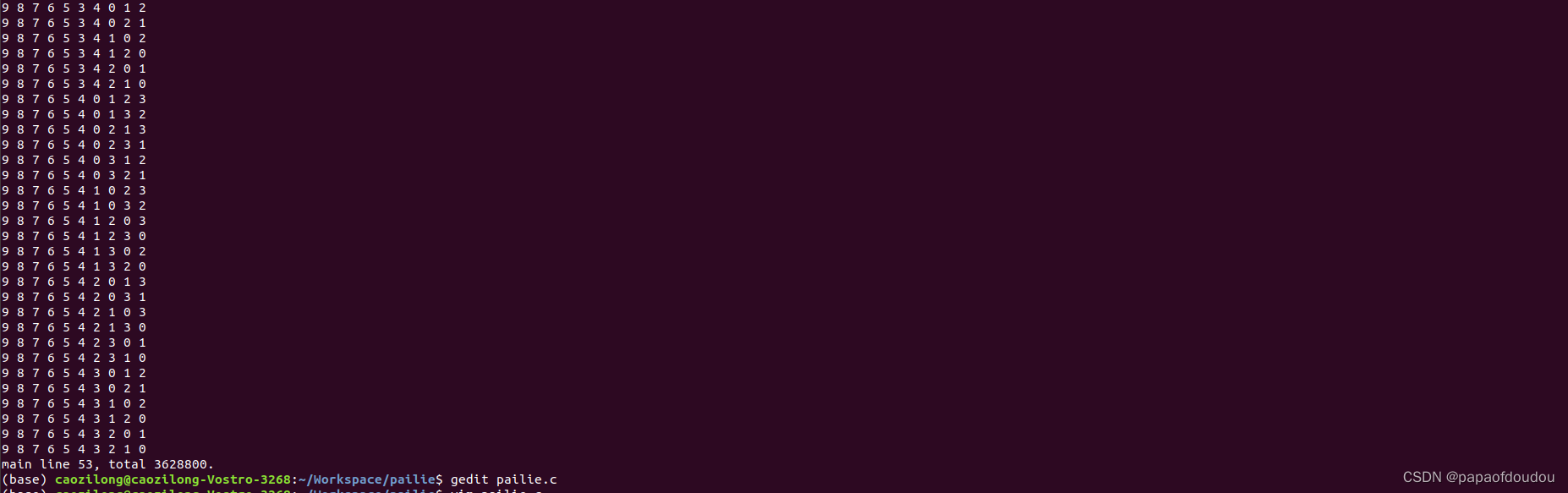

10的阶乘:
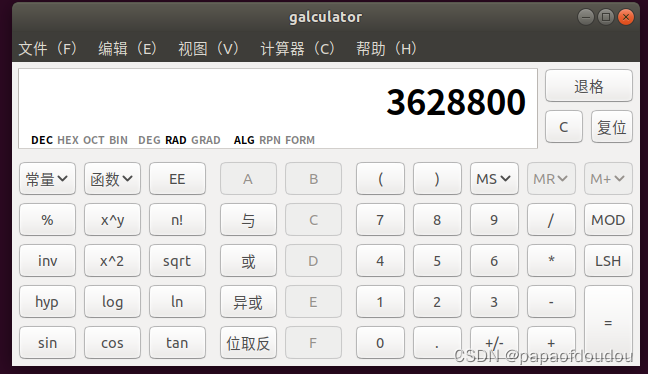
另一种方式,由于内部已经包含了排列组合公式,不是一个好方案,相当于手工代替机器做了很多额外的工作:
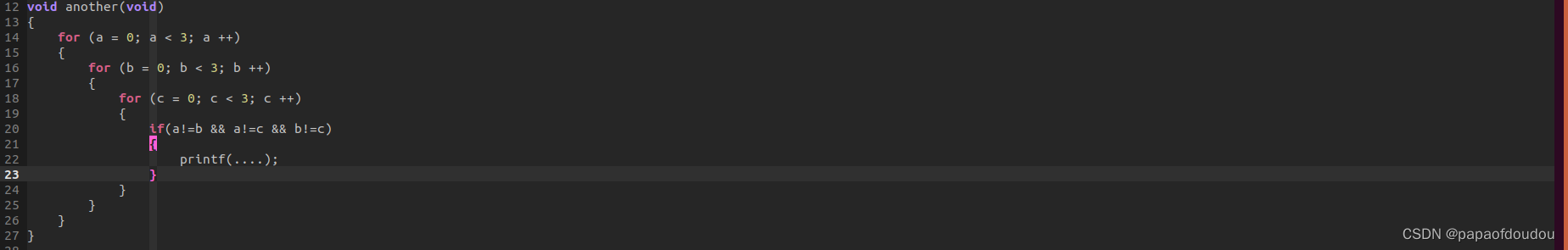
如何判断一个链表是否存在循环?
