- 1java第十版第九章答案_Java语言程序设计(基础篇)原书第十一版 梁勇 第9章 课后题答案...
- 2OpenAI“杀疯了”,GPT–4o模型保姆级使用教程!一遍就会!_gpt4o使用教程
- 3从Products表中检索所有的产品名称以及对应的销售总数
- 4带你全面了解 RAG,深入探讨其核心范式、关键技术及未来趋势_rag技术
- 5基于 Hive 数据仓库的教育大数据分析平台(伪分布式)_hive大数据教育平台
- 6数据库系统概论原理及应用期末专升本考研试题三套供参考_t0 read (a) a=10 t1 a=a*a
- 7堆排序(最小堆)_最小堆排序
- 8word2vec在PyTorch中的实现_pytorch的word2vec模型
- 9【LeetCode力扣】287.寻找重复数(中等)_力扣287题
- 10小红书接口加密参数X-sign
android串口通信——android-serialport-api
赞
踩
一.串口通信原理
串口通信(Serial Communications)的概念非常简单,串口按位(bit)发送和接收字节。尽管比按字节(byte)的并行通信慢,但是串口可以在使用一根线发送数据的同时用另一根线接收数据。它很简单并且能够实现远距离通信。
波特率:这是一个衡量符号传输速率的参数。
二、android-serialport-api
主要介绍一下内容:
1.android-serialport-api简单介绍
2.硬件地址和波特率的获取
3.发送和数据和接收数据
1.android-serialport-api简单介绍
android-serialport-api下有两个主要的类
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SerialPort | 获取串口的类(其实就是获取输入输出流) |
| SerialPortFinder | 获取硬件地址的类 |
1.1 SerialPort的介绍
1.1.1调用的顺序如下:
SerialPort构造方法 –> jni open –>c open
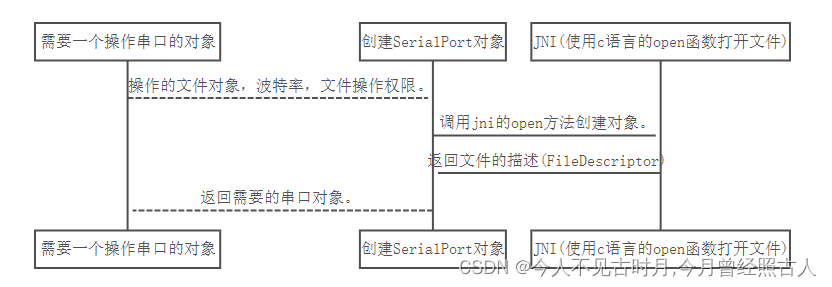
需要一个操作串口的对象
创建SerialPort对象
JNI(使用c语言的open函数打开文件)
操作的文件对象,波特率,文件操作权限。
调用jni的open方法创建对象。
返回文件的描述(FileDescriptor)
返回需要的串口对象。
1.1.2 SerialPort的构造函数
public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int flags)
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| device | 要操作的文件对象 |
| baudrate | 波特率 |
| flags | 文件操作的标志 |
1.1.3 C语言中的open函数
c语言中open函数是用来打开一个文件的。具体可以看这里C语言open()函数:打开文件函数
int open(const char * pathname, int flags);
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pathname | pathname 指向欲打开的文件路径字符串 |
| flags | 文件的打开打开方式: O_RDONLY 以只读方式打开文件O_WRONLY 以只写方式打开文件O_RDWR 以可读写方式打开文件 |
返回值:若所有欲核查的权限都通过了检查则返回0 值, 表示成功, 只要有一个权限被禁止则返回-1.
