- 1Java数据存储之---ArrayList
- 2DatawhaleAI夏令营第三期 - 基于论文摘要的文本分类与关键词抽取挑战
- 3openstack 管理 四十一 创建自己的 glance image_虚机镜像制作glance imange
- 4HW自学:蓝队初级到中级_蓝队初级要干什么
- 5[已解决]OSError: Unable to load weights from pytorch checkpoint file
- 6Doris系列1-Doris介绍
- 7鸿蒙core是什么,一文看懂HMS Core到底是什么
- 8玩客云内置EMMC存储刷入Armbian_玩客云可以刷成小主机吗
- 9Python元组:不可变的神话_fpj movie
- 10[AIGC] SQL中的数据添加和操作:数据类型介绍
接触网绝缘子缺陷检测项目_缺陷检测 电网
赞
踩
目录
1. 接触网绝缘子作用
绝缘子是接触网中广泛应用的重要部件之一,绝缘子用悬吊的支持接触悬挂并使用带电体与接地之间保持电气绝缘。我国电网正处于快速、健康、持续发展的新时期,绝缘子在输电线路的安全稳定运行中发挥重要作用,所以对绝缘子的需求很大。
高压电线连接塔的一端挂了很多盘状的绝缘体,它是为了增加爬电距离的,通常由玻璃或陶瓷制成,就叫绝缘子。绝缘子是一种绝缘控件,在架空输电线路中起到重要作用,即起到支撑导线和防止电流回地的作用。以前绝缘子多用于电线杆,现在已逐步发展成为挂在高压电线连接塔一端的盘状绝缘体,通常是由陶瓷或玻璃制成的。绝缘子要保证在环境和电负荷条件发生变化时,各种机电应力保持不变,否则不仅起不到应有的作用,反而会损害整条线路的使用寿命。

2. 接触网绝缘子破损原因及危害
(1)产品质量不良。由于雨季吸潮,绝缘子的绝缘性能低,而发生绝缘子闪络击穿或受热膨胀爆炸,导致炸裂,最终使绝缘子丧失绝缘。
(2)施工不当损伤绝缘子。由于外力原因使绝缘子产生裂纹、损伤或缺釉现象,在阴雨天气导致闪络、击穿故障的发生。

3.接触网绝缘子缺陷检测图像数据集介绍
图像数据的收集是接触网绝缘子缺陷检测的第一步,也是至关重要的一步,本项目共收集接触网绝缘子缺陷检测图像数据480幅。图像分辨率均为416×416,采集手段为夜间巡检,并利用labelimg软件对其中包含的缺陷进行标注,标签类型为两类(1.正常绝缘子;2. 损坏绝缘子)。


