利用Nginx+Squid搭建简易CDN缓存服务器_nginx搭建cdn服务器
赞
踩
1、 CDN概述
CDN,即内容分发网络,是构建在现有网络基础之上的智能虚拟网络,依靠部署在各地的边缘服务器,通过中心平台的负载均衡、内容分发、调度等功能模块,使用户就近获取所需内容,降低网络拥塞,提高用户访问响应速度和命中率。通常情况下,CDN的关键技术主要有内容存储和分发技术。(引自©百度百科:CDN)
CDN的搭建方式有很多种,并且所使用的软件也有很多种,在本文中以老牌的squid为例进行搭建和实验。
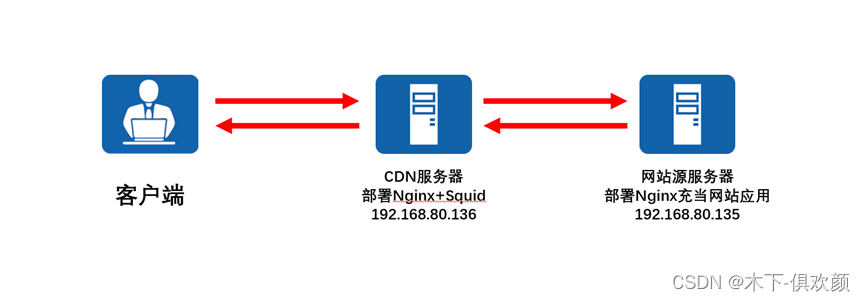
2、 本实验CDN拓扑
在本文中,旨在通过nginx+squid这样的方式搭建一个简易的CDN服务器,用于缓存源服务器上的内容,从而提高达到提高访问速度和流量分摊的目的,我们使用两台服务器进行实验,其中一台安装nginx充当源服务器,另一台则是安装nginx和squid充当CDN缓存服务器,相关拓扑如下:
3、 配置步骤
3.1、网站源服务器(操作系统为debian)
(1)安装nginx
apt install nginx -y
- 1
(2)修改nginx的初始页面,以便区分
echo 'This is test webpage!!!!' > /var/www/html/index.nginx-debian.html
- 1
(3)重启nginx
systemctl restart nginx
- 1
需要注意的是,debian默认的防火墙为iptables,因为该防火墙默认是没有规则的,因此不用专门关闭。
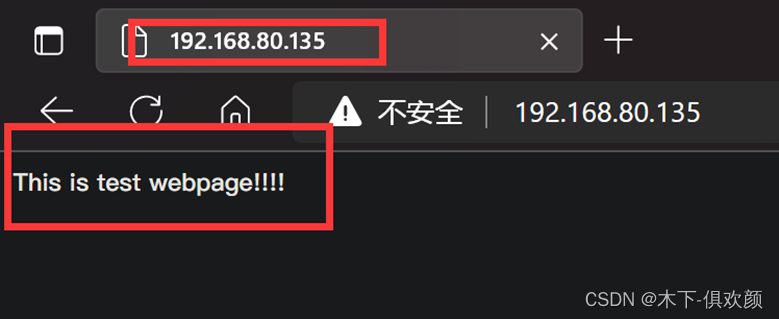
上述配置完成后,客户端输入网站源服务器的IP地址,可以看到访问是正常的如下图所示:
3.2、CDN服务器(操作系统为CentOS-Stream 9)
针对于CDN服务器,相应的部署步骤如下:
(1)关闭防火墙以及防火墙自启动,也可写入具体的安全策略至防火墙
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
- 1
- 2
(2)安装nginx和squid
yum install nginx -y
yum install squid -y
- 1
- 2
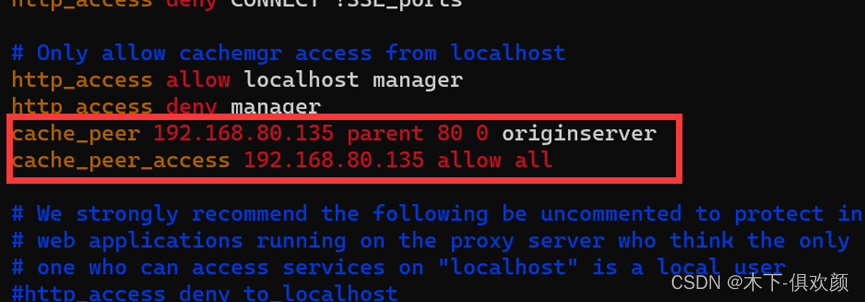
(3)输入命令“vim /etc/squid/squid.conf”,修改该配置文件,增加如下图红框中所示的内容,以达到将squid缓存代理服务指向网站源服务器的IP地址和端口(192.168.80.135:80)之目的
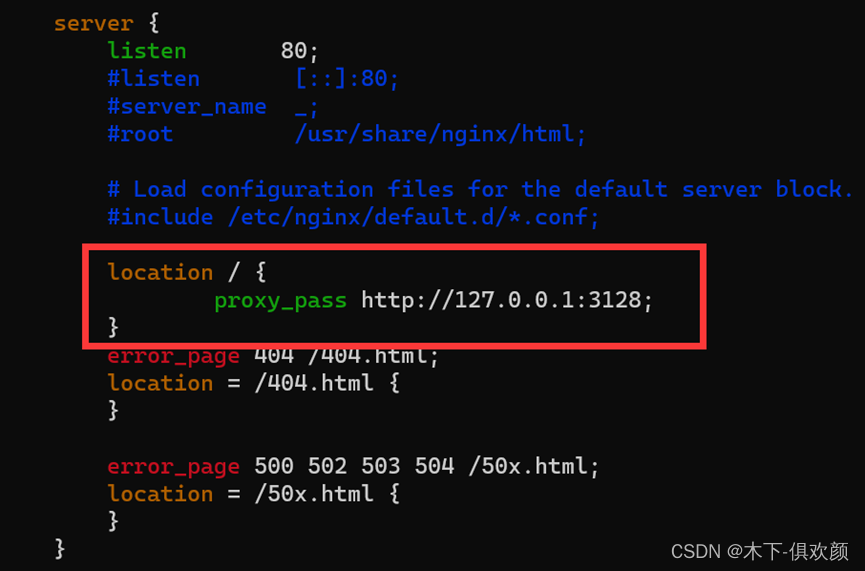
(4)输入命令“vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf”,修改该配置文件,在server结构体下,增加如下图红框中所示的内容,以达到CDN上的nginx指向squid代理服务(默认监听端口是3128)之目的
(5)配置完成后,重启nginx和squid
systemctl restart nginx
systemctl restart squid
- 1
- 2
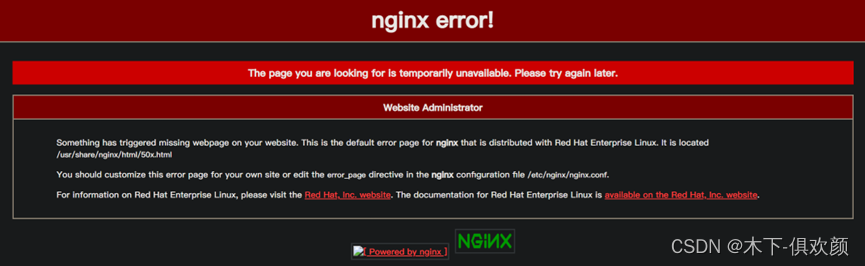
(6)输入以下命令修改SELinux安全上下文的布尔值,如果在CentOS上遗失此步骤,会出现因为SELinux的httpd_can_network_connect模块阻拦,而导致nginx和squid无法建立通信,缓存不到网站源服务器的资源,最终使得客户端访问CDN服务器时报“502 bad Gateway”错误,如下图
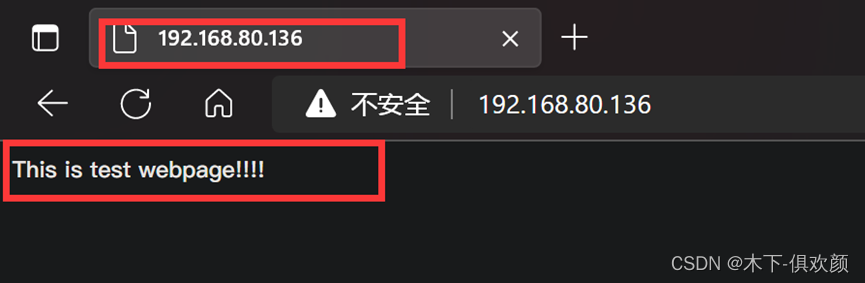
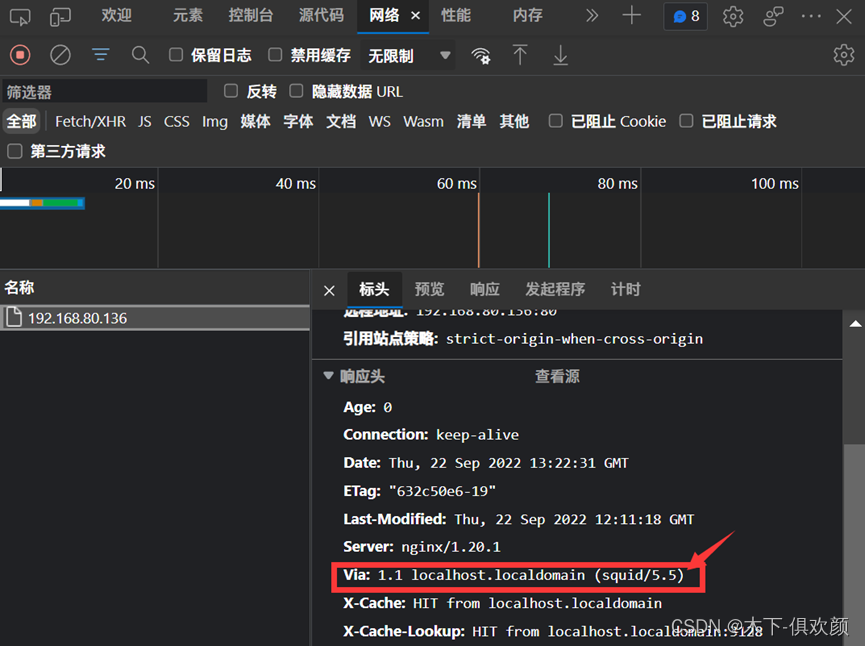
输入命令“setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1”后,然后在客户端的浏览器上输入CDN服务器的IP地址192.168.80.136,发现可以成功访问到网站源服务器(192.168.80.135)上的页面,通过浏览器的开发者工具也可以看到访问过程中经过了squid,说明此时CDN服务器缓存成功
4、附:nginx和squid的配置文件
4.1、/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# For more information on configuration, see: # * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/ # * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/ user nginx; worker_processes auto; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; pid /run/nginx.pid; # Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic. include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; keepalive_timeout 65; types_hash_max_size 4096; include /etc/nginx/mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; # Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory. # See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include # for more information. include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; server { listen 80; #listen [::]:80; #server_name _; #root /usr/share/nginx/html; # Load configuration files for the default server block. #include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:3128; } error_page 404 /404.html; location = /404.html { } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } } # Settings for a TLS enabled server. # # server { # listen 443 ssl http2; # listen [::]:443 ssl http2; # server_name _; # root /usr/share/nginx/html; # # ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt"; # ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key"; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 10m; # ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # # # Load configuration files for the default server block. # include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; # # error_page 404 /404.html; # location = /40x.html { # } # # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # location = /50x.html { # } # } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
4.2、/etc/squid/squid.conf
# # Recommended minimum configuration: # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing # should be allowed acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN) acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN) acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines acl SSL_ports port 443 acl Safe_ports port 80 # http acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp acl Safe_ports port 443 # https acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http # # Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration: # # Deny requests to certain unsafe ports http_access deny !Safe_ports # Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports # Only allow cachemgr access from localhost http_access allow localhost manager http_access deny manager cache_peer 192.168.80.135 parent 80 0 originserver cache_peer_access 192.168.80.135 allow all # We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent # web applications running on the proxy server who think the only # one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user #http_access deny to_localhost # # INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks # from where browsing should be allowed http_access allow localnet http_access allow localhost # And finally deny all other access to this proxy #http_access deny all #http_access allow all # Squid normally listens to port 3128 http_port 3128 accel vhost vport # Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory. cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 # Leave coredumps in the first cache dir coredump_dir /var/spool/squid # # Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these. # refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080 refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78



