- 1AI绘画最强修脸插件还能控制表情哦!_ad修脸
- 2【开源鸿蒙】编译OpenHarmony轻量系统QEMU RISC-V版_openharmony qemu
- 3多旋翼无人机仿真 rotors_simulator 是如何悬停的(一)_msgmultidofjointtrajectoryfrompositionyaw
- 4auto cad破解_lockup.lsp
- 5网络层_路由器使用层次跟处理对象
- 6与 AI/ML 一起领导创新,减少技术债务,提高效率_ml系统的技术债都有什么
- 7ELK性能优化实战总结:java的list集合详解_java elk技术分享
- 8基于OpenCV的人脸检测软件(含Python源码+UI界面+图文详解)_人脸分析程序
- 9HTML parser_htmldocumentparser
- 10【Scopus稳定检索】第五届城市工程与管理科学国际会议(ICUEMS 2024)_icuems2024
【数据结构】栈和队列的实现及应用_栈、队列的实际应用
赞
踩

需要云服务器等云产品来学习Linux的同学可以移步/-->腾讯云<--/-->阿里云<--/-->华为云<--/官网,轻量型云服务器低至112元/年,新用户首次下单享超低折扣。
栈和队列是一种数据结构,只规定了性质,并没有规定实现方式。
本文以顺序结构实现栈,链表方式实现队列。
一、栈的概念
栈:是一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在栈顶进行插入和删除元素操作。
栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈\压栈\入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