4. 缺陷检测模型介绍
本项目采用YOLOv3及轻量级网络efficientnet改进的YOLOv3对接触网缺陷绝缘子进行检测。
4.1 efficientnet模型介绍
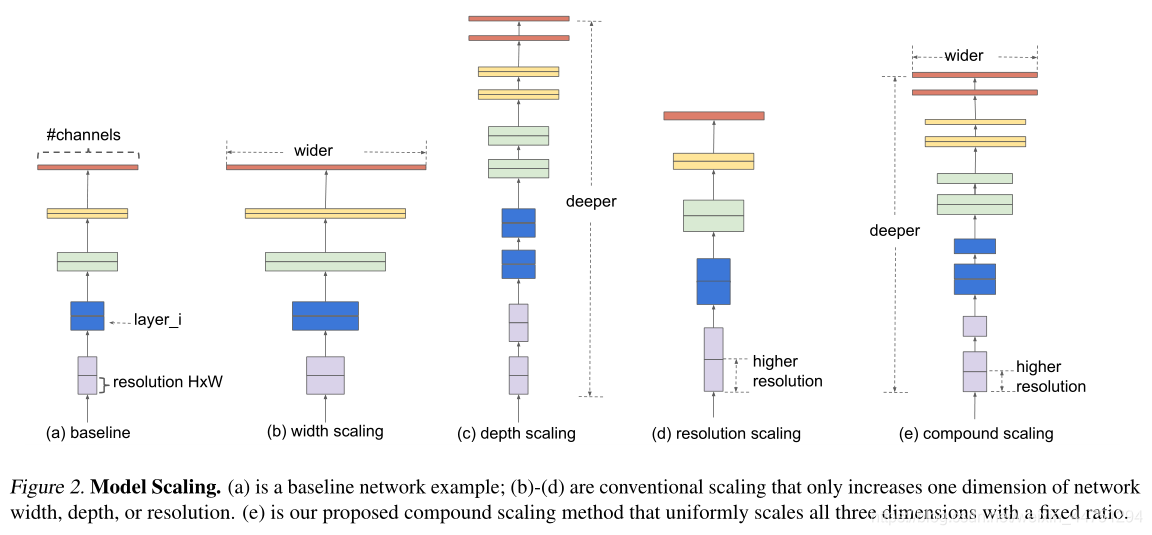
EfficientNet提出的compound scaling(depth, width, resolution)的方法也在论文中实验用到MobileNet v1/v2和ResNet-50上,在增加FLOPs与提升accuracy之间找最佳的trade-off。
EfficientNet v2在v1基础上提高了训练速度,同时也以损失一部分accuracy的同时大大减少了参数量,加快了推理速度(跟芯片有关,加速这个未必是确定的)。
tensorflow2版本的efficientnet实现方法:
- import math
- from copy import deepcopy
-
- import tensorflow as tf
- from tensorflow.keras import backend, layers
-
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
- DEFAULT_BLOCKS_ARGS = [
- {'kernel_size': 3, 'repeats': 1, 'filters_in': 32, 'filters_out': 16,
- 'expand_ratio': 1, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 1, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 3, 'repeats': 2, 'filters_in': 16, 'filters_out': 24,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 2, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 5, 'repeats': 2, 'filters_in': 24, 'filters_out': 40,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 2, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 3, 'repeats': 3, 'filters_in': 40, 'filters_out': 80,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 2, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 5, 'repeats': 3, 'filters_in': 80, 'filters_out': 112,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 1, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 5, 'repeats': 4, 'filters_in': 112, 'filters_out': 192,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 2, 'se_ratio': 0.25},
-
- {'kernel_size': 3, 'repeats': 1, 'filters_in': 192, 'filters_out': 320,
- 'expand_ratio': 6, 'id_skip': True, 'strides': 1, 'se_ratio': 0.25}
- ]
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER = {
- 'class_name': 'VarianceScaling',
- 'config': {
- 'scale': 2.0,
- 'mode': 'fan_out',
- 'distribution': 'normal'
- }
- }
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- def correct_pad(inputs, kernel_size):
- img_dim = 1
- input_size = backend.int_shape(inputs)[img_dim:(img_dim + 2)]
-
- if isinstance(kernel_size, int):
- kernel_size = (kernel_size, kernel_size)
-
- if input_size[0] is None:
- adjust = (1, 1)
- else:
- adjust = (1 - input_size[0] % 2, 1 - input_size[1] % 2)
-
- correct = (kernel_size[0] // 2, kernel_size[1] // 2)
-
- return ((correct[0] - adjust[0], correct[0]),
- (correct[1] - adjust[1], correct[1]))
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- def round_filters(filters, divisor, width_coefficient):
- filters *= width_coefficient
- new_filters = max(divisor, int(filters + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
- if new_filters < 0.9 * filters:
- new_filters += divisor
- return int(new_filters)
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- def round_repeats(repeats, depth_coefficient):
- return int(math.ceil(depth_coefficient * repeats))
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
- # efficient_block
- #-------------------------------------------------#
- def block(inputs, activation_fn=tf.nn.swish, drop_rate=0., name='',
- filters_in=32, filters_out=16, kernel_size=3, strides=1,
- expand_ratio=1, se_ratio=0., id_skip=True):
-
- filters = filters_in * expand_ratio
- #-------------------------------------------------#
- if expand_ratio != 1:
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters, 1,
- padding='same',
- use_bias=False,
- kernel_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name=name + 'expand_conv')(inputs)
- x = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=name + 'expand_bn')(x)
- x = layers.Activation(activation_fn, name=name + 'expand_activation')(x)
- else:
- x = inputs
-
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- if strides == 2:
- x = layers.ZeroPadding2D(padding=correct_pad(x, kernel_size),
- name=name + 'dwconv_pad')(x)
- conv_pad = 'valid'
- else:
- conv_pad = 'same'
-
- x = layers.DepthwiseConv2D(kernel_size,
- strides=strides,
- padding=conv_pad,
- use_bias=False,
- depthwise_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name=name + 'dwconv')(x)
- x = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=name + 'bn')(x)
