- 1Vue2.x 源码剖析之响应式原理_vue2源码阅读:响应式原理zhouweicsu
- 2docker的简单安装_libltdl.so.7
- 3Python 学习笔记——代码基础
- 410、Django开发总结:Django缓存Cache应用场景、设置以及高级使用技巧_vary_on_cookiez作用
- 5【数据结构】红黑树(RBTree)详解——C++实现_c语言实现rbtree
- 6居民健康监测小程序|基于微信小程序的居民健康监测小程序设计与实现(源码+数据库+文档)
- 7stable-diffusion-webui-forge 介绍,安装,运行_stable diffusion froge ui
- 8实测!华为鸿蒙比 Android系统快60%!_开发鸿蒙应用和开发安卓应用哪个容易
- 9常见排序算法时间复杂度和空间复杂度_n个数排序的时间复杂度
- 10NLP中的alignment 对齐 的理解_nlp句子对齐
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第22天| 二叉搜索树的操作:插入、删除、修剪、转换
赞
踩
相关推荐
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第12天| 二叉树:理论基础
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第13天| 二叉树的深度优先遍历
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第14天| 二叉树的广度优先遍历
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第15天| 二叉树:翻转二叉树、对称二叉树
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第16天| 二叉树:完全二叉树、平衡二叉树、二叉树的所有路径、左叶子之和
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第17天| 二叉树:找树左下角的值、路径总和
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第18天| 二叉树:从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树、最大二叉树
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第19天| 二叉树:合并二叉树
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第20天| 二叉搜索树:搜索、验证、最小绝对差、众数
python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第21天| 二叉树:最近公共祖先
二叉搜索树的插入操作
Key Points
BST的性质:对于每个节点,其左子树只包含小于当前节点的数,其右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
相关题目
视频讲解
重点分析

方法一:递归法
def insertIntoBST(root, val):
# 如果当前节点为空,创建一个新节点并返回
if not root:
return TreeNode(val)
# 如果新值小于当前节点的值,递归地插入到左子树
if val < root.val:
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val)
# 如果新值大于当前节点的值,递归地插入到右子树
else:
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val)
# 返回根节点
return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
方法二:迭代法
def insertIntoBST(root, val): if not root: return TreeNode(val) current = root while True: if val < current.val: if current.left: current = current.left else: current.left = TreeNode(val) break # 插入完成,退出循环 else: # val > current.val if current.right: current = current.right else: current.right = TreeNode(val) break # 插入完成,退出循环 return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
删除二叉搜索树的节点
Key Points
分类讨论:
- 没找到节点
- 叶子节点
- 只有一个孩子的节点
- 有两个孩子的节点
相关题目
视频讲解
重点分析
我们需要从根节点开始,使用二叉搜索树的性质来定位要删除的节点。这意味着:
如果 key 小于当前节点的值,则我们应该在左子树中查找 key。
如果 key 大于当前节点的值,则我们应该在右子树中查找 key。
如果 key 等于当前节点的值,那么我们就找到了要删除的节点。
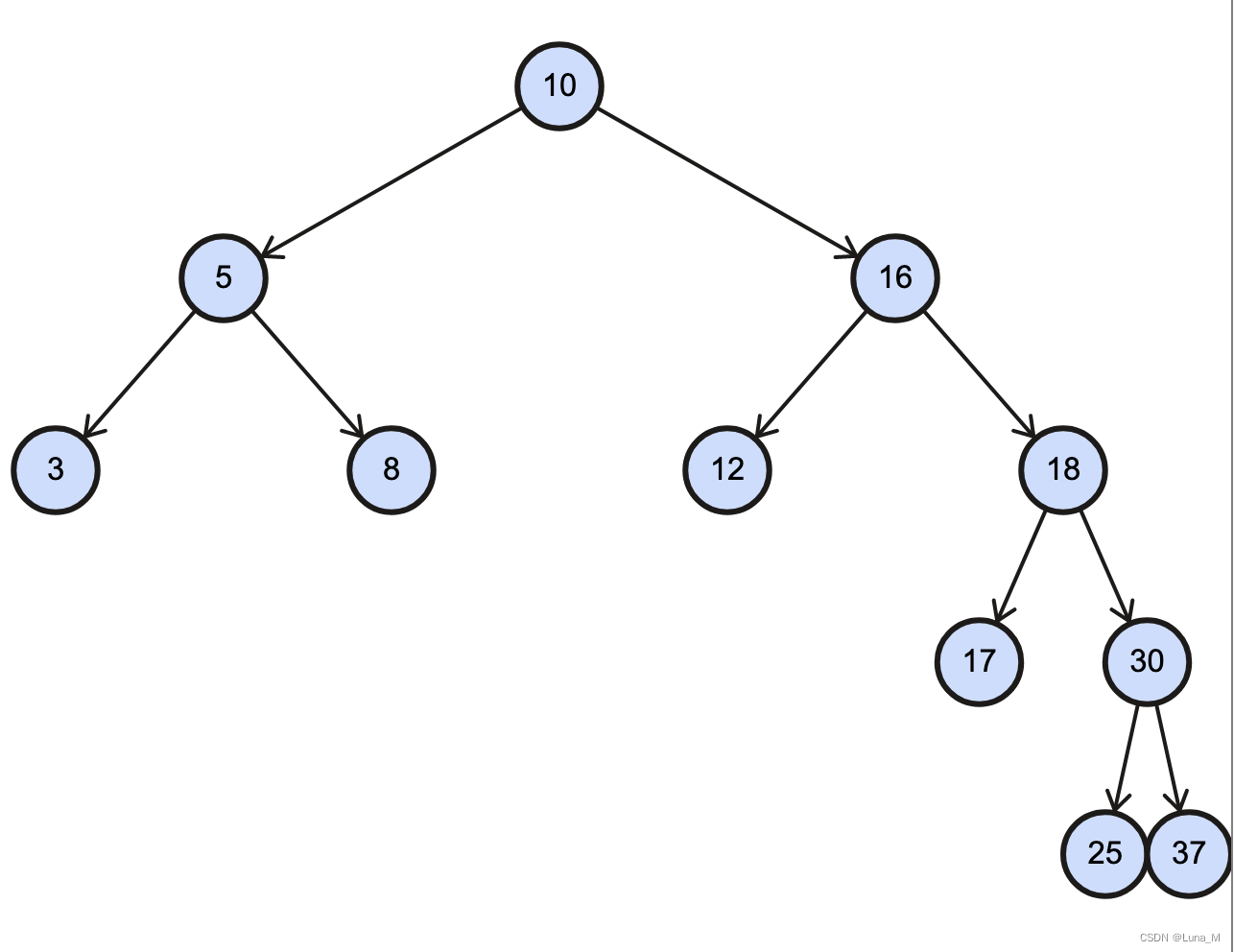
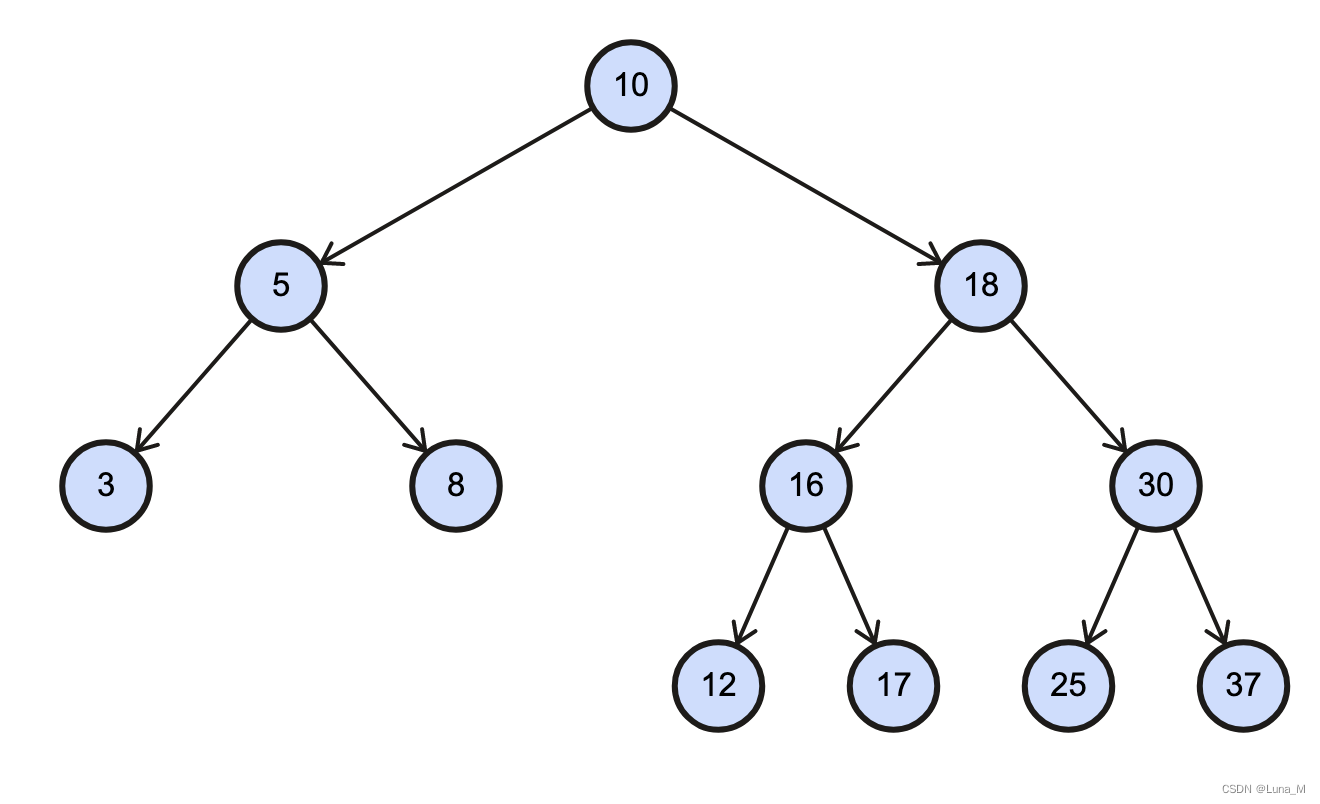
例如:删除如下二叉树值为20的节点

其中,删除有两个孩子的节点是最重要的,主要有两种思路:
- 用删除节点的左孩子替换删除节点,把删除节点的右孩子整个放在左孩子的最大节点的右侧。
- 优点:不用递归调用删除节点的函数
- 缺点:新二叉树结构改变会很大(如:平衡->不平衡)
- 用删除节点的左孩子的最大值替换删除节点,然后递归删除左孩子的最大节点。
- 优点:新二叉树结构变化较小
- 缺点:需要递归调用
方法一:
 方法二:
方法二:
方法一:
递归法:
def get_max_child(node): while node.right: node = node.right return node def deleteNode(root, key): if not root: return root if root.val > key: root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key) return root # 返回root才完整 if root.val < key: root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key) return root else: if not root.left and not root.right: return None if not root.left: return root.right if not root.right: return root.left node = get_max_child(root.left) node.right = root.right return root.left
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
写递归的逻辑:
某个情形的逻辑要完整(return)
方法一:
迭代法
