- 1[vscode] vscode中配置GIT_{"code":"y1vskl"}
- 2Clickhouse集群化(二)单节点部署
- 3【深度学习】OCR的图像处理方式,如何提升OCR效果
- 4学习笔记(一)----CLIP_clip 知乎
- 5CSS 结构伪类选择器 伪元素选择器 盒子模型_伪结构选择器
- 6ESP32作为从机实现BLE蓝牙功能浅析_esp32 ble
- 7IDEA中pom文件变成蜘蛛如何解决_add as ant build file
- 8大数据系列——Kafka理论_大数据采集kafka的关系
- 9tsconfig.json 详解与常用配置(笔记)
- 10FFmpeg —— 硬解码视频并渲染多路网络及本地视频(附源码)
C++ —— unordered_set、unordered_map的介绍及使用_c++中unorderedset的用法
赞
踩
目录
unordered系列关联式容器
在C++98中,STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时的效率可达到O ( l o g N ) O(logN)O(logN),即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的结点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11中,STL又提供了4个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同。
unordered_set的介绍
1.unordered_set是不按特定顺序存储键值的关联式容器,其允许通过键值快速的索引到对应的元素。
2.在unordered_set中,元素的值同时也是唯一地标识它的key。
在内部,unordered_set中的元素没有按照任何特定的顺序排序,为了能在常数范围内找到指定的3.key,unordered_set将相同哈希值的键值放在相同的桶中。
4.unordered_set容器通过key访问单个元素要比set快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器。
unordered_set的使用
unordered_set的定义方式
方式一: 构造一个某类型的空容器。
unordered_set<int> us1; //构造int类型的空容器
方式二: 拷贝构造某同类型容器的复制品。
unordered_set<int> us2(us1); //拷贝构造同类型容器us1的复制品
方式三: 使用迭代器拷贝构造某一段内容。
- string str("abcedf");
- unordered_set<char> us3(str.begin(), str.end()); //构造string对象某段区间的复制品
定义unordered_set的一般方式如下:
- #include <unordered_set>
- #include <iostream>
-
- int main() {
- // 定义一个存储int类型元素的unordered_set
- std::unordered_set<int> mySet;
-
- // 插入元素
- mySet.insert(1);
- mySet.insert(2);
- mySet.insert(3);
-
- // 打印元素
- for (const auto& elem : mySet) {
- std::cout << elem << " ";
- }
-
- return 0;
- }

unordered_set接口的使用
unordered_set当中常用的成员函数如下:

unordered_set当中迭代器相关函数如下:
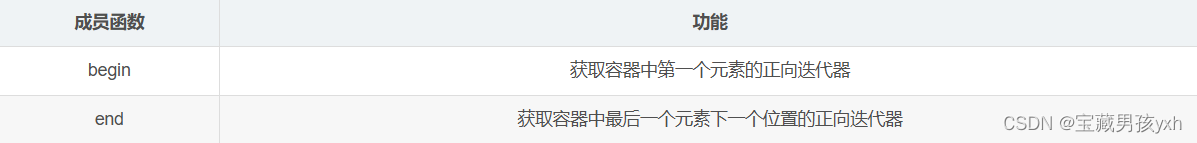
使用示例:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <unordered_set>
-
- using namespace std;
-
- int main() {
- unordered_set<int> us;
-
- // 插入元素(自动去重)
- us.insert(1);
- us.insert(4);
- us.insert(3);
- us.insert(3); // 重复元素,不会插入
- us.insert(2);
- us.insert(2); // 重复元素,不会插入
- us.insert(3); // 重复元素,不会插入
-
- // 遍历容器方式一(范围for)
- for (auto e : us) {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; // 1 4 3 2(元素顺序可能会不同,因为是无序的)
-
- // 删除元素方式一
- us.erase(3); // 删除值为3的元素
-
- // 删除元素方式二
- unordered_set<int>::iterator pos = us.find(1); // 查找值为1的元素
- if (pos != us.end()) {
- us.erase(pos); // 删除找到的元素
- }
-
- // 遍历容器方式二(迭代器遍历)
- unordered_set<int>::iterator it = us.begin();
- while (it != us.end()) {
- cout << *it << " ";
- it++;
- }
- cout << endl; // 4 2(元素顺序可能会不同,因为是无序的)
-
- // 容器中值为2的元素个数
- cout << us.count(2) << endl; // 1
-
- // 容器大小
- cout << us.size() << endl; // 2
-
- // 清空容器
- us.clear();
-
- // 容器判空
- cout << us.empty() << endl; // 1(true)
-
- // 交换两个容器的数据
- unordered_set<int> tmp{11, 22, 33, 44};
- us.swap(tmp);
- for (auto e : us) {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; // 11 22 33 44(元素顺序可能会不同,因为是无序的)
-
- return 0;
- }