- x = layers.Activation(activation_fn, name=name + 'activation')(x)
-
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- if 0 < se_ratio <= 1:
- filters_se = max(1, int(filters_in * se_ratio))
- se = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(name=name + 'se_squeeze')(x)
- se = layers.Reshape((1, 1, filters), name=name + 'se_reshape')(se)
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- se = layers.Conv2D(filters_se, 1,
- padding='same',
- activation=activation_fn,
- kernel_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name=name + 'se_reduce')(se)
- se = layers.Conv2D(filters, 1,
- padding='same',
- activation='sigmoid',
- kernel_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name=name + 'se_expand')(se)
- x = layers.multiply([x, se], name=name + 'se_excite')
-
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- x = layers.Conv2D(filters_out, 1,
- padding='same',
- use_bias=False,
- kernel_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name=name + 'project_conv')(x)
- x = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=name + 'project_bn')(x)
-
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- if (id_skip is True and strides == 1 and filters_in == filters_out):
- if drop_rate > 0:
- x = layers.Dropout(drop_rate,
- noise_shape=(None, 1, 1, 1),
- name=name + 'drop')(x)
- x = layers.add([x, inputs], name=name + 'add')
-
- return x
-
- def EfficientNet(width_coefficient,
- depth_coefficient,
- drop_connect_rate=0.2,
- depth_divisor=8,
- activation_fn=tf.nn.swish,
- blocks_args=DEFAULT_BLOCKS_ARGS,
- inputs=None,
- **kwargs):
- img_input = inputs
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- x = img_input
- x = layers.ZeroPadding2D(padding=correct_pad(x, 3),
- name='stem_conv_pad')(x)
- x = layers.Conv2D(round_filters(32, depth_divisor, width_coefficient), 3,
- strides=2,
- padding='valid',
- use_bias=False,
- kernel_initializer=CONV_KERNEL_INITIALIZER,
- name='stem_conv')(x)
- x = layers.BatchNormalization(axis=3, name='stem_bn')(x)
- x = layers.Activation(activation_fn, name='stem_activation')(x)
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- blocks_args = deepcopy(blocks_args)
-
- #-------------------------------------------------#
-
- b = 0
- blocks = float(sum(args['repeats'] for args in blocks_args))
-
- feats = []
- filters_outs = []
- #------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
-
- for (i, args) in enumerate(blocks_args):
- assert args['repeats'] > 0
- args['filters_in'] = round_filters(args['filters_in'], depth_divisor, width_coefficient)
- args['filters_out'] = round_filters(args['filters_out'], depth_divisor, width_coefficient)
-
- for j in range(round_repeats(args.pop('repeats'), depth_coefficient)):
- if j > 0:
- args['strides'] = 1
- args['filters_in'] = args['filters_out']
- x = block(x, activation_fn, drop_connect_rate * b / blocks,
- name='block{}{}_'.format(i + 1, chr(j + 97)), **args)
- b += 1
- feats.append(x)
- if i == 2 or i == 4 or i == 6:
- filters_outs.append(args['filters_out'])
- return feats, filters_outs
-
-
- def EfficientNetB0(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.0, 1.0, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB1(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.0, 1.1, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB2(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.1, 1.2, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB3(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.2, 1.4, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB4(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.4, 1.8, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB5(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.6, 2.2, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
-
- def EfficientNetB6(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(1.8, 2.6, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- def EfficientNetB7(inputs=None, **kwargs):
- return EfficientNet(2.0, 3.1, inputs=inputs, **kwargs)
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- print(EfficientNetB0())