快慢指针的方式,代码如下:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- struct node head;
- struct node *phead;
-
- struct node {
- struct node *next;
- int val;
- };
-
- void add_node(struct node *n)
- {
- struct node *no = phead;
-
- while(no->next) no = no->next;
-
- no->next = n;
-
- return;
- }
-
- int check_loop(void)
- {
- int ret = 0;
- struct node *n1, *n2;
-
- n1 = n2 = phead;
-
- while(n1 && n2)
- {
- n1 = n1->next;
- if(!n1) {
- ret = 0;
- printf("exit in zero.\n");
- break;
- }
- n2 = n2->next;
- if(!n2) {
- ret = 0;
- printf("exit in one.\n");
- break;
- }
- n2 = n2->next;
- if(n1 == n2) {
- ret = 1;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- if(!n1)
- {
- printf("n1 is null.\n");
- }
-
- if(!n2)
- {
- printf("n2 is null.\n");
- }
-
- printf("exit in two.\n");
- return ret;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- struct node array[100];
- struct node *no;
- phead = &head;
-
- head.next = NULL;
- head.val = 255;
-
- for(i = 0; i < 100; i ++)
- {
- array[i].next = NULL;
- array[i].val = i;
- add_node(&array[i]);
- }
-
- no = phead;
- while(no)
- {
- printf("%s line %d, val %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, no->val);
- no = no->next;
- }
-
- // add loop node.
- add_node(&array[6]);
-
- #if 0
- no = phead;
- while(no)
- {
- printf("%s line %d, val %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, no->val);
- no = no->next;
- }
- #endif
-
- printf("%s line %d, checkloop %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, check_loop() ? "have loop" : "no loop");
-
- return 0;
- }

证明,假设当前1倍速节点的位置为(n+k),则二倍速节点的位置为(2n+s).则最差情况下,存在着(n+k)*(2n+s)步,使两个节点同时达到这里。得证。对于不同速度遍历的两个指针,假如速度为N和M,则最差在公约数NM时相遇。
快速排序为何从GUARD VALUE的对向开始验证程序
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quickSort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- int k;
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[j] > temp)
- j--;
-
- while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- i++;
-
- k = arr[j];
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- arr[i] =k;
- }
-
- for(int s = begin; s < j; s ++)
- arr[s] = arr[s+1];
-
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- arr[j] = temp;
- //此时的i即为基准元素的位置
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,begin,i-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,i+1,end);
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int num[12] = {23,45,17,11,13,89,72,26,3,17,11,13};
- //int num[12] = {13,12,11,10,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
- int n = 12;
-
- quickSort(num,0,n-1);
- printf("排序后的数组为:\n");
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- printf("%d ", num[i]);
-
- printf("\n");
- return 0;
- }
快速排序是一种分治算法,它的核心思想是将待排序序列分成两个子序列,其中一个子序列的元素都比另一个子序列的原则小,然后对这两个子序列进行递归排序,直到整个序列有序。在这个过程中,需要一个基准数,通常选择序列的第一个或者最后一个元素作为基准。
从基准数的对面开始移移指针,是为了保证算法的正确性。如果从基准数的同侧开始移动指针,可能会出现左右指针相遇时,集注疏左侧仍然有比基准数大的情况,导致排序结果不正确,从基准数对面开始移动指针,可以避免这种情况。下面的程序展示了从左边开始动,需要做一次相遇时的大小判断才能正确排序:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
- static void dump_array(int *arr, int n)
- {
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- printf("%d ", arr[i]);
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quickSort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- int k;
-
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- i++;
-
- while(i<j && arr[j] >= temp)
- j--;
-
- k = arr[j];