unordered_multiset
unordered_multiset容器与unordered_set容器的底层数据结构是一样的,都是哈希表,其次,它们所提供的成员函数的接口都是基本一致的,这里就不再列举了,这两种容器唯一的区别就是,unordered_multiset容器允许键值冗余,即unordered_multiset容器当中存储的元素是可以重复的。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <unordered_set>
- using namespace std;
-
- int main()
- {
- unordered_multiset<int> ums;
- //插入元素(允许重复)
- ums.insert(1);
- ums.insert(4);
- ums.insert(3);
- ums.insert(3);
- ums.insert(2);
- ums.insert(2);
- ums.insert(3);
- for (auto e : ums)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //1 4 3 3 3 2 2
- return 0;
- }

由于unordered_multiset容器允许键值冗余,因此该容器中成员函数find和count的意义与unordered_set容器中的也有所不同:
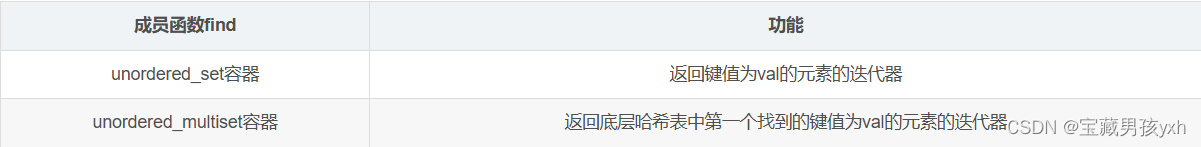
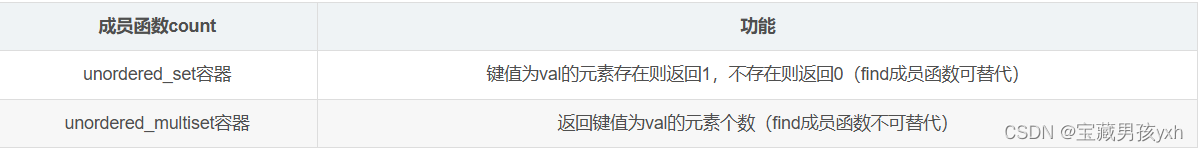
unordered_map的介绍
1.unordered_map是存储<key, value>键值对的关联式容器,其允许通过key值快速的索引到与其对应是value。
2.在unordered_map中,键值通常用于唯一地标识元素,而映射值是一个对象,其内容与此键关联。键和映射值的类型可能不同。
3.在内部,unordered_map没有对<key, value>按照任何特定的顺序排序,为了能在常数范围内找到key所对应的value,unordered_map将相同哈希值的键值对放在相同的桶中。
4.unordered_map容器通过key访问单个元素要比map快,但它通常在遍历元素子集的范围迭代方面效率较低。
5.unordered_map实现了直接访问操作符(operator[ ]),它允许使用key作为参数直接访问value。
6.它的迭代器至少是前向迭代器。
unordered_map的使用
unordered_map的定义方式
方式一: 指定key和value的类型构造一个空容器。
unordered_map<int, double> um1; //构造一个key为int类型,value为double类型的空容器
方式二: 拷贝构造某同类型容器的复制品。
unordered_map<int, double> um2(um1); //拷贝构造同类型容器um1的复制品
方式三: 使用迭代器拷贝构造某一段内容。
unordered_map<int, double> um3(um2.begin(), um2.end()); //使用迭代器拷贝构造um2容器某段区间的复制品
示例如下
- #include <unordered_map>
- #include <iostream>
-
- int main() {
- // 定义一个键为string类型,值为int类型的unordered_map
- std::unordered_map<std::string, int> myMap;
-
- // 插入键值对
- myMap["one"] = 1;
- myMap["two"] = 2;
- myMap["three"] = 3;
-
- // 打印键值对
- for (const auto& pair : myMap) {
- std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;
- }
-
- return 0;
- }