SerialPort类
- package android_serialport_api;
-
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileDescriptor;
- import java.io.FileInputStream;
- import java.io.FileOutputStream;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.InputStream;
- import java.io.OutputStream;
-
- import android.util.Log;
- /**
- 1. 串口类
- 2. @author qiwenming
- 3. */
- public class SerialPort {
-
- private static final String TAG = "SerialPort";
-
- /*
- * Do not remove or rename the field mFd: it is used by native method close();
- */
- private FileDescriptor mFd;//文件描述
- private FileInputStream mFileInputStream;
- private FileOutputStream mFileOutputStream;
-
- /**
- *获得一个窗口
- * @param device 设备
- * @param baudrate 波特率
- * @param flags 标志
- * @throws SecurityException
- * @throws IOException
- */
- public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int flags) throws SecurityException, IOException {
-
- /* Check access permission */ //检查权限
- if (!device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
- try {
- //如果丢失权限,就再获取权限
- /* Missing read/write permission, trying to chmod the file */
- Process su;
- su = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("/system/bin/su");
- String cmd = "chmod 666 " + device.getAbsolutePath() + "\n" + "exit\n";
- //写命令
- su.getOutputStream().write(cmd.getBytes());
- if ((su.waitFor() != 0) || !device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
- throw new SecurityException();
- }
- } catch (Exception e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- throw new SecurityException();
- }
- }
- //打开设备,这里面调用jni 的open方法
- mFd = open(device.getAbsolutePath(), baudrate, flags);
- if (mFd == null) {
- Log.e(TAG, "native open returns null");
- throw new IOException();
- }
- mFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(mFd);
- mFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(mFd);
- }
-
- // Getters and setters
- public FileInputStream getInputStream() {
- return mFileInputStream;
- }
-
- public FileOutputStream getOutputStream() {
- return mFileOutputStream;
- }
-
- //============== JNI=========================================
- /**
- * 打开串口设备的方法
- * @param path 设备的绝对路径
- * @param baudrate 波特率
- * @param flags 标志
- * @return
- */
- private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudrate, int flags);
- //关闭设备
- public native void close();
- //加载库文件
- static {
- System.loadLibrary("serial_port");
- }
- }

SerialPort.c 中open函数
- /*
- * Class: android_serialport_SerialPort
- * Method: open
- * Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;II)Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;
- */
- JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL Java_android_1serialport_1api_SerialPort_open
- (JNIEnv *env, jclass thiz, jstring path, jint baudrate, jint flags)
- {
- //变量定义,参数检查
- ......
-
-
- /* Opening device */
- //打开设备
- {
- jboolean iscopy;
- const char *path_utf = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, path, &iscopy);
- LOGD("Opening serial port %s with flags 0x%x", path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
- //使用c语言的open函数打开文件
- fd = open(path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
- LOGD("open() fd = %d", fd);
- (*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, path, path_utf);
- if (fd == -1)
- {
- /* Throw an exception */
- LOGE("Cannot open port");
- /* TODO: throw an exception */
- return NULL;
- }
- }
-
- //设备的一些设置
- ......
-
- /* Create a corresponding file descriptor */
- //创建我们需要的 file descriptor
- {
- jclass cFileDescriptor = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/io/FileDescriptor");
- jmethodID iFileDescriptor = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, cFileDescriptor, "<init>", "()V");
- jfieldID descriptorID = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, cFileDescriptor, "descriptor", "I");
- mFileDescriptor = (*env)->NewObject(env, cFileDescriptor, iFileDescriptor);
- (*env)->SetIntField(env, mFileDescriptor, descriptorID, (jint)fd);
- }
-
- return mFileDescriptor;
- }

2.发送和数据和接收数据
2.1数据的发送
数据的发送很简单,通过SerialPort对象的getOutputStream()方法获取到输出流,然后把数据写入到这个流中就行了。
- .....
- mOutputStream = mSerialPort.getOutputStream();
-
- // 把字符指令转为字节
- byte[] text = StringUtils.hexStringToBytes(sendData.commandStr);
- try {
- mOutputStream.write(text);
- mOutputStream.flush();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
2.2 数据的接收
数据的接收,通过SerialPort对象的getInputStream()方法获取到输入流,然后读流的就行了。不过一般会开一个线程去读数据
- ......
- try {
- mSerialPort = mApplication.getSerialPort();
- mOutputStream = mSerialPort.getOutputStream();
- mInputStream = mSerialPort.getInputStream();
-
- /* Create a receiving thread */
- mReadThread = new ReadThread();
- mReadThread.start();
- } catch (SecurityException e) {
- DisplayError(R.string.error_security);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- DisplayError(R.string.error_unknown);
- } catch (InvalidParameterException e) {
- DisplayError(R.string.error_configuration);
- }
- ....