def deleteNode(root, key): current = root parent = None while current: if current.val > key: parent = current current = current.left elif current.val < key: parent = current current = current.right else: if not current.left and not current.right: if not parent: return None else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = None else: parent.right = None return root elif not current.right: if not parent: return current.left else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = current.left else: parent.right = current.left return root elif not current.left: if not parent: return current.right else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = current.right else: parent.right = current.right return root else: node = get_max_child(current.left) node.right = current.right if not parent: return current.left else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = current.left else: parent.right = current.left return root return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
迭代法注意考虑parent为None的情况
方法二:
递归法
def deleteNode(root, key): if not root: return root if root.val > key: root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key) return root if root.val < key: root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key) return root else: if not root.left and not root.right: return None if not root.left: return root.right if not root.right: return root.left node = get_max_child(root.left) root.val = node.val root.left = deleteNode(root.left, node.val) return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
方法二:
迭代法
current = root parent = None while current: if current.val > key: parent = current current = current.left elif current.val < key: parent = current current = current.right else: if not current.left and not current.right: if not parent: return None else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = None else: parent.right = None return root elif not current.right: if not parent: return current.left else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = current.left else: parent.right = current.left return root elif not current.left: if not parent: return current.right else: if parent.left == current: parent.left = current.right else: parent.right = current.right return root else: node = get_max_child(current.left) current.val = node.val current.left = deleteNode(current.left, node.val) return root return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
修剪二叉搜索树
Key Points
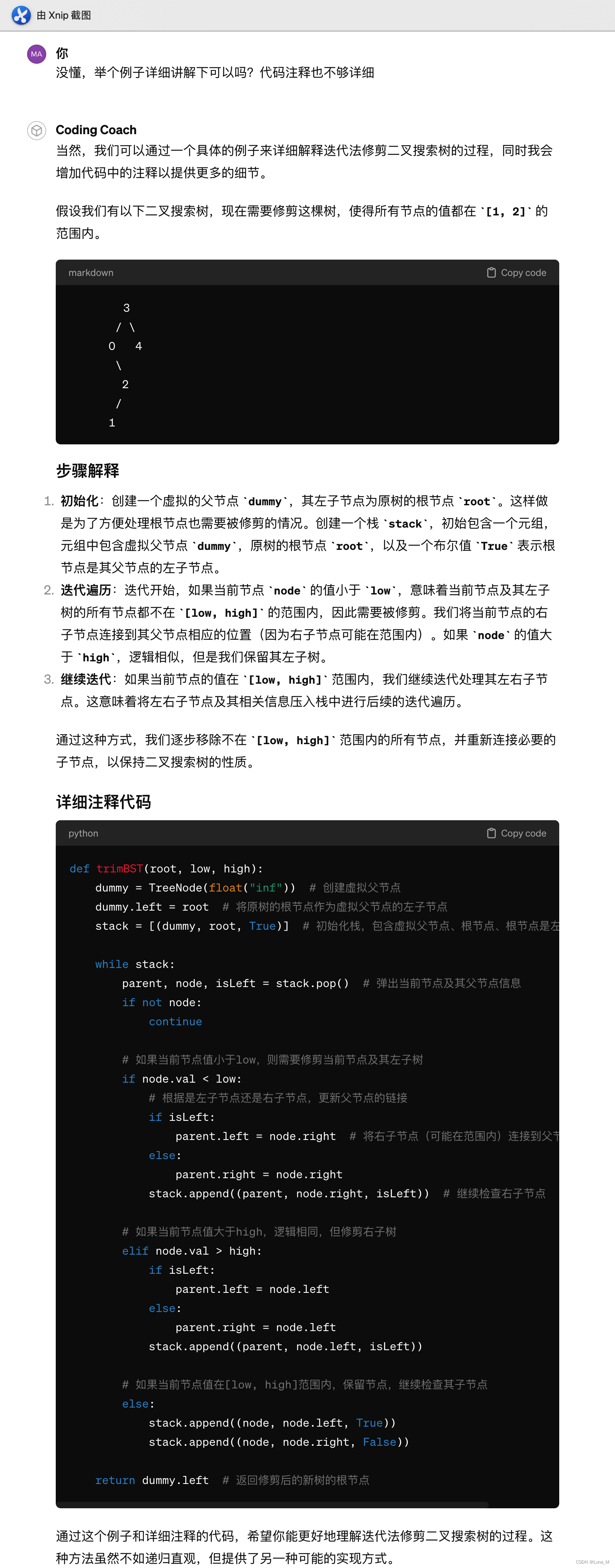
易错点:
3
/ \
0 4
\
2
/
1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
[1,3]
相关题目
视频讲解
重点分析
方法一: 递归法
def trimBST(root, low, high): if not root: return None # 如果节点值小于low,那么它的左子树都不在范围内,应修剪掉左子树 if root.val < low: root = trimBST(root.right, low, high) # 如果节点值大于high,那么它的右子树都不在范围内,应修剪掉右子树 elif root.val > high: root = trimBST(root.left, low, high) # 如果节点值在[low, high]范围内,递归修剪其左右子树 else: root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high) root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high) return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
方法二:迭代法
def trimBST(root, low, high): dummy = TreeNode(float("inf")) # 创建虚拟父节点 dummy.left = root # 将原树的根节点作为虚拟父节点的左子节点 stack = [(dummy, root, True)] # 初始化栈,包含虚拟父节点、根节点、根节点是左子节点的信息 while stack: parent, node, isLeft = stack.pop() # 弹出当前节点及其父节点信息 if not node: continue # 如果当前节点值小于low,则需要修剪当前节点及其左子树 if node.val < low: # 根据是左子节点还是右子节点,更新父节点的链接 if isLeft: parent.left = node.right # 将右子节点(可能在范围内)连接到父节点 else: parent.right = node.right stack.append((parent, node.right, isLeft)) # 继续检查右子节点 # 如果当前节点值大于high,逻辑相同,但修剪右子树 elif node.val > high: if isLeft: parent.left = node.left else: parent.right = node.left stack.append((parent, node.left, isLeft)) # 如果当前节点值在[low, high]范围内,保留节点,继续检查其子节点 else: stack.append((node, node.left, True)) stack.append((node, node.right, False)) return dummy.left # 返回修剪后的新树的根节点
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
这段代码使用了一个栈来追踪遍历过程中的节点以及它们的父节点和是否为左子节点的信息。对每个节点,我们检查它是否需要被修剪(即它的值是否在 [low, high] 范围之外)。如果是,则根据它是左子节点还是右子节点,更新父节点的相应链接。如果节点的值在范围内,我们将继续处理它的子节点。
请注意,这个方法虽然避免了递归,但逻辑复杂度增加了,特别是在管理父节点和子节点关系时。对于二叉树的修改操作,递归方法通常更为直观和易于理解。
将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
Key Points
分而治之的策略:选取中间元素作为根节点,然后对左右子数组分别执行同样的操作
相关题目
视频讲解
重点分析
关键在于每次都要选取数组中间的元素作为树的根节点,这样可以确保树的左右两边保持平衡。
方法一:递归法
def sortedArrayToBST(nums):
if not nums:
return None
mid = len(nums) // 2
root_val = nums[mid]
root = TreeNode(root_val)
root.left = sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
root.right = sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid+1:])
return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
方法二:迭代法
def sortedArrayToBST(nums): if not nums: return None # 用于保存处理节点的栈 node_stack = [] # 用于保存数组范围的栈 range_stack = [(0, len(nums) - 1)] # 创建一个虚拟的根节点 root = TreeNode(0) node_stack.append((root, True)) while range_stack: left, right = range_stack.pop() parent, is_left = node_stack.pop() if left > right: continue mid = (left + right) // 2 # 创建当前节点 current_node = TreeNode(nums[mid]) # 将当前节点连接到父节点 if is_left: parent.left = current_node else: parent.right = current_node # 处理左子树 node_stack.append((current_node, True)) range_stack.append((left, mid - 1)) # 处理右子树 node_stack.append((current_node, False)) range_stack.append((mid + 1, right)) return root.left