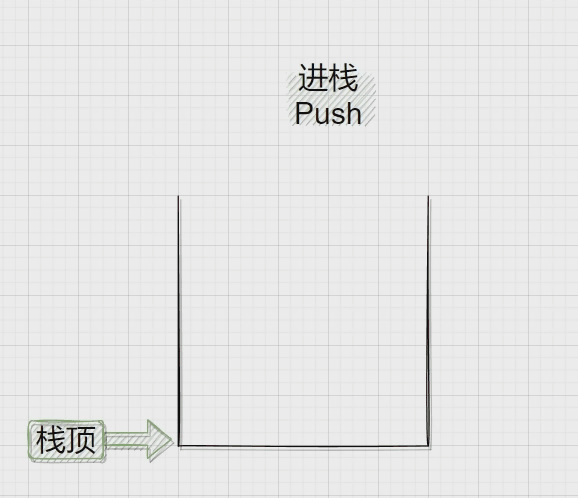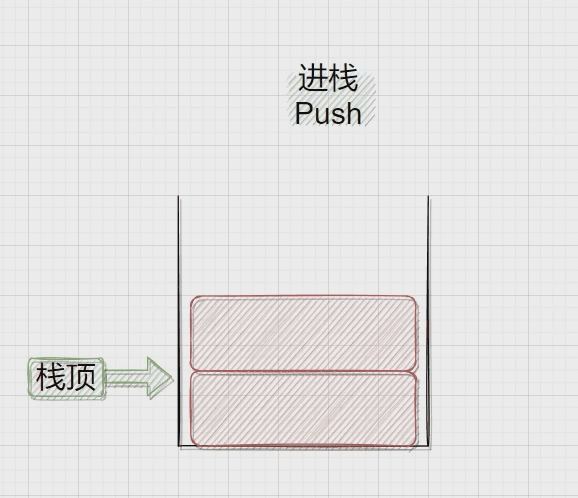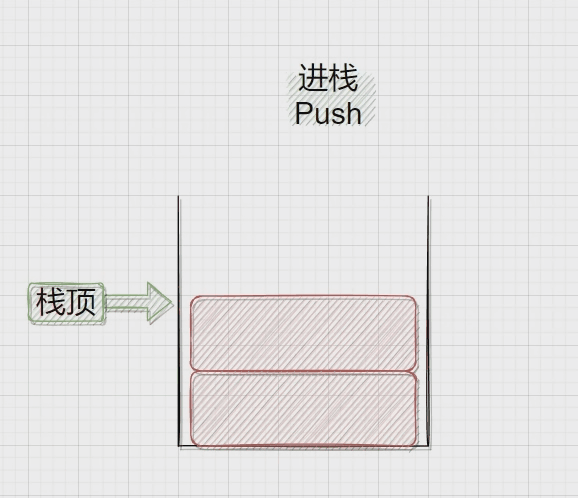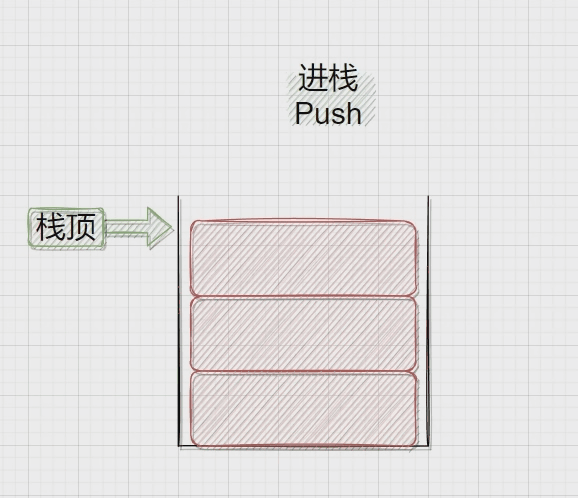
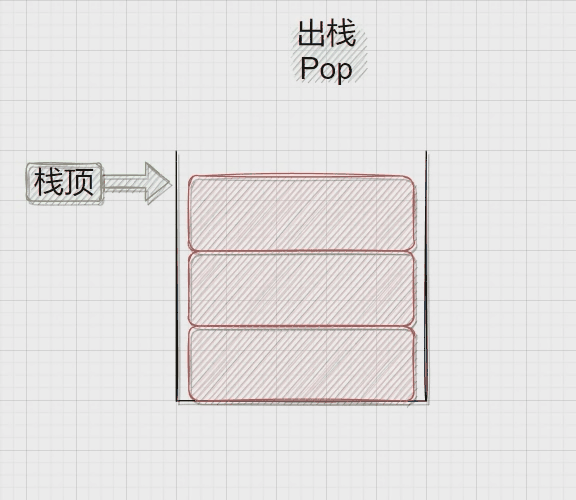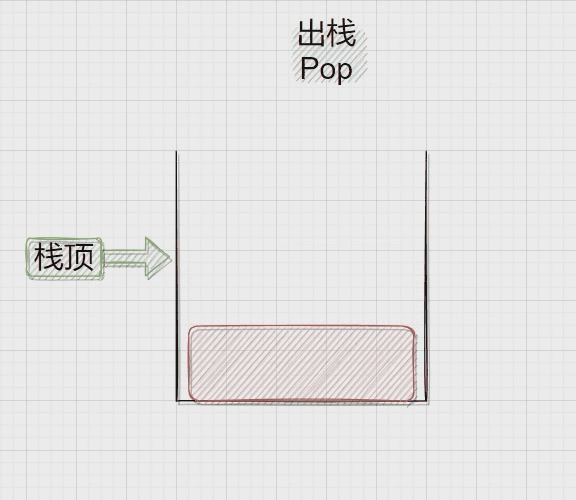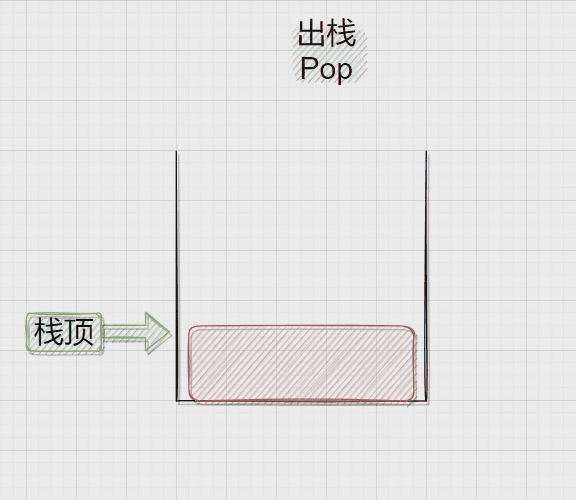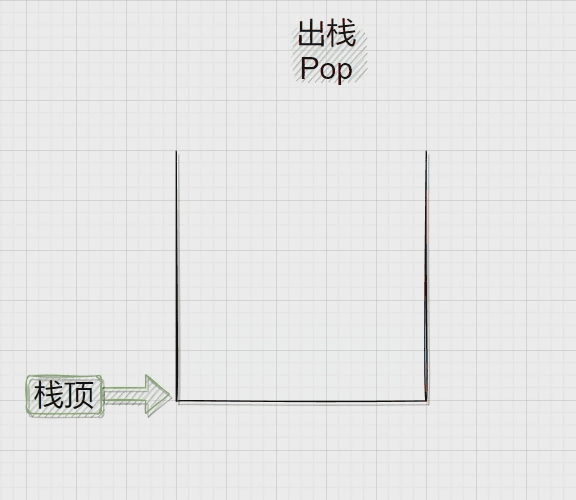
二、Stack.h
- #pragma once
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <stdbool.h>
- typedef int STDataType;
- typedef struct stack
- {
- STDataType* arr;
- int top;//数组元素个数(top-1为最后一个元素的下标)就是顺序表的size
- int capacity;//总容量
- }ST;
- void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps);//销毁
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//压栈
- void StackPop(ST* ps);//出栈
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);//判断栈是不是为空
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);//访问栈顶元素
- int StackSize(ST* ps);//数组元素个数