- /**
- *读取流中的数据
- */
- private class ReadThread extends Thread {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- super.run();
- while(!isInterrupted()) {
- int size;
- try {
- byte[] buffer = new byte[64];
- if (mInputStream == null) return;
- size = mInputStream.read(buffer);
- if (size > 0) {
- onDataReceived(buffer, size);
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- }

具体的话可以看项目中的SerialPortActivity这个类,但是这个只是一个例子而已,真正在使用中,我们要根据自己的要求来修改,后面的blog中会介绍。
3.硬件地址和波特率的获取
我们都知道要操作一个串口设备,我们需要知道它的地址和波特率。其中波特率的话是一般根据硬件的说明来设定的,所以这个的话,我们只需要看说明就行了,当然在选择的波特率的时候,我们可以提供一些值来做选择。
3.1 波特率
我们可以创建一个集合来存储波特率,用到的时候来选择就行。
- /**
- * @author qiwenming
- * @creation 2015-6-18 下午4:10:00
- * @instruction 波特率的集合
- */
- public class BaudRateListConstants {
-
- private static List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
- public static List<Integer> getBaudRateList(){
- if(list.size()<=0){
- list.add(50);
- list.add(75);
- list.add(110);
- list.add(134);
- list.add(150);
- list.add(200);
- list.add(300);
- list.add(600);
- list.add(1200);
- list.add(1800);
- list.add(2400);
- list.add(4800);
- list.add(9600);
