热门标签
热门文章
- 1Linux本地docker一键部署traefik+内网穿透工具实现远程访问Web UI管理界面_traefik docker
- 2JuthAuth实现第三方扫码登录之微信登录_jushauth
- 3RuntimeError: There were no tensor arguments to this function (e.g., you passed an empty list of Ten_notimplementederror: there were no tensor argument
- 4(含源码notebook和环境配置)加速Pytorch SSD 目标检测模型推理_pytorch ssd camera
- 5Linux 安装配置maven3.2 以及搭建nexus私服
- 6高并发下,如何解决接口幂等性?常用解决方案必知必会_高并发接口幂等解决方案
- 7linux+find参数详解,Linux下find命令详解
- 8Docker在面试中常见的48道问题_docker面试题
- 9如何远程调试线上代码_远程调试 hotcode
- 10【STM32】MCU HardFault异常处理分析流程及总结(一)_stm32 nmi
当前位置: article > 正文
EASYX键盘交互_c语言easyx键盘交互
作者:Cpp五条 | 2024-02-16 14:07:41
赞
踩
c语言easyx键盘交互
eg1:使用键盘的上下左右按钮控制小球的上下左右移动
#include <stdio.h> #include <easyx.h> #include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <conio.h> #define PI 3.14 int main() { // 键盘交互 initgraph(800, 600); setorigin(400, 300); setaspectratio(1, -1); setbkcolor(RGB(164, 225, 202)); cleardevice(); setfillcolor(WHITE); // x y 表示圆心的坐标 int x = 0; int y = 0; solidcircle(x, y, 50); while (1) { /* getchar函数: 1: 从缓冲区中读取一个字符 2: 如果字符读取成功,就返回读取到的字符 3: 若是缓冲区中没有数据,就会阻塞函数,直到缓冲区中有数据 getch函数: getch函数可以不阻塞缓冲区及时响应的,使用该函数需要引入头文件conio.h才能被使用 使用平台提供的函数时需要在前面添加下划线以便和c语言提供的函数做一个区分 */ char c = _getch(); // 选择分支语句 switch (c) { case 'w': y = y + 50; break; case 's': y = y - 50; break; case 'a': x = x - 50; break; case 'd': x = x + 50; break; } // 清空窗体,重新绘制圆形 cleardevice(); solidcircle(x, y, 50); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
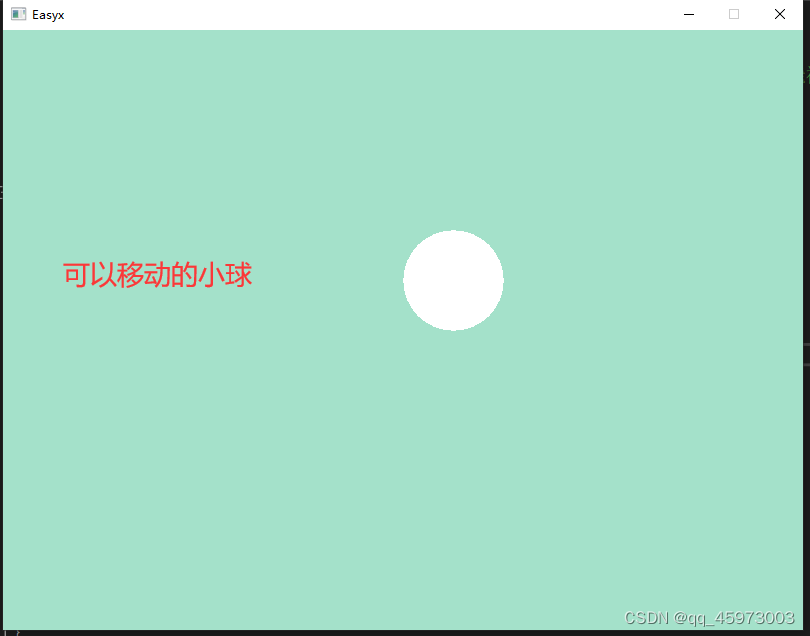
eg2:一直变化的场景实现键盘控制
#include <stdio.h> #include <easyx.h> #include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <conio.h> #define PI 3.14 int main() { // 键盘交互 initgraph(800, 600); setorigin(400, 300); setaspectratio(1, -1); setbkcolor(RGB(164, 225, 202)); cleardevice(); setfillcolor(WHITE); // x y 表示圆心的坐标 int x = -400,y = 0; // 相邻帧之间移动的距离 int dx = 5, dy = 0; solidcircle(x, y, 50); while (1) { cleardevice(); solidcircle(x, y, 50); Sleep(40); /* kbhit函数可以检查getch函数输入缓存区中是否有数据 如果没有数据就返回0,如果有数据就返回非0 */ if (_kbhit() != 0) { char c = _getch(); // 选择分支语句 switch (c) { case 'w': dx = 0; dy = 5; break; case 's': dx = 0; dy = -5; break; case 'a': dx = -5; dy = 0; break; case 'd': dx = 5; dy = 0; break; } x += dx; y += dy; } } getchar(); closegraph(); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Cpp五条/article/detail/94080
推荐阅读
相关标签