unordered_map接口的使用
unordered_map当中常用的成员函数如下:
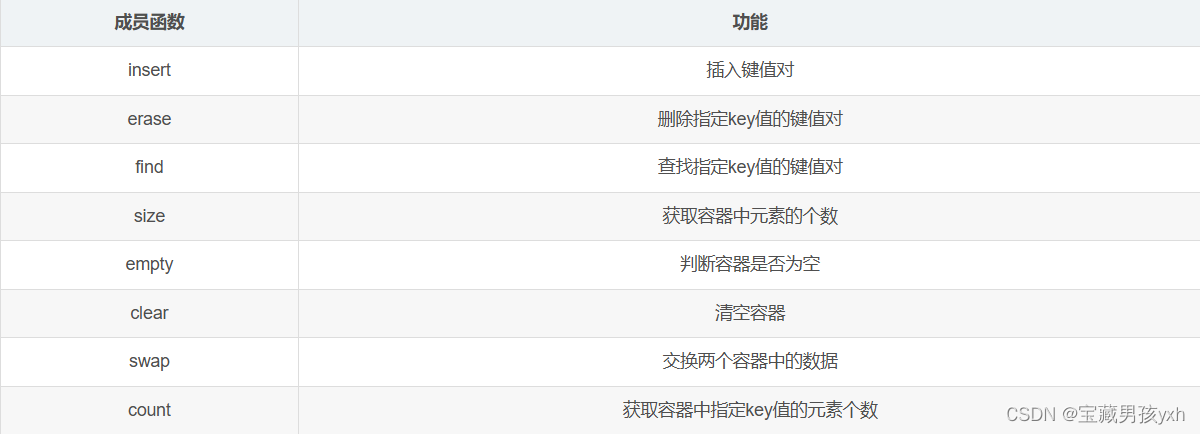
除了上述的成员函数之外,unordered_map容器当中还实现了[ ]运算符重载函数,该重载函数的功能非常强大:[key]
1.若当前容器中已有键值为key的键值对,则返回该键值对value的引用。
2.若当前容器中没有键值为key的键值对,则先插入键值对<key, value()>,然后再返回该键值对中value的引用。
unordered_map当中迭代器相关函数如下:
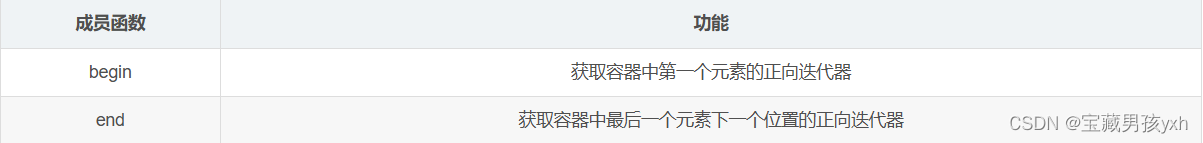
示例如下:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <unordered_map>
- using namespace std;
-
- int main()
- {
- unordered_map<int, string> um;
- //插入键值对方式一:构造匿名对象插入
- um.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "one"));
- um.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "two"));
- um.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "three"));
- //遍历方式一:范围for
- for (auto e : um)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //1->one 2->two 3->three
- //插入键值对方式二:调用make_pair函数模板插入
- um.insert(make_pair(4, "four"));
- um.insert(make_pair(5, "five"));
- um.insert(make_pair(6, "six"));
- //遍历方式二:迭代器遍历
- unordered_map<int, string>::iterator it = um.begin();
- while (it != um.end())
- {
- cout << it->first << "->" << it->second << " ";
- it++;
- }
- cout << endl; //1->one 2->two 3->three 4->four 5->five 6->six
- //插入键值对方式三:利用[]运算符重载函数进行插入(常用)
- um[7] = "seven";
- um[8] = "eight";
- um[9] = "nine";
- for (auto e : um)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //9->nine 1->one 2->two 3->three 4->four 5->five 6->six 7->seven 8->eight
- //删除键值对方式一:根据key值删除
- um.erase(5);
- //删除键值对方式二:根据迭代器删除
- unordered_map<int, string>::iterator pos = um.find(7); //查找键值为7的键值对
- if (pos != um.end())
- {
- um.erase(pos);
- }
- for (auto e : um)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //9->nine 1->one 2->two 3->three 4->four 6->six 8->eight
- //修改键值对方式一:通过find获得迭代器,通过迭代器修改
- pos = um.find(1);
- if (pos != um.end())
- {
- pos->second = "one/first";
- }
- //修改键值对方式二:利用[]运算符重载函数进行修改(常用)
- um[2] = "two/second";
- for (auto e : um)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //9->nine 1->one/first 2->two/second 3->three 4->four 6->six 8->eight
- //容器中key值为3的键值对的个数
- cout << um.count(3) << endl;
- //容器的大小
- cout << um.size() << endl;
- //清空容器
- um.clear();
- //容器判空
- cout << um.empty() << endl;
- //交换两个容器的数据
- unordered_map<int, string> tmp{ { 2021, "before" }, { 2022, "now" } };
- um.swap(tmp);
- for (auto e : um)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //2021->before 2022->now
- return 0;
- }

unordered_multimap
unordered_multimap容器与unordered_map容器的底层数据结构是一样的,都是哈希表,其次,它们所提供的成员函数的接口都是基本一致的,这里就不再列举了,这两种容器唯一的区别就是,unordered_multimap容器允许键值冗余,即unordered_multimap容器当中存储的键值对的key值是可以重复的。
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <unordered_map>
- using namespace std;
-
- int main()
- {
- unordered_multimap<int, string> umm;
- //插入键值对(允许键值重复)
- umm.insert(make_pair(2022, "吃饭"));
- umm.insert(make_pair(2022, "睡觉"));
- umm.insert(make_pair(2022, "敲代码"));
- for (auto e : umm)
- {
- cout << e.first << "->" << e.second << " ";
- }
- cout << endl; //2022->吃饭 2022->睡觉 2022->敲代码
- return 0;
- }

由于unordered_multimap容器允许键值对的键值冗余,因此该容器中成员函数find和count的意义与unordered_map容器中的也有所不同:
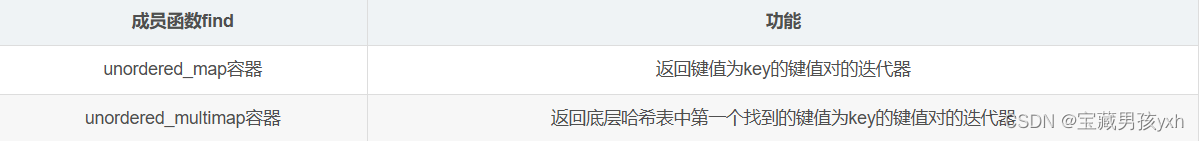

其次,由于unordered_multimap容器允许键值对的键值冗余,调用[ ]运算符重载函数时,应该返回键值为key的哪一个键值对的value的引用存在歧义,因此在unordered_multimap容器当中没有实现[ ]运算符重载函数。