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
Key Points
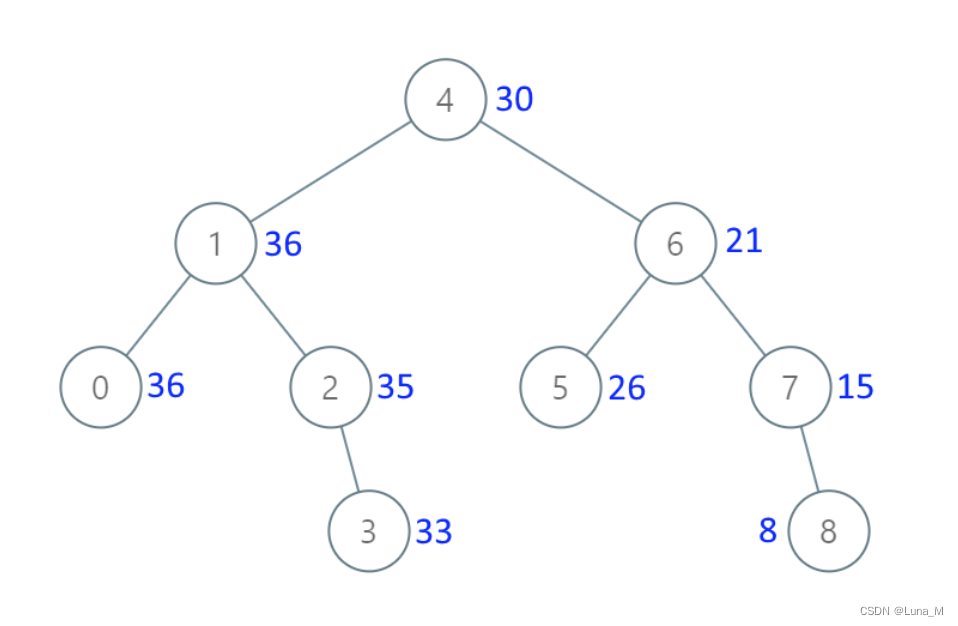
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
相关题目
视频讲解
重点分析
方法一:递归法
class Solution(object): def __init__(self): self.sum_value = 0 def convertBST(self, root): """ :type root: TreeNode :rtype: TreeNode """ if not root: return root root.right = self.convertBST(root.right) self.sum_value += root.val root.val = self.sum_value root.left = self.convertBST(root.left) return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
方法二:迭代法 反向中序遍历
按照反向中序遍历(右->节点->左)的顺序,使用栈来迭代地遍历树
def convertBST(root): if not root: return root current = root stack = [] sum_value = 0 while current or stack: # 将当前节点及其所有右子节点压入栈 while current: stack.append(current) current = current.right current = stack.pop() # 访问栈顶元素(当前最大节点) sum_value += current.val current.val = sum_value current = current.left # 转向左子树 return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
方法二:迭代法 统一迭代法(颜色标记)
详见 python coding with ChatGPT 打卡第13天| 二叉树的深度优先遍历 中的迭代遍历 拓展 统一的迭代法
def convertBST(root): if not root: return root WHITE = 0 # 使用常量来提高代码可读性 GREY = 1 stack = [(root, WHITE)] sum_value = 0 # 累加变量,用于更新节点的值 while stack: node, color = stack.pop() if color == WHITE: # 节点首次访问,先处理右子节点 stack.append((node, GREY)) if node.right: stack.append((node.right, WHITE)) else: # 节点第二次访问,更新节点值并处理左子节点 sum_value += node.val node.val = sum_value if node.left: stack.append((node.left, WHITE)) return root
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
GPT4点评:




