热门标签
热门文章
- 1微信小程序源码_微信小程序源代码
- 2【kotlin】使用MPAndroidChart实现PieChart(饼图)并设置每个数据的颜色、标签等属性_android studio kotlin 中调用mpandroidchart
- 3Java题目详解——LeetCode206.反转链表(包含三种解法,迭代,栈,递归)_java 链表反转 迭代
- 4shell中使用正则表达式_shell 加减乘除表达式 正则
- 5蓝牙应用层协议介绍
- 6Markdown中如何输入上标、下标?_markdown 向上箭头怎么打
- 7【第二章:OpenCv算法的基本介绍与应用】_opencv 常用算法
- 8kakka rebalance解决方案_如何解决kafka rebalance问题
- 9Python机器学习实例-逻辑回归模型预测泰坦尼克号生还_机器学习,使用python scikit-learn中提供的算法类搭建回归模型。选用泰坦尼克号幸
- 10使用eric5.5.4+PYQT5.0+python3.3.2=最强python GUI开发组合_eric 编写qt5
当前位置: article > 正文
LATEX模板总结
作者:Monodyee | 2024-03-15 02:07:38
赞
踩
latex模板

写本篇文章的目的在于记录一下自己学习的亚太杯建模LATEX论文排版过程,模板是从一位西交前辈的个人网站得来的首页 · Heishan Press,这位大佬的博客当中有很多有意思的内容,大家可以去研读一下。
目录
一、公式部分
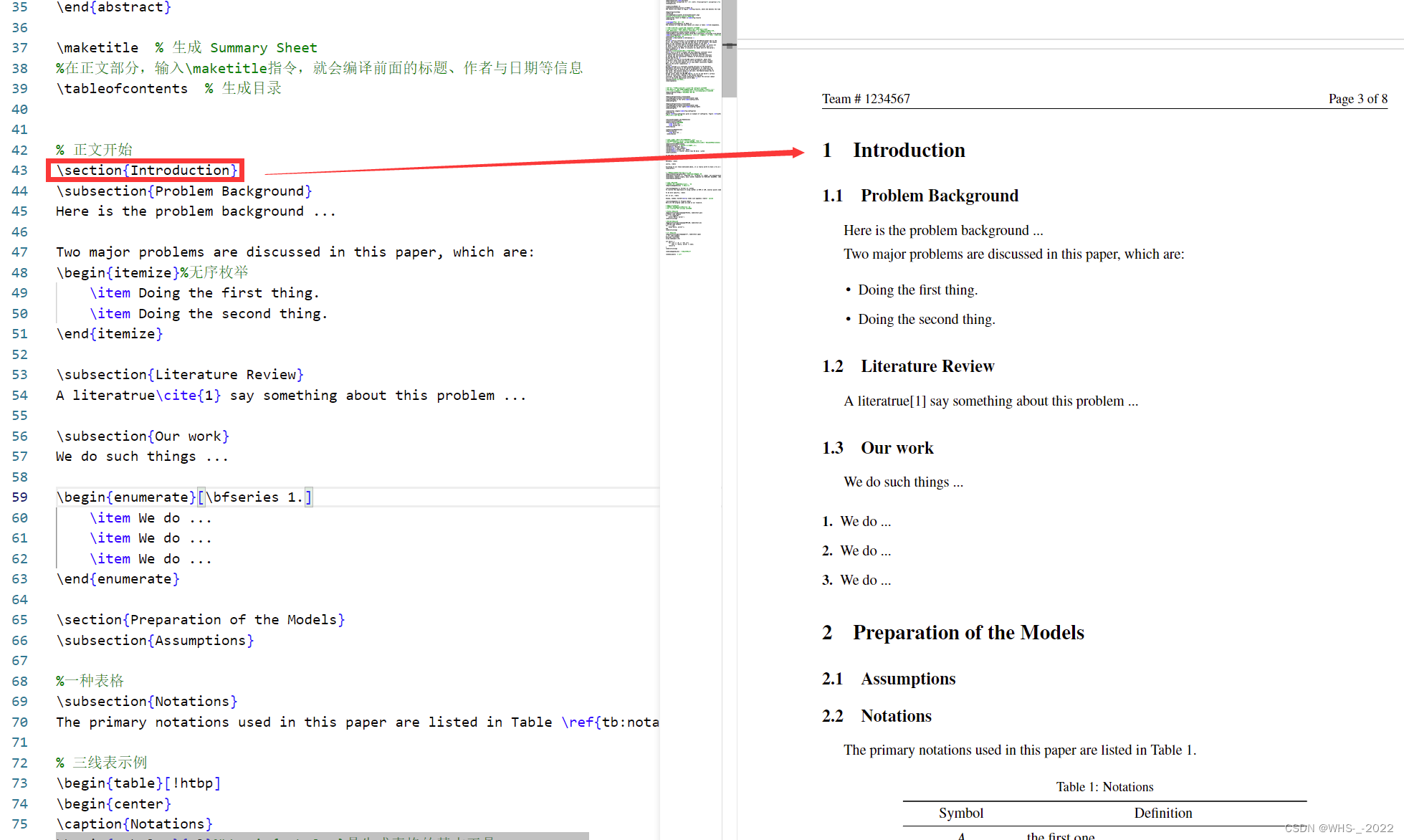
建模最重要的就是公式的编写了,我们可以利用在线的可视化LATEX公式编辑器大大降低难度,网址如下在线LaTeX公式编辑器-编辑器。它甚至贴心的提供了图片识别功能。
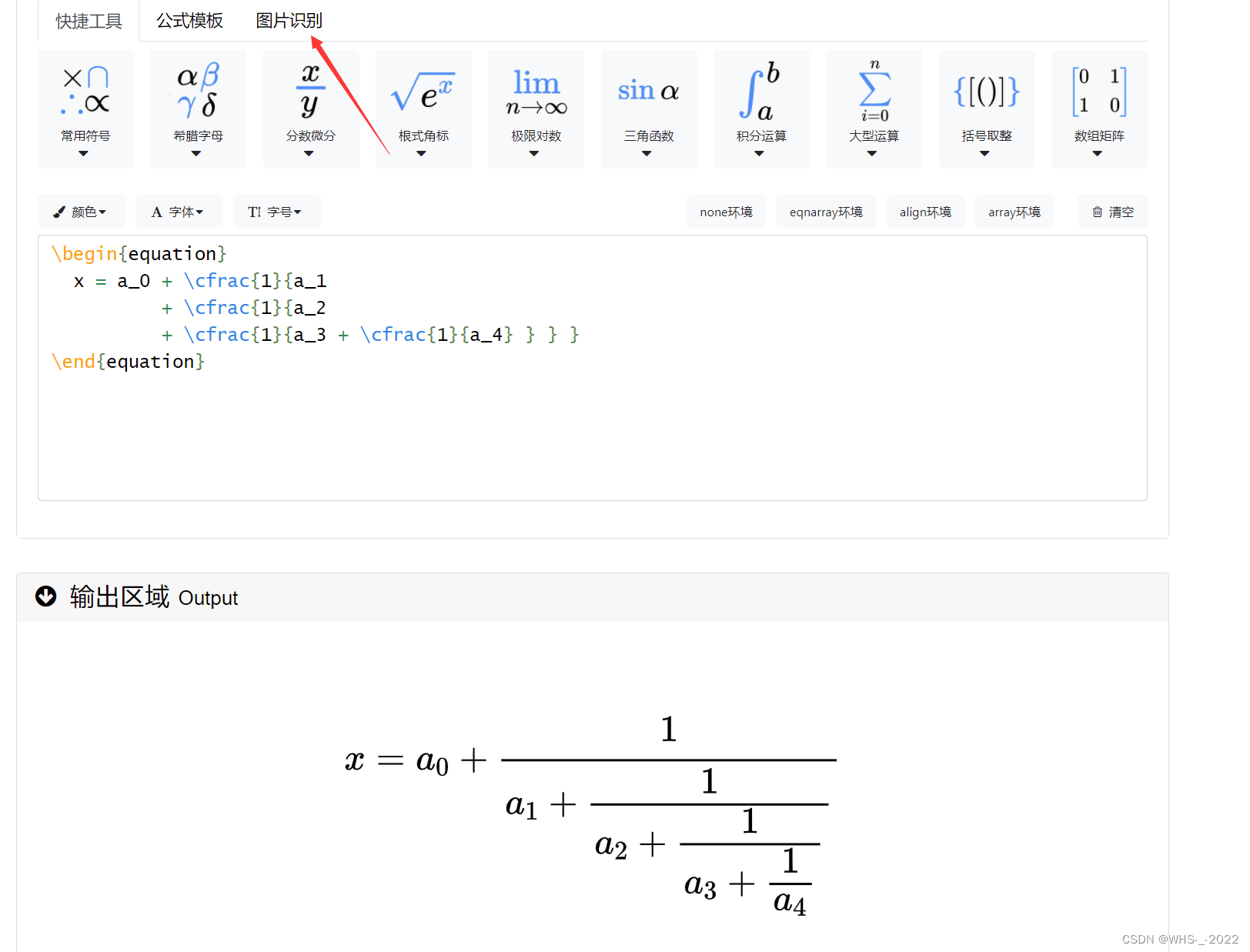
在这里我务必要推荐一下VSCODE的LATEX编辑器,鼠标悬停在代码上方就可以查看效果,值得推荐,至于如何配置VSCODE可以看我的另一篇文章。
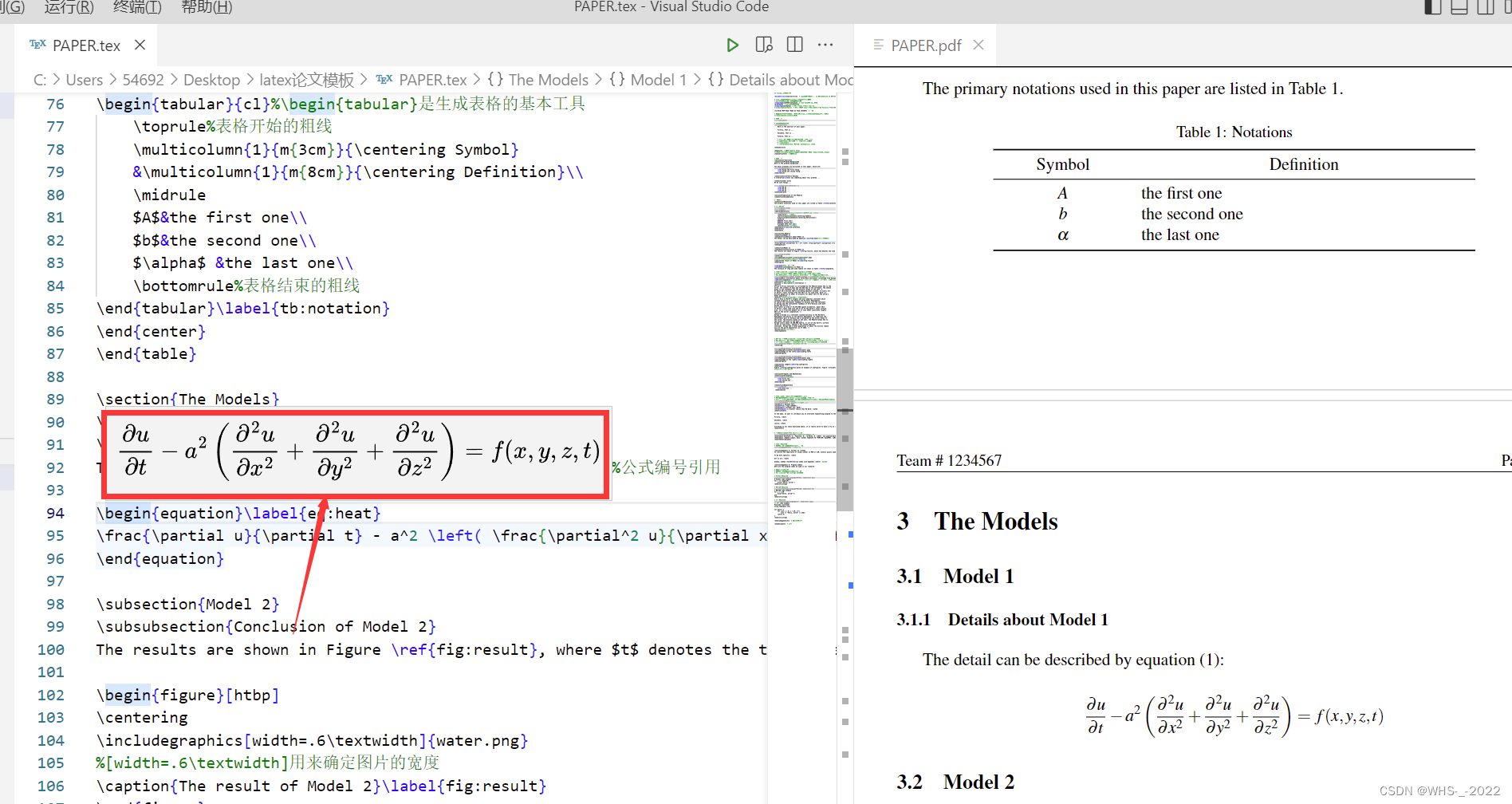
这种是插入文段的公式,通常我们需要
- \begin{equation}\label{eq:heat}
- \frac{\partial u}{\partial t} - a^2 \left( \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial y^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial z^2} \right) = f(x, y, z, t)
- \end{equation}
如果是嵌入在文本中的公式,我们可以用——$你需要展现的公式代码$,这种方式。

- \begin{itemize}
- \item $\mu$ is the mean of the distribution
- \item $\sigma$ is the standard deviation
- \end{itemize}
行间公式的话,可以采用这样的格式

- %表示行间的公式
- \[G^\mu\nu+G^{\mu\nu}\]
- %张量的上下标写法
- \[F^{ab}_{cd}+F^{ab} {}_{cd}\]
- %求和和积分公式
- \[ \int_a^b \sum_{i=0}^\infty \lim_{n\to\infty}\]
- %求和表达式的上下标问题,在\sum后面加入\nolimits
- \[ \int_a^b \sum\nolimits_{i=0}^\infty \lim_{n\to\infty}\]
- %根号的表达
- \[ \sqrt{1+2}+\sqrt[\frac{1}{x}]{\alpha}\]
二、 文档开头的宏定义
话不多说,给大家看看格式效果
- \documentclass[12pt]{article} % 官方要求字号不小于 12 号,此处选择 12 号字体
-
- % 本模板不需要填写年份,以当前电脑时间自动生成
- % 请在以下的方括号中填写队伍控制号
- \usepackage[1234567]{easymcm} % 载入 EasyMCM 模板文件
- \problem{A} % 请在此处填写题号
- \usepackage{mathptmx} % 这是 Times 字体,中规中矩
- %\usepackage{mathpazo} % 这是 COMAP 官方杂志采用的更好看的 Palatino 字体,可替代以上的 mathptmx 宏包
-
- \title{An MCM Paper Made by Team 1234567} % 标题
-
- % 如需要修改题头(默认为 MCM/ICM),请使用以下命令(此处修改为 MCM)
- %\renewcommand{\contest}{MCM}

三、文章的各个部分
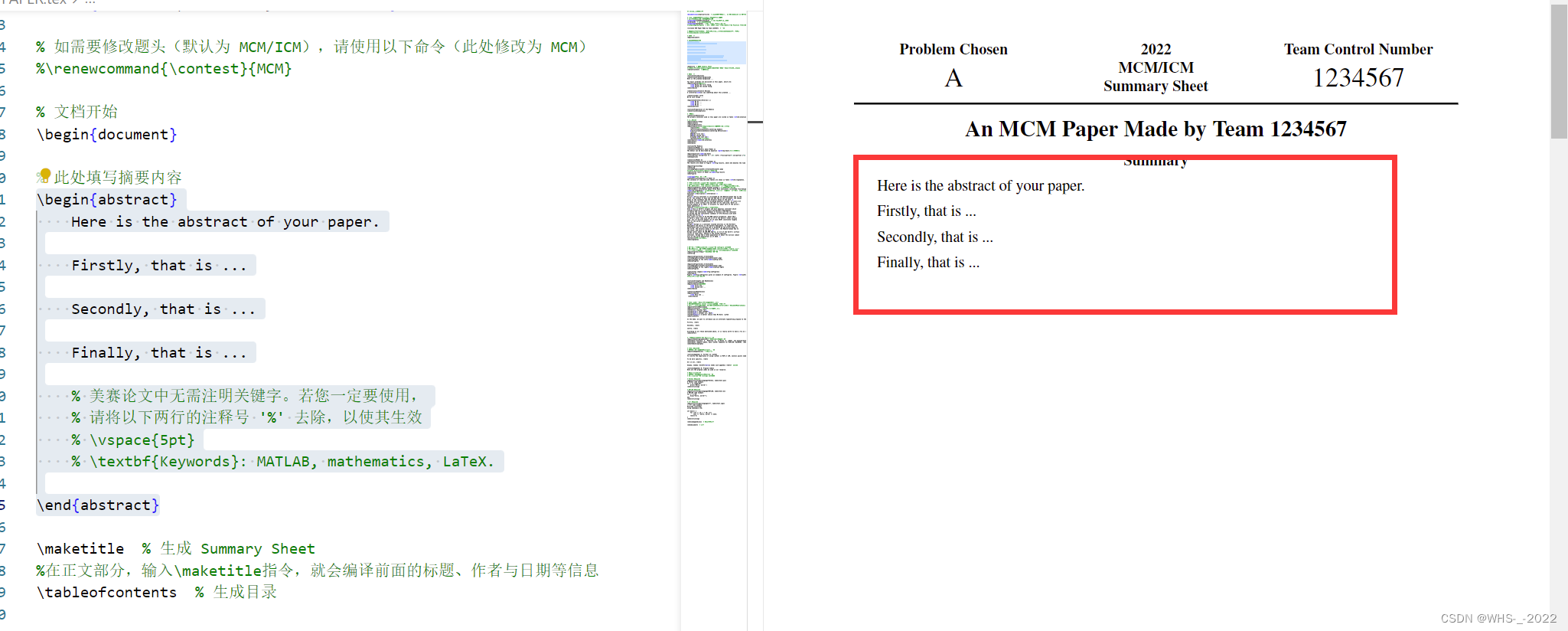
1、摘要
摘要的作用主要是概述你文章的整体思路
- \begin{abstract}
- Here is the abstract of your paper.
-
- Firstly, that is ...
-
- Secondly, that is ...
-
- Finally, that is ...
-
- % 美赛论文中无需注明关键字。若您一定要使用,
- % 请将以下两行的注释号 '%' 去除,以使其生效
- % \vspace{5pt}
- % \textbf{Keywords}: MATLAB, mathematics, LaTeX.
-
- \end{abstract}
2、目录
目录十分容易 ,只需要调用 \tableofcontents 命令就可以
\tableofcontents % 生成目录
3、正文部分
- % 正文开始
- \section{Introduction}
四、代码
- %% 美赛模板:正文部分
-
- \documentclass[12pt]{article} % 官方要求字号不小于 12 号,此处选择 12 号字体
-
- % 本模板不需要填写年份,以当前电脑时间自动生成
- % 请在以下的方括号中填写队伍控制号
- \usepackage[1234567]{easymcm} % 载入 EasyMCM 模板文件
- \problem{A} % 请在此处填写题号
- \usepackage{mathptmx} % 这是 Times 字体,中规中矩
- %\usepackage{mathpazo} % 这是 COMAP 官方杂志采用的更好看的 Palatino 字体,可替代以上的 mathptmx 宏包
-
- \title{An MCM Paper Made by Team 1234567} % 标题
-
- % 如需要修改题头(默认为 MCM/ICM),请使用以下命令(此处修改为 MCM)
- %\renewcommand{\contest}{MCM}
-
- % 文档开始
- \begin{document}
-
- % 此处填写摘要内容
- \begin{abstract}
- Here is the abstract of your paper.
-
- Firstly, that is ...
-
- Secondly, that is ...
-
- Finally, that is ...
-
- % 美赛论文中无需注明关键字。若您一定要使用,
- % 请将以下两行的注释号 '%' 去除,以使其生效
- % \vspace{5pt}
- % \textbf{Keywords}: MATLAB, mathematics, LaTeX.
-
- \end{abstract}
-
- \maketitle % 生成 Summary Sheet
- %在正文部分,输入\maketitle指令,就会编译前面的标题、作者与日期等信息
- \tableofcontents % 生成目录
-
-
- % 正文开始
- \section{Introduction}
- \subsection{Problem Background}
- Here is the problem background ...
-
- Two major problems are discussed in this paper, which are:
- \begin{itemize}%无序枚举
- \item Doing the first thing.
- \item Doing the second thing.
- \end{itemize}
-
- \subsection{Literature Review}
- A literatrue\cite{1} say something about this problem ...
-
- \subsection{Our work}
- We do such things ...
-
- \begin{enumerate}[\bfseries 1.]
- \item We do ...
- \item We do ...
- \item We do ...
- \end{enumerate}
-
- \section{Preparation of the Models}
- \subsection{Assumptions}
-
- %一种表格
- \subsection{Notations}
- The primary notations used in this paper are listed in Table \ref{tb:notation}.
-
- % 三线表示例
- \begin{table}[!htbp]
- \begin{center}
- \caption{Notations}
- \begin{tabular}{cl}%\begin{tabular}是生成表格的基本工具
- \toprule%表格开始的粗线
- \multicolumn{1}{m{3cm}}{\centering Symbol}
- &\multicolumn{1}{m{8cm}}{\centering Definition}\\
- \midrule
- $A$&the first one\\
- $b$&the second one\\
- $\alpha$ &the last one\\
- \bottomrule%表格结束的粗线
- \end{tabular}\label{tb:notation}
- \end{center}
- \end{table}
-
- \section{The Models}
- \subsection{Model 1}
- \subsubsection{Details about Model 1}
- The detail can be described by equation \eqref{eq:heat}:%公式编号引用
-
- \begin{equation}\label{eq:heat}
- \frac{\partial u}{\partial t} - a^2 \left( \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial y^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial z^2} \right) = f(x, y, z, t)
- \end{equation}
-
- \subsection{Model 2}
- \subsubsection{Conclusion of Model 2}
- The results are shown in Figure \ref{fig:result}, where $t$ denotes the time in seconds, and $c$ refers to the concentration of water in the boiler.
-
- \begin{figure}[htbp]
- \centering
- \includegraphics[width=.6\textwidth]{water.png}
- %[width=.6\textwidth]用来确定图片的宽度
- \caption{The result of Model 2}\label{fig:result}
- \end{figure}
-
- \clearpage%另起一页继续写
- \subsubsection{Commetary on Model 2}
- The instance of long and wide tables are shown in Table \ref{tb:longtable}.
-
- % 长表格示例,更多用法请参考 longtable 宏包文档
- % 以下环境及对应参数可实现表格内的自动换行与表格的自动断页
- % 您也可以选择自行载入 tabularx 宏包,并通过 X 参数指定对应列自动换行
- \begin{longtable}{ p{4em} p{14em} p{14em} } %用来调整表格的宽度
- \caption{Basic Information about Three Main Continents (scratched from Wikipedia)}%说明文字
- \label{tb:longtable}\\ %\label可以给一个公式,一个章节,一个图片,一个表格打上标签,然后使用\ref进行引用
- \toprule%表格顶部的粗线。
- Continent & Description & Information \\
- \midrule
- Africa & Africa Continent is surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the
- north, the Isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea to the northeast, the Indian
- Ocean to the southeast and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. &
- At about 30.3 million km$^2$ including adjacent islands, it covers 6\%
- of Earth's total surface area and 20\% of its land area. With 1.3
- billion people as of 2018, it accounts for about 16\% of the world's
- human population. \\
- \midrule %\midrule命令:表格中间的细分隔线
- Asia & Asia is Earth's largest and most populous continent which
- located primarily in the Eastern and Northern Hemispheres.
- It shares the continental landmass of Eurasia with the continent
- of Europe and the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both
- Europe and Africa. &
- Asia covers an area of 44,579,000 square kilometres, about 30\%
- of Earth's total land area and 8.7\% of the Earth's total surface
- area. Its 4.5 billion people (as of June 2019) constitute roughly
- 60\% of the world's population. \\
- \midrule
- Europe & Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern
- Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It comprises the
- westernmost part of Eurasia and is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to
- the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to
- the south, and Asia to the east. &
- Europe covers about 10,180,000 km$^2$, or 2\% of the Earth's surface
- (6.8\% of land area), making it the second smallest
- continent. Europe had a total population of about 741 million (about
- 11\% of the world population) as of 2018. \\
- \bottomrule%表格底部的粗线
- \end{longtable}
-
-
-
-
- % 子图(多图并列)示例,更多用法请参考 subfigure 宏包文档
- % 如果您只希望几张图并列,不需要额外的 caption,那么在 figure 环境中
- % 连续插入总宽度不超过 \textwidth 的多个 \includegraphics 命令即可
- \begin{figure}[!htbp]%图片排版的位置参数
- \centering
-
- \begin{subfigure}[b]{.3\textwidth}
- \includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{water.png}
- \caption{Image on the left}\label{subfig:left}
- \end{subfigure}
-
- \begin{subfigure}[b]{.3\textwidth}
- \includegraphics[width=\textwidth]{water.png}
- \caption{Image on the right}\label{subfig:right}
- \end{subfigure}
-
- \caption{Two images}\label{fig:subfigures}
- \end{figure}
- Figure \ref{fig:subfigures} gives an example of subfigures. Figure \ref{subfig:left} is on the left, and Figure \ref{subfig:right} is on the right.
- %以上部分是插入图片部分
-
-
- \section{Strengths and Weaknesses}
- \subsection{Strengths}
- \begin{itemize}%逐条列记
- \item First one...
- \item Second one ...
- \end{itemize}
-
- \subsection{Weaknesses}
- \begin{itemize}
- \item Only one ...
- \end{itemize}
-
-
-
- % 以下为信件/备忘录部分,不需要可自行去掉
- % 如有需要可将整个 letter 环境移动到文章开头或中间
- % 请在第二个花括号内填写标题,如「信件」(Letter)或「备忘录」(Memorandum)
- \begin{letter}{Memorandum}
- \begin{flushleft} % 左对齐环境,无首行缩进
- \textbf{To:} Heishan Yan\\
- \textbf{From:} Team 1234567\\
- \textbf{Date:} October 1st, 2019\\
- \textbf{Subject:} A better choice than MS Word: \LaTeX
- \end{flushleft}
-
- In the memo, we want to introduce you an alternate typesetting program to the prevailing MS Word: \textbf{\LaTeX}. In fact, the history of \LaTeX\ is even longer than that of MS Word. In 1970s, the famous computer scientist Donald Knuth first came out with a typesetting program, which named \TeX\ \ldots
-
- Firstly, \ldots
-
- Secondly, \ldots
-
- Lastly, \ldots
-
- According to all those mentioned above, it is really worth to have a try on \LaTeX!
- \end{letter}
-
-
- % 参考文献,此处以 MLA 引用格式为例
- \begin{thebibliography}{99}%参考文献的个数最大为99
- \bibitem{1} Einstein, A., Podolsky, B., \& Rosen, N. (1935). Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be considered complete?. \emph{Physical review}, 47(10), 777.
- \bibitem{2} \emph{A simple, easy \LaTeX\ template for MCM/ICM: EasyMCM}. (2018). Retrieved December 1, 2019, from\url{https://www.cnblogs.com/xjtu-blacksmith/p/easymcm.html}
- \end{thebibliography}
-
-
- % 以下为附录内容
- % 如您的论文中不需要附录,请自行删除
- \begin{subappendices} % 附录环境
-
- \section{Appendix A: Further on \LaTeX}
- To clarify the importance of using \LaTeX\ in MCM or ICM, several points need to be covered, which are \ldots
-
- To be more specific, \ldots
-
- All in all, \ldots
-
- Anyway, nobody \textbf{really} needs such appendix \ldots%加粗命令
-
- \section{Appendix B: Program Codes}
- Here are the program codes we used in our research.
-
- % 代码环境示例三则
- % 如您的论文不需要展示代码,请删除
- % 更多用法,请参考 listings 宏包文档
-
- % Python 代码示例
- \begin{lstlisting}[language=Python, name={test.py}]
- # Python code example
- for i in range(10):
- print('Hello, world!')
- \end{lstlisting}
-
- % MATLAB 代码示例
- \begin{lstlisting}[language=MATLAB, name={test.m}]
- % MATLAB code example
- for i = 1:10
- disp("hello, world!");
- end
- \end{lstlisting}
-
- % C++ 代码示例
- \begin{lstlisting}[language=C++, name={test.cpp}]
- // C++ code example
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
-
- int main() {
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- cout << "hello, world" << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- \end{lstlisting}
-
- \end{subappendices} % 附录内容结束
-
- \end{document} % 结束

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Monodyee/article/detail/238423
推荐阅读
相关标签