4.2 YOLOv3模型介绍
YOLOv3相比于之前的yolo1和yolo2,改进较大,主要改进方向有:
1、使用了残差网络Residual,残差卷积就是进行一次3X3、步长为2的卷积,然后保存该卷积layer,再进行一次1X1的卷积和一次3X3的卷积,并把这个结果加上layer作为最后的结果, 残差网络的特点是容易优化,并且能够通过增加相当的深度来提高准确率。其内部的残差块使用了跳跃连接,缓解了在深度神经网络中增加深度带来的梯度消失问题。
2、提取多特征层进行目标检测,一共提取三个特征层,特征层的shape分别为(13,13,75),(26,26,75),(52,52,75),最后一个维度为75是因为该图是基于voc数据集的,它的类为20种,yolo3只有针对每一个特征层存在3个先验框,所以最后维度为3x25;
如果使用的是coco训练集,类则为80种,最后的维度应该为255 = 3x85,三个特征层的shape为(13,13,255),(26,26,255),(52,52,255)
3、其采用反卷积UmSampling2d设计,逆卷积相对于卷积在神经网络结构的正向和反向传播中做相反的运算,其可以更多更好的提取出特征。

tensorflow2.0版本的darknet53结构
- from functools import wraps
-
- from tensorflow.keras.initializers import RandomNormal
- from tensorflow.keras.layers import (Add, BatchNormalization, Conv2D, LeakyReLU,
- ZeroPadding2D)
- from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
- from utils.utils import compose
-
- #------------------------------------------------------#
-
- @wraps(Conv2D)
- def DarknetConv2D(*args, **kwargs):
- darknet_conv_kwargs = {'kernel_initializer' : RandomNormal(stddev=0.02), 'kernel_regularizer' : l2(kwargs.get('weight_decay', 5e-4))}
- darknet_conv_kwargs['padding'] = 'valid' if kwargs.get('strides')==(2, 2) else 'same'
- try:
- del kwargs['weight_decay']
- except:
- pass
- darknet_conv_kwargs.update(kwargs)
- return Conv2D(*args, **darknet_conv_kwargs)
-
- #---------------------------------------------------#
- def DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(*args, **kwargs):
- no_bias_kwargs = {'use_bias': False}
- no_bias_kwargs.update(kwargs)
- return compose(
- DarknetConv2D(*args, **no_bias_kwargs),
- BatchNormalization(),
- LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1))
-
- #---------------------------------------------------------------------#
- def resblock_body(x, num_filters, num_blocks, weight_decay=5e-4):
- x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x)
- x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3), strides=(2,2), weight_decay=weight_decay)(x)
- for i in range(num_blocks):
- y = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters//2, (1,1), weight_decay=weight_decay)(x)
- y = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(num_filters, (3,3), weight_decay=weight_decay)(y)
- x = Add()([x,y])
- return x
-
- #---------------------------------------------------#
-
- def darknet_body(x, weight_decay=5e-4):
- # 416,416,3 -> 416,416,32
- x = DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(32, (3,3), weight_decay=weight_decay)(x)
- # 416,416,32 -> 208,208,64
- x = resblock_body(x, 64, 1)
- # 208,208,64 -> 104,104,128
- x = resblock_body(x, 128, 2)
- # 104,104,128 -> 52,52,256
- x = resblock_body(x, 256, 8)
- feat1 = x
- # 52,52,256 -> 26,26,512
- x = resblock_body(x, 512, 8)
- feat2 = x
- # 26,26,512 -> 13,13,1024
- x = resblock_body(x, 1024, 4)
- feat3 = x
- return feat1, feat2, feat3
-

