- 1python区间数之和_Python求区间正整数内所有素数之和的方法实例
- 2java 检验精确度_java数值计算的精确度
- 3人工智能与伦理道德
- 4Android 使用Room 生成不了数据库文件_java room 数据库没有生成 impl 文件
- 5vite+vue3+ts项目构建详细步骤(配置多语言版本)_vite+vue+ts
- 6linux vi 中替换不可见字符^@\^A\^M等_linux 文件 vi 多了^a
- 7html之列表元素_html列表元素的作用
- 8纯血鸿蒙来画龙!基于HarmonyOS ArkTS来操作SVG图片_arkts image图片切换
- 9Ubuntu下使用docker部署WordPress
- 10List与LinkedList_linkedlist和list
SpringBoot—三大特性_springboot特点
赞
踩
随着spring使用的越来越广泛,项目的各种配置文件也随之越来越多,大量的配置文件让开发者很烦恼。springboot的诞生简化了spring应用的创建、运行、部署。
在JDK1.5之后引入的注解也在springboot中大量使用,springboot也提供了一些注解(集成了spring的注解),如SpringBootApplication注解标注了该类是一个启动类。
另外,在过去的springmvc项目中,使用第三方包需要在maven中配置很多行,为了简化我们的配置,很多第三方包也提供了基于springboot的maven包,我们只需引用做简单的配置及可使用。
1.内置Servlet Container
在pom.xml中,添加spring-boot-starter-web的maven依赖,使其成为一个web项目,其中这个spring-boot-starter-web中包含了spring-boot-starter-tomcat,使得项目能在内置的tomcat容器中运行。
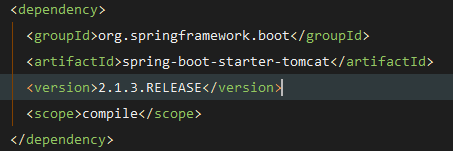
另外springboot也可以使用其他容器的starter替换tomcat,包括Jetty以及undertow等。这里以undertow为例,具体方法如下:

springboot内置了servlet容器,项目可以直接打包成jar形式,使用java -jar命令运行,而不必像以前打包成war包形式放到tomcat下运行。正因为这个机制,结合Jenkins、Docker自动化运维得以实现。
2.生产准备特性
springboot提供的actuator插件提供了大量的生产级特性,可以帮助监控和管理springBoot应用,比如健康检查、审计、统计和HTTP追踪。这在微服务中,可以通过actutor提供的端点与外部应用监控系统进行整合,比如Prometheus、DataDog来进行服务监控。
SpringBoot-Actuator提供了很多监控端点
| 端点 | 描述 | http方法 |
|---|---|---|
| autoconfig | 显示自动配置信息 | GET |
| beans | 显示应用程序上下文所有的spring bean | GET |
| configprops | 显示所有@ConfigurationProperties的配置属性列表 | GET |
| dump | 显示线程活动的快照 | GET |
| env | 显示应用的环境变量 | GET |
| health | 显示应用程序的健康指标,这些值由HealthIndicator的实现类提供 | GET |
| info | 显示应用的信息,可使用info.*属性自定义info端点公开的数据 | GET |
| mappings | 显示所有的URL路径 | GET |
| metrics | 显示应用的度量标准信息 | GET |
| shutdown | 关闭应用(默认情况下不启用,如需启用,需设置endpoints.shutdown.enabled=true) | POST |
| trace | 显示跟踪信息(默认情况下为最近的100个HTTP请求) | GET |
actuator配置,为项目引入以下依赖
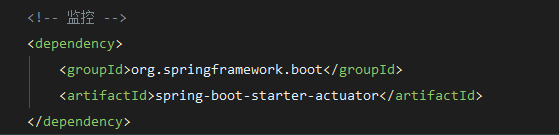
这里需要注意的是,在springboot2.0之后,actuator通过jmx暴露端点,对HTTP屏蔽了对外的访问端点,只提供health和info端点,另外使用 http://{ip}:{port}/actuator/{endpoint}的形式访问,需要做以下的配置才能访问。
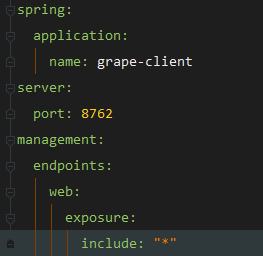
这里表示对http开发所有端口节点。
/health endpoint
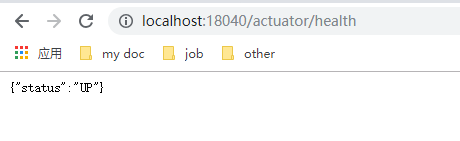
UP表示运行正常,除UP外,还有Down、OUT_OF_SERVICE、UN_KNOWN等状态。health只简单显示了应用的UP状态,如果想要知道详细的信息,需要做如下配置:


这里Redis没有连接上,所以状态会变为DOWM
/metrics endpoint
用于追踪应用的度量信息
在浏览器输入http://{ip}:{port}/actuator/metrics,显示所有支持的度量

可使用http://{ip}:{port}/actuator/metrics/{detailName}查看具体的度量信息,比如http://localhost:18762/actuator/metrics/jvm.threads.states

/loggers endpoint
展示了应用中logger相关的日志等级和列表,与metrics类似,通过访问
http://{ip}:{port}/actuator/loggers查看所有的logger列表,并使用name访问具体的logger信息
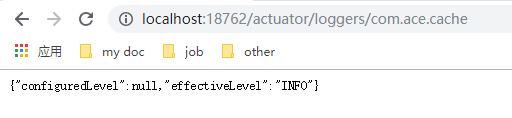
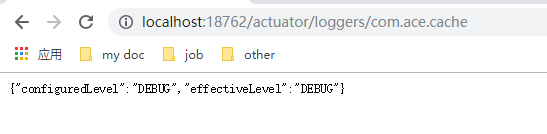
可通过给以上logger地址发送post请求的方式动态的改变日志等级。

再次查看日志等级变为DEBUG
actuator的应用场景:结合普罗米修斯等做服务监控(借用一篇大老杨的文章)
Prometheus
一套开源的系统监控报警框架,可以将Prometheus理解为一个数据库,通过配置http://localhost:8762/actuator/prometheus,爬取actuator接口提供的metric等数据。
官网地址:https://prometheus.io/
Grafana
能够把不同来源的数据(这里数据来源于Prometheus)以图形化的形式进行展示,并通过邮件等形式通知。
官网地址:https://grafana.com/
springboot集成Prometheus具体实现步骤
- 添加依赖

- 配置yml文件

- 设置启动类

启动springboot项目后访问 http://localhost:8762/actuator/prometheus ,可以看到一些度量指标

- 使用Docker下载和运行Prometheus
https://prometheus.io/docs/prometheus/latest/getting_started/
$ docker pull prom/prometheus
- 1

配置prometheus.yml文件

5. 卷和绑定安装
prometheus.yml通过运行以下命令将您从主机绑定:
docker run -p 9090:9090 -v /tmp/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
prom/prometheus
- 1
- 2
或者为配置使用额外的卷:
docker run -p 9090:9090 -v /prometheus-data \
prom/prometheus --config.file=/prometheus-data/prometheus.yml
- 1
- 2
-
访问prometheus http://[host]:9090

第一个endpoint是prometheus自己的健康健康端点
第二个是我的springboot应用的actuator/prometheus端点 -
prometheus自带的图形界面

-
使用Docker下载和运行Grafana
http://docs.grafana.org/installation/docker/
docker search grafana
docker pull grafana/grafana
docker images
$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 grafana/grafana
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
安装完后访问http://[host]:3000 ,并使用默认账号密码登录admin,admin
- 配置Grafana导入Prometheus中的metrics数据





3.装配模式
springboot能很方便的使用第三方包,只需做简单的配置即可使用,例如:jdbc、web-mvc等。那么springboot是如何加载这些模块的呢?
首先springboot项目的启动都是从带有@SpringBootApplication的启动类开始的,让我们来看看@SpringBootApplication这个注解。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这里有三个注解@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponenetScan,
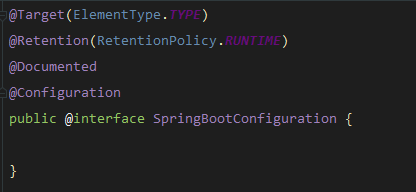
从SpringBootConfiguration注解可以看出,这就是个@Configuration,即被@SpringBootApplication标注的类是一个配置类。
而@ComponenetScan是一个包扫描注解,由于没有指定扫描范围,所以它会扫描同级包目录下的所有类,即@SpringBootApplication标注的启动类同级包下的所有类(com.grape.client下的所有类)。
最后我们来看@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
这里通过@Import注解引入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector这个类,根据字面意思理解(自动装配选择器)
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry( autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
这里我删掉了其他的一些方法,只留下了selectImports这个方法,AutoConfigurationImportSelector实现了DeferredImportSelector接口,DeferredImportSelector又继承自ImportSelector接口
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
那么在AutoConfigurationImportSelector选择器中,selectImports这个方法又做了什么呢?

