- 1tomcat安装、部署JSPGOU项目、Tomcat多实例
- 2惠氏桥测量电阻_pt1000测量电路
- 3对 Python 代码使用的词语标记化器 tokenize,你懂了吗?【Python|标准库|tokenize】_python tokenize
- 4git-常用命令
- 5阿里通义灵码实测使用,强大,好用!_阿里灵码
- 6用knn算法对鸢尾花数据集进行分类
- 7模拟电路设计(10)--- 运算放大器简介_模拟集成