以顺序结构实现栈,本质上仍是一个顺序表,只是这个顺序表加上了栈先进后出的规则。
数组的头是栈底,数组尾是栈顶。栈主要的压栈、出栈、访问栈顶等接口非常契合顺序表的尾插、尾删、随机访问的特点。
三、Stack.c
1、栈的初始化和销毁
- void StackInit(ST* ps)//初始化
- {
- assert(ps);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
- void StackDestroy(ST* ps)//销毁
- {
- assert(ps);
- free(ps->arr);
- ps->arr = NULL;
- ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
- }
和顺序表的初始化、销毁方式一样
2、栈的进栈、出栈
- void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)//进栈
- {
- assert(ps);
- //判断扩容
- if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
- {
- int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
- STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
- if (tmp == NULL)
- {
- perror("realloc fail:\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- ps->arr = tmp;
- ps->capacity = newCapacity;
- }
- ps->arr[ps->top] = x;
- ps->top++;
- }
- void StackPop(ST* ps)//出栈
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- ps->top--;
- }

进栈需要判断栈的空间,空间不够则需要扩容
出栈时,先判空,再将top--即可
3、栈的判空、访问栈顶元素、栈内元素个数
- bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)//判断栈是不是为空
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top == 0;
- }
- STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)//访问栈顶元素
- {
- assert(ps);
- assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
- return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
- }
- int StackSize(ST* ps)//数组元素个数
- {
- assert(ps);
- return ps->top;
- }

注意访问栈顶元素这个接口,要先判断栈是不是空。
四、队列的概念
队列:一端进行插入数据操作,另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)的特点。
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头

队列参照现实生活中的排队
五、Queue.h
- #pragma once
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <stdbool.h>
- typedef int QDataType;
- typedef struct QueueNode
- {
- struct QueueNode* next;
- QDataType data;
- }QNode;
- typedef struct Queue
- {
- QNode* head;
- QNode* tail;
- int size;//加个size,方便统计长度
- }Queue;
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//初始化
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//销毁
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq,QDataType x);//入队(尾插)
- bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判断队列是否为空
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//出队(头删)
- int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//统计队列长度
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//访问队头数据
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);//访问队尾数据

因为顺序结构不适合头删,这里使用单链表来实现队列。
结构体QNode用于模拟单链表,结构体Queue中存放了单链表的头、尾指针、链表节点个数。使用Queue来操纵单链表。
单链表的头head是队头(头删出数据),tail是队尾(尾插录数据)
六、Queue.c
1、队列的初始化和销毁
- void QueueInit(Queue* pq)//初始化
- {
- assert(pq);
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- pq->size = 0;
- }
- void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)//销毁
- {
- assert(pq);
- QNode* cur = pq->head;
- //逐个销毁释放空间
- while (cur)
- {
- QNode* del = cur;
- cur = cur->next;
- free(del);
- }
- pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
- }

和单链表的销毁方式一样,注意销毁时需要逐个节点销毁。
2、队列的入队、出队
- void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//入队,尾插
- {
- assert(pq);
- //创建一个新节点
- QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
- if (newnode == NULL)
- {
- perror("malloc fail:\n");
- exit(-1);
- }
- newnode->data = x;
- newnode->next = NULL;
- //队列为空时的尾插和不为空的尾插
- if (QueueEmpty(pq))
- pq->head=pq->tail = newnode;
- else
- {
- pq->tail->next = newnode;
- pq->tail = newnode;
- }
- pq->size++;
- }
- void QueuePop(Queue* pq)//出队(头删)
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- QNode* next = pq->head->next;
- free(pq->head);
- pq->head = next;
- pq->size--;
- }

入队:尾插一个节点
出队:头删一个节点
3、队列的判空
- bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)//判断队列是否为空
- {
- assert(pq);
- return pq->head == NULL;
- }
4、访问队头、队尾数据、统计队列长度
- int QueueSize(Queue* pq)//统计队列长度
- {
- assert(pq);
- return pq->size;
- }
- QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//访问队头数据
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- return pq->head->data;
- }
- QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)//访问队尾数据
- {
- assert(pq);
- assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
- return pq->tail->data;
- }

访问接口,注意先判空。
七、力扣中栈和队列OJ题
1、有效的括号

使用队列来解决,创建一个栈,碰到左括号将其进栈,碰到右括号则访问栈顶元素,不相符则为false,迭代比较相符则为true
- bool isValid(char * s){
- ST st;
- StackInit(&st);
- while(*s)
- {
- if(*s=='('||*s=='{'||*s=='[')
- {
- StackPush(&st,*s);//压栈
- }
- else//比较时的情况
- {
- if(StackEmpty(&st))
- return false;
- else if(StackTop(&st)=='('&&*s!=')')//访问栈顶元素
- {
- return false;
- }
- else if(StackTop(&st)=='{'&&*s!='}')
- {
- return false;
- }
- else if(StackTop(&st)=='['&&*s!=']')
- {
- return false;
- }
- StackPop(&st);
- }
- ++s;
- }
- if(!StackEmpty(&st))
- return false;
- StackDestroy(&st);
- return true;
- }

注:上述代码还需要将栈的实现的代码拷贝一份上去。
2、用队列实现栈

入栈:选择非空队列进行入栈
出栈:队列中只留一个元素,将其他元素Pop至另一个队列,再对那个遗留的元素执行出队列操作即可模拟出栈动作
- typedef struct {
- Queue q1;
- Queue q2;
- } MyStack;
- MyStack* myStackCreate() {
- MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
- QueueInit(&obj->q1);
- QueueInit(&obj->q2);
- return obj;
- }
-
- void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);//入队,尾插
- }
- else
- {
- QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);//入队,尾插
- }
- }
-
- int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
- Queue* empty=&obj->q1;
- Queue* unEmpty=&obj->q2;
- if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
- {
- empty=&obj->q2;
- unEmpty=&obj->q1;
- }
- while(QueueSize(unEmpty)>1)//将非空元素导入到空队列,留下最后一个
- {
- QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(unEmpty));//入队,尾插
- QueuePop(unEmpty);//出队(头删)
- }
- int top=QueueFront(unEmpty);
- QueuePop(unEmpty);//出队(头删)
- return top;
- }
-
- int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
- if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q1);//访问队尾数据
- }
- else
- {
- return QueueBack(&obj->q2);//访问队尾数据
- }
- }
-
- bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
- return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
- }
-
- void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
- QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);//销毁
- QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);//销毁
- free(obj);
- }

注:上述代码还需要将队列的实现的代码拷贝一份上去。
3、用栈实现队列

现在有两个栈,第一个栈用于入栈、出栈至第二个栈的操作,第二个栈仅用于出栈操作。
入栈:在第一个栈中压入数据
出栈:如果第二个栈为空,则第一个栈中 数据全部出栈至第二个栈,由第二个栈专门执行出栈操作。等第二个栈再次为空,再次执行上述动作
- MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
- MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
- StackInit(&obj->st1);
- StackInit(&obj->st2);
- return obj;
- }
-
- void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
- StackPush(&obj->st1, x);//压栈
- }
-
- int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
- if(StackEmpty(&obj->st2))
- {
- while(!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
- {
- StackPush(&obj->st2, StackTop(&obj->st1));//压栈
- StackPop(&obj->st1);
- }
- }
- int val=StackTop(&obj->st2);
- StackPop(&obj->st2);
- return val;
- }
-
- int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
- if(StackEmpty(&obj->st2))
- {
- while(!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
- {
- StackPush(&obj->st2, StackTop(&obj->st1));//压栈
- StackPop(&obj->st1);
- }
- }
- return StackTop(&obj->st2);
- }
-
- bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
- return StackEmpty(&obj->st1)&&StackEmpty(&obj->st2);
- }
-
- void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
- StackDestroy(&obj->st1);
- StackDestroy(&obj->st2);
- free(obj);
- }

注:上述代码还需要将栈的实现的代码拷贝一份上去。
4、设计循环队列

- typedef struct {
- int* arr;
- int front;//记录首
- int tail;//记录尾的下一个
- int capacity;//用于处理边界问题的一个变量
- } MyCircularQueue;
- MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
- MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
- obj->arr=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
- obj->front=obj->tail=0;
- obj->capacity=k+1;//这里一定要写成k+1,写成k的话,后续处理边界问题要额外考虑分支情况
- return obj;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- return obj->front==obj->tail;
- }
-
- bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->capacity)==obj->front;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
- return false;
- obj->arr[obj->tail]=value;
- obj->tail++;
- obj->tail%=obj->capacity;
- return true;
- }
-
- bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return false;
- obj->front++;
- obj->front%=obj->capacity;
- return true;
- }
-
- int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- return obj->arr[obj->front];
- }
-
- int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- return obj->arr[(obj->tail-1+obj->capacity)%obj->capacity];
- }
- void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- free(obj->arr);
- obj->arr=NULL;
- free(obj);
- }

因为循环队列无法区分队列为空和为满的情况,因为为空和未满,首位下标是一样的。
所以这道题有两种解法,计数确定栈空栈满,或者多开辟一个空间。本题采用后者。
可选的数据结构也有两种,顺序和链表。本题采用顺序。
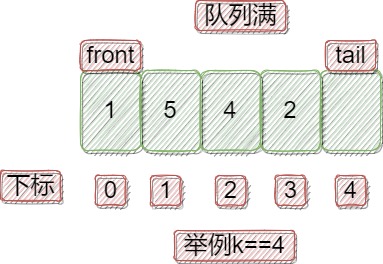
上表为队列满的情况,无法再执行插入。运用顺序表,本题的难点在于如何处理tail和front在数组尾部的情况。
强烈建议在初始化的接口中将capacity定义为k+1,因为入队出队接口中%capacity后,可以同时满足正常和极端位置下的情况。(详见代码,一读就懂,后续读者可以逝一下将capacity定义为k,感受下区别)
capacity定义为k时的代码如下:
- typedef struct {
- int* arr;
- int front;//记录首
- int tail;//记录尾的下一个
- int capacity;//总容量
- } MyCircularQueue;
-
-
- MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
- MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
- obj->arr=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
- obj->front=obj->tail=0;
- obj->capacity=k;
- return obj;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- return obj->front==obj->tail;
- }
-
- bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->capacity+1)==obj->front;
- }
- bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
- return false;
- obj->arr[obj->tail]=value;
- obj->tail++;
- if(obj->tail>obj->capacity)
- obj->tail=obj->tail%obj->capacity-1;
- return true;
- }
-
- bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return false;
- obj->front++;
- if(obj->front>obj->capacity)
- obj->front=obj->front%obj->capacity-1;
- return true;
- }
-
- int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- return obj->arr[obj->front];
- }
-
- int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
- return -1;
- if(obj->tail!=0)
- return obj->arr[(obj->tail-1+obj->capacity)%obj->capacity];
- return obj->arr[obj->capacity];
- }
- void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
- free(obj->arr);
- obj->arr=NULL;
- free(obj);
- }

主要区别就是入队出队代码,常规情况和边界情况不能统一。