- list.add(38400);
- list.add(57600);
- list.add(115200);
- list.add(230400);
- list.add(460800);
- list.add(500000);
- list.add(576000);
- list.add(921600);
- list.add(1000000);
- list.add(1152000);
- list.add(1500000);
- list.add(2000000);
- list.add(2500000);
- list.add(3000000);
- list.add(3500000);
- list.add(4000000);
- }
- return list;
- }
- }

3.2 硬件地址的获取
其实硬件地址,也是一个集合来存储着,用得使用,指定硬件地址。我们说andorid-serialport-api中主要的java文件有两个,其中SerialPort我们已经说了,剩下的SerialPortFinder就是获取硬件地址的类。
获取硬件地址的基本步骤:
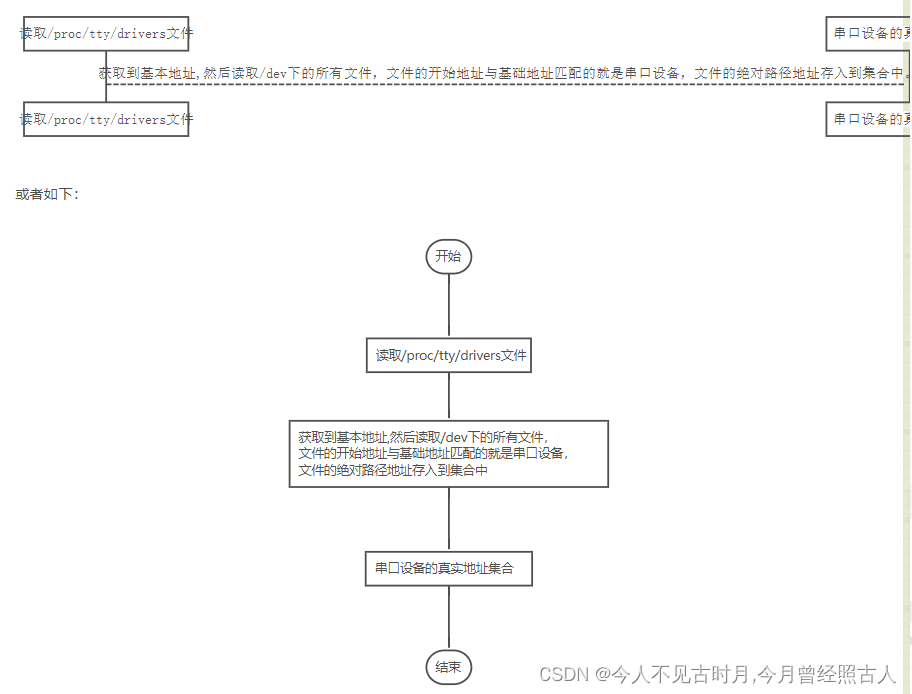
读取/proc/tty/drivers文件
获取到基本地址,然后读取/dev下的所有文件,文件的开始地址与基础地址匹配的就是串口设备,文件的绝对路径地址存入到集合中。
串口设备的真实地址集合
或者如下:
开始
读取/proc/tty/drivers文件
获取到基本地址,然后读取/dev下的所有文件, 文件的开始地址与基础地址匹配的就是串口设备, 文件的绝对路径地址存入到集合中
串口设备的真实地址集合
结束
3.2.1读取 /proc/tty/drivers 文件中的内容
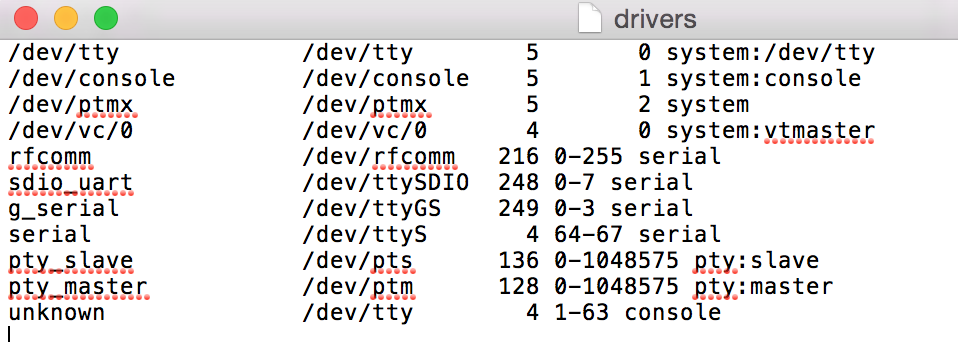
读取 /proc/tty/drivers 文件中的内容,判断哪些是串口设备的基础地址(通过serail这个关键字来判断)。我们可以看到drivers的文件内容如下(外设不同,文件内容不同)
流程图如下: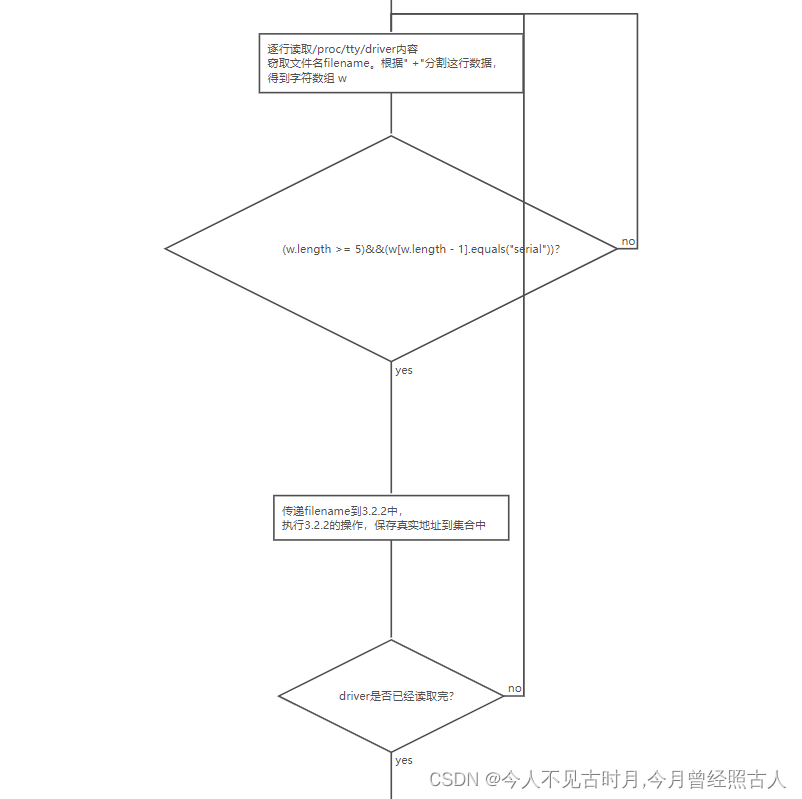
1.在读取文件的内容的时候,是一行一行的读取的。(如下面的那条数据)
2.读取到一行数据的时候,窃取第一串字符为文件名。(如下面的那条数据,文件名为:serial)
3.按照” +”(一个或者多个空格)分割一行数据。(如下面的数据分割后的结果是: w[0]=”serial”,w[1]=”/dev/ttyS”,w[2]=”4”,w[3]=”64-67”,w[4]=”serial”)
4.判断上面分割的字符数组的长度是否大于等于5,并且最后一个字符串是不是”serial”,满足条件传递filename到3.2.2中执行 3.2.2 。不满足读取下一行,直到读取完成。
serial /dev/ttyS 4 64-67 serial
3.2.2通过获取到基础地址,去查找真正的串口设备地址。把地址集合存起来。
流程图如下:
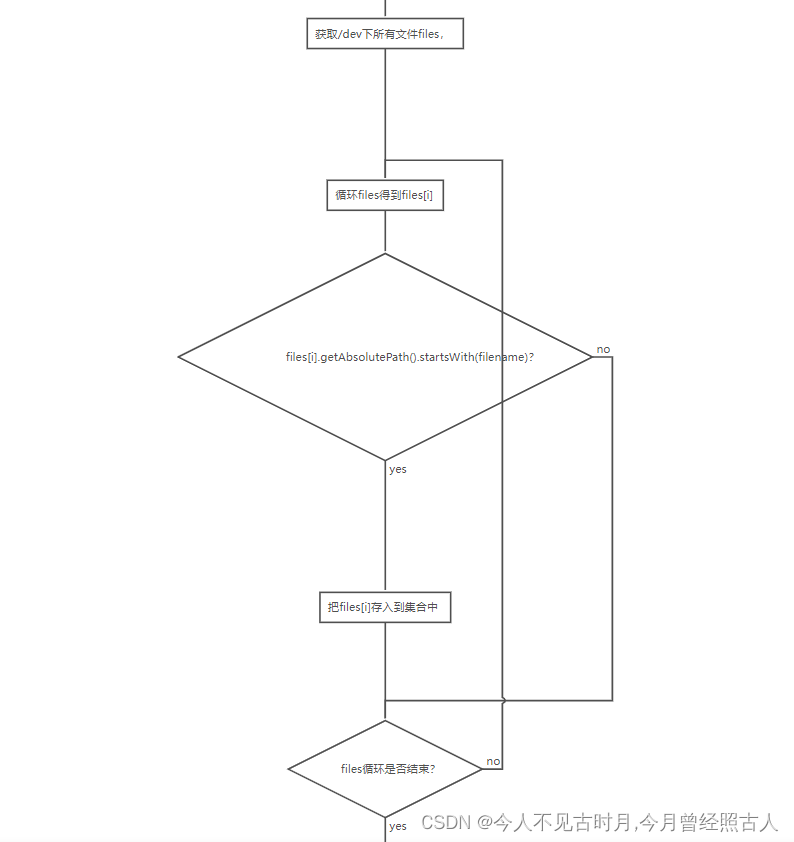
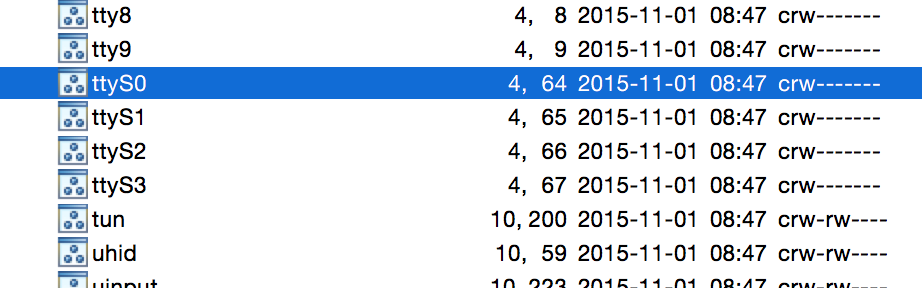
下面是/dev 目录的切图(部分)
1.获取/dev下的所有文件,得到一个文件数组files。
2.循环files,等到files[i]。
3.获取files[i]的绝度路径,判断这个绝对路径是不是以3.2.1中传递过来的基础地址filename开头。(例如:我们传递过来的是基础地址是:/dev/ttyS,那么我们这里满足条件的就是:/dev/ttyS0,/dev/ttyS1,/dev/ttyS2,/dev/ttyS3,这四个设备就是串口设备)
4.满足3说明是串口设备,保存到集合中,不满足执行5。
5.判读是否已经循环结束。结束返回集合,没有结束执行2。
SerialPortFinder
- /*
- * Copyright 2009 Cedric Priscal
- *
- * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
- * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
- * You may obtain a copy of the License at
- *
- * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
- *
- * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
- * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
- * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
- * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
- * limitations under the License.