首先会判断是否进行自动装配,接着执行
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
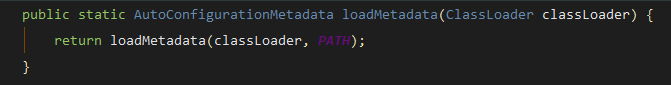
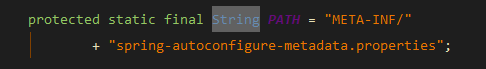
这里会从META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties读取元数据和元数据相关的属性,获取所有支持自动装配的信息。
接着执行
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(
autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);


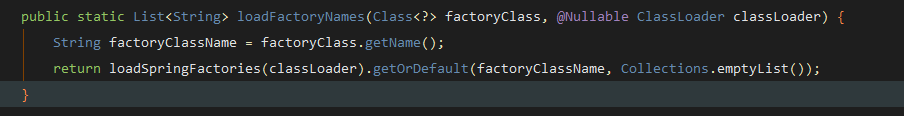

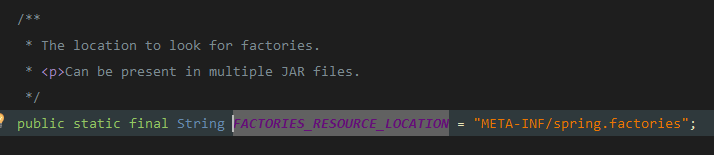
这里会读取META-INF/spring.factories下的配置,接着进行排除和过滤得到需要装配的类。最后让 META-INF/spring.factories下的装配类执行fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents这个方法,加载应用监听。
以上确定了哪些类需要被装配,但springboot是在何时装配这些类的呢?
在启动类的main方法中,会调用SpringApplication.run()方法,参数是启动类的Class。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances( SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass) .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
该方法会创建一个ApplicationContext并返回
1.准备Context所需的参数、环境
- 【SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners】,对SpringApplicationRunListeners的解释是 A collection of {@link SpringApplicationRunListener},SpringApplicationRunListener是用于SpringApplication@run方法的监听器
- 【ApplicationArguments applicationArguments】提供用于运行SpringApplication的参数
- 【ConfigurableEnvironment environment】提供运行环境
- 【Banner printedBanner】
2.prepareContext
为context添加相应的运行环境和监听, 创建一个beanFactory用于加载单例的springApplicationArguments、springBootBanner,获取启动配置类,将需要加载的bean加载到context中,为context添加监听
3.refreshContext
调用AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(),执行refresh里的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,该类主要处理@Configuration注解的
/** * Prepare the Configuration classes for servicing bean requests at runtime * by replacing them with CGLIB-enhanced subclasses. */ @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory); if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory); } this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId); if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) { // BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported... // Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then. processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory); } enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory)); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
/** * Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of * {@link Configuration} classes. */ public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>(); String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); } } // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; } // Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return Integer.compare(i1, i2); }); // Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null; if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) { BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); if (generator != null) { this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } } if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } // Parse each @Configuration class ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser( this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size()); do { parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); // Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content if (this.reader == null) { this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader( registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment, this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } } while (!candidates.isEmpty()); // Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { // Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op // for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext. ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); } else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); } else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex); } } this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
public void process() {
List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
try {
if (deferredImports != null) {
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR);
deferredImports.forEach(handler::register);
handler.processGroupImports();
}
}
finally {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
在这里将会对DeferredImportSelector进行处理,这样我们就和AutoConfigurationSelectImporter结合到一起了
public void processGroupImports() { for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) { grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> { ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get( entry.getMetadata()); try { processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass), asSourceClasses(entry.getImportClassName()), false); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex); } }); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
到此执行自动装配的所有操作
4.afterRefresh
5.总结
- 自动装配利用SpringFactoriesLoader来加载META-INF/spring.factoires文件里所有配置的EnableAutoConfgruation,它会经过exclude和filter等操作,最终确定要装配的类
- 实现自动装配主要是 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();这个方法