tensorflow2版本的FPN结构
- def yolo_body(input_shape, anchors_mask, num_classes, weight_decay=5e-4):
- inputs = Input(input_shape)
-
- #---------------------------------------------------#
- C3, C4, C5 = darknet_body(inputs, weight_decay)
-
- #---------------------------------------------------#
-
- # 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512 -> 13,13,1024 -> 13,13,512
- x = make_five_conv(C5, 512, weight_decay)
- P5 = make_yolo_head(x, 512, len(anchors_mask[0]) * (num_classes+5), weight_decay)
-
- # 13,13,512 -> 13,13,256 -> 26,26,256
- x = compose(DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(256, (1,1), weight_decay=weight_decay), UpSampling2D(2))(x)
-
- # 26,26,256 + 26,26,512 -> 26,26,768
- x = Concatenate()([x, C4])
- #---------------------------------------------------#
-
- # 26,26,768 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256 -> 26,26,512 -> 26,26,256
- x = make_five_conv(x, 256, weight_decay)
- P4 = make_yolo_head(x, 256, len(anchors_mask[1]) * (num_classes+5), weight_decay)
-
- # 26,26,256 -> 26,26,128 -> 52,52,128
- x = compose(DarknetConv2D_BN_Leaky(128, (1,1), weight_decay=weight_decay), UpSampling2D(2))(x)
- # 52,52,128 + 52,52,256 -> 52,52,384
- x = Concatenate()([x, C3])
- #---------------------------------------------------#
-
- # 52,52,384 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128 -> 52,52,256 -> 52,52,128
- x = make_five_conv(x, 128, weight_decay)
- P3 = make_yolo_head(x, 128, len(anchors_mask[2]) * (num_classes+5), weight_decay)
- return Model(inputs, [P5, P4, P3])

4.3 efficientnet-YOLOv3模型介绍
2019年,谷歌新出EfficientNet,网络如其名,这个网络非常的有效率,主要为以下几点:
1、网络要可以训练,可以收敛。
2、参数量要比较小,方便训练,提高速度。
3、创新神经网络的结构,学到更深层语义特征。
5. 模型训练与测试
5.1 模型训练
将接触网绝缘子检测图像数据集按9:1随机选取训练集及测试集。训练环境tensorflow2.2,3080显卡。采用带动量的随机梯度下降优化算法(SGDM)进行训练, 动量 = 0.937,权值衰减系数=0.0005。训练过程中损失值曲线如下:




5.2 检测性能测试
经测试YOLOv3对接触网绝缘子检测的mAP值=90.42%,FPS=28.97。efficientnet-YOLOv3对接触网绝缘子检测的mAP值=88.99%,FPS=58.42。




利用预测框的尺寸对原图像中目标检测裁剪的python代码:
- for i, c in list(enumerate(out_boxes)):
- top, left, bottom, right = out_boxes[i]
- top = max(0, np.floor(top).astype('int32'))
- left = max(0, np.floor(left).astype('int32'))
- bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom).astype('int32'))
- right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right).astype('int32'))
-
- dir_save_path = "img_crop"
- if not os.path.exists(dir_save_path):
- os.makedirs(dir_save_path)
- crop_image = image.crop([left, top, right, bottom])
- crop_image.save(os.path.join(dir_save_path, "crop_" + str(i) + ".png"), quality=95, subsampling=0)
- print("save crop_" + str(i) + ".png to " + dir_save_path)