- */
-
- package android_serialport_api;
-
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.io.LineNumberReader;
- import java.util.Iterator;
- import java.util.Vector;
-
- import android.util.Log;
-
- /**
- * 串口通讯的 寻检器
- *
- * @author qiwenming
- *
- */
- public class SerialPortFinder {
-
- /**
- * 设备类
- *
- * @author qiwenming
- */
- public class Driver {
- public Driver(String name, String root) {
- mDriverName = name;
- mDeviceRoot = root;
- }
-
- private String mDriverName;//设备名称
- private String mDeviceRoot;//设备根节点
- Vector<File> mDevices = null;//设备集合
-
- /**
- * 获取设备集合 这个是特定类型的设备 比如USB等
- * @return
- */
- public Vector<File> getDevices() {
- //如果设备已经添加过,就不添加了,否则就必须添加
- if (mDevices == null) {//如果
- mDevices = new Vector<File>();
- File dev = new File("/dev");
- //获取 /dev 下的设备
- File[] files = dev.listFiles();
- int i;
- for (i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
- //这里是拿文件的路径和我们 传递进来的路径进行对比,看看开头是不是我们传递捡来的 ,传递进来的函数是 外部类 getDrivers()
- //比如 我们传递进来的文件路径是: /dev/ttyUSB 那么我们获取道的文件的绝对路径 如:/dev/ttyUSB1 /dev/ttyUSB2
- //就满足下面这个条件 ,就会加到集合中去
- if (files[i].getAbsolutePath().startsWith(mDeviceRoot)) {
- Log.d(TAG, "Found new device: " + files[i]);
- mDevices.add(files[i]);
- }
- }
- }
- return mDevices;
- }
-
- public String getName() {
- return mDriverName;
- }
- }
-
- private static final String TAG = "SerialPort";
-
- private Vector<Driver> mDrivers = null;
-
- /**
- * 获取设备
- * @return
- * @throws IOException
- * 其实就是读取 /proc/tty/drivers 这个文件
- * drivers中有设备的地址的总地址添加到一个集合中
- */
- Vector<Driver> getDrivers() throws IOException {
- if (mDrivers == null) {
- mDrivers = new Vector<Driver>();
- //读取行的流对象
- LineNumberReader r = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader(
- "/proc/tty/drivers"));
- String l;
- while ((l = r.readLine()) != null) {
- // Issue 3:
- // Since driver name may contain spaces, we do not extract
- // driver name with split()
- //看下面这个会发现 原来我们的 这个第一字符到第二个字符之间是21个,这也就是为什么这里面要用的 0x15 这个原因了
- //dev/tty /dev/tty 5 0 system:/dev/tty
- String drivername = l.substring(0, 0x15).trim();//其实就是获取第一个非空格字符串
- String[] w = l.split(" +");//这里是正则表达式:" +" 表示有一个或者多个空格
- if ((w.length >= 5) && (w[w.length - 1].equals("serial"))) {
- Log.d(TAG, "Found new driver " + drivername + " on "
- + w[w.length - 4]);
- mDrivers.add(new Driver(drivername, w[w.length - 4]));
- }
- }
- r.close();//关闭流
- }
- return mDrivers;
- }
-
- /**
- * 得到所有的设备的名称
- * @return
- */
- public String[] getAllDevices() {
- Vector<String> devices = new Vector<String>();
- // Parse each driver
- Iterator<Driver> itdriv;
- try {
- itdriv = getDrivers().iterator();//获取道设备的根地址
- while (itdriv.hasNext()) {//迭代获取具体的根路径
- Driver driver = itdriv.next();
- Iterator<File> itdev = driver.getDevices().iterator();//获取道包含根地址的设备对象的集合
- while (itdev.hasNext()) {//迭代获得具体的设备
- String device = itdev.next().getName();
- String value = String.format("%s (%s)", device,
- driver.getName());
- devices.add(value);
- }
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return devices.toArray(new String[devices.size()]);
- }
-
- /**
- * 获取道设备的路径
- * @return
- */
- public String[] getAllDevicesPath() {
- Vector<String> devices = new Vector<String>();
- // Parse each driver
- Iterator<Driver> itdriv;
- try {
- itdriv = getDrivers().iterator();
- while (itdriv.hasNext()) {
- Driver driver = itdriv.next();
- Iterator<File> itdev = driver.getDevices().iterator();
- while (itdev.hasNext()) {
- //获取
- String device = itdev.next().getAbsolutePath();
- devices.add(device);
- }
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return devices.toArray(new String[devices.size()]);
- }
- }

————————————————
转载于:https://blog.csdn.net/qiwenmingshiwo/article/details/49557889