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- arr[i] =k;
- dump_array(arr, 12);
- }
-
- int pos = j;
-
- if(arr[i] > temp) {
- pos = i - 1;
- }
-
- for(int s = begin; s < pos; s ++)
- arr[s] = arr[s+1];
-
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- arr[pos] = temp;
-
- printf("%s line %d, i %d, j %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, i, j);
- dump_array(arr, 12);
- //此时的i即为基准元素的位置
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,begin,pos-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,pos+1,end);
-
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int num[12] = {23,45,17,11,13,89,72,26,3,17,11,13};
- //int num[12] = {13,12,11,10,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
- int n = 12;
-
- quickSort(num,0,n-1);
- printf("排序后的数组为:\n");
-
- dump_array(num, 12);
-
- return 0;
- }

逆序排同样要从对对向开始:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
- static void dump_array(int *arr, int n)
- {
- for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
- printf("%d ", arr[i]);
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quickSort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- int k;
-
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- //while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- while(i<j && arr[i] >= temp)
- i++;
-
- //while(i<j && arr[j] > temp)
- while(i<j && arr[j] <= temp)
- j--;
-
- k = arr[j];
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- arr[i] =k;
- dump_array(arr, 12);
- }
-
- int pos = j;
-
- if(arr[i] < temp) {
- pos = i - 1;
- }
- for(int s = begin; s < pos; s ++)
- arr[s] = arr[s+1];
-
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- arr[pos] = temp;
-
- printf("%s line %d, i %d, j %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, i, j);
- dump_array(arr, 12);
- //此时的i即为基准元素的位置
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,begin,pos-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,pos+1,end);
-
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int num[12] = {23,45,17,11,13,89,72,26,3,17,11,13};
- //int num[12] = {13,12,11,10,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
- int n = 12;
-
- quickSort(num,0,n-1);
- printf("排序后的数组为:\n");
-
- dump_array(num, 12);
-
- return 0;
- }

采用对抗式算法,用前面的程序进行排列组合,然后用快速排序重新排序,验证排序算法的正确性!
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
-
- #define NUMS 20
-
- static int num[NUMS];
- static int flag[NUMS];
- static int res[NUMS];
- static int depth = 0;
- static long total = 0;
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quick_sort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[j] > temp)
- j--;
- //将右边小于等于基准元素的数填入右边相应位置
- arr[i] = arr[j];
- //当左边的数小于等于基准数时,略过,继续向右查找
- //(重复的基准元素集合到左区间)
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的i对应的元素是大于等于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- i++;
- //将左边大于基准元素的数填入左边相应位置
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- }
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- arr[i] = temp;
- //此时的i即为基准元素的位置
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quick_sort(arr,begin,i-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quick_sort(arr,i+1,end);
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- //快速排序算法(从小到大)
- //arr:需要排序的数组,begin:需要排序的区间左边界,end:需要排序的区间的右边界
- void quickSort(int *arr,int begin,int end)
- {
- //如果区间不只一个数
- if(begin < end)
- {
- int temp = arr[begin]; //将区间的第一个数作为基准数
- int i = begin; //从左到右进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前左位置
- int j = end; //从右到左进行查找时的“指针”,指示当前右位置
- //不重复遍历
- while(i < j)
- {
- int k;
-
- //当左边的数小于等于基准数时,略过,继续向右查找
- //(重复的基准元素集合到左区间)
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的i对应的元素是大于等于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[i] <= temp)
- i++;
-
- //当右边的数大于基准数时,略过,继续向左查找
- //不满足条件时跳出循环,此时的j对应的元素是小于基准元素的
- while(i<j && arr[j] >= temp)
- j--;
-
- //交换j,i;
- k = arr[j];
- arr[j] = arr[i];
- arr[i] = k;
- }
-
- int pos = j;
-
- if(arr[i] > temp) {
- pos = i - 1;
- }
-
- for(int s = begin; s < pos; s ++)
- arr[s] = arr[s+1];
-
- //将基准元素填入相应位置
- //此时的pos即为基准元素的位置
- arr[pos] = temp;
-
- //对基准元素的左边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,begin,pos-1);
- //对基准元素的右边子区间进行相似的快速排序
- quickSort(arr,pos+1,end);
- }
- //如果区间只有一个数,则返回
- else
- return;
- }
-
- void total_pailie(void)
- {
- int i;
-
- if(depth == NUMS)
- {
- int j = 0;
- int *ptemp = malloc(sizeof(int)*NUMS);
-
- memset(ptemp, 0xff, sizeof(int)*NUMS);
- for (j = 0; j < NUMS ;j ++) {
- //printf("%d ", res[j]);
- ptemp[j] = res[j];
- }
- //quick_sort(ptemp, 0, NUMS-1);
- quickSort(ptemp, 0, NUMS-1);
- for (j = 0; j < NUMS ;j ++) {
- printf("%d ", ptemp[j]);
- if(ptemp[j] != j)
- {
- while(1)
- printf("%s line %d. fata error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- }
- }
- total ++;
- free(ptemp);
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUMS; i ++)
- {
- if(flag[i] == 1) continue;
-
- flag[i] = 1;
- res[depth] = num[i];
- depth ++;
- total_pailie();
- depth --;
- flag[i] = 0;
- }
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
-
- for(i = 0; i < NUMS; i ++)
- {
- num[i] = i;
- flag[i] = 0;
- res[i] = 0;
- }
-
- total_pailie();
-
- printf("%s line %d, total %ld.\n", __func__, __LINE__, total);
- return 0;
- }
以NUMS=12为例,我们对12个数作全排列的结果进行排序,排序进行了12!=479001600,全部排正确,算法稳定运行。

简单的说,如果从同侧开始,则相遇点的数值可能大于基准数,导致需要进行比对会退一位。
最简单的排序算法
那种排序算法最为简单呢,这实际上取决于你对简单的定义,但选择排序很可能是不错的选择,这个算法的思想是不断的找出最小元素,并将其移到左边,你可以使用两个FOR循环加上一个条件交换来实现它,外层循环将过程分成N个阶段,在每个阶段,都会执行内层循环来寻找下一个最小值。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- void sort(int *array, int len)
- {
- int i;
- int j;
- int tmp;
-
- for(i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
- for(j = i+1; j < len; j ++) {
- if(array[i] > array[j]) {
- tmp = array[j];
- array[j] = array[i];
- array[i] = tmp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- int num[10] = {9, 4, 8, 6, 7, 2, 5, 0, 1, 3};
- sort(num, 10);
-
- printf("\n");
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
- printf("%d ", num[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
-
- return 0;
- }
选择排序和插入排序的组合,它们的组合方式确保了只有插入排序起作用。
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- void sort(int *array, int len)
- {
- int i;
- int j;
- int tmp;
-
- for(i = 0; i < len; i ++) {
- //for(j = 0; j < len; j ++) {
- for(j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
- if(array[i] > array[j]) {
- tmp = array[j];
- array[j] = array[i];
- array[i] = tmp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- int i;
- int num[10] = {9, 4, 8, 6, 7, 2, 5, 0, 1, 3};
- sort(num, 10);
-
- printf("\n");
- for(i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
- printf("%d ", num[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
-
- return 0;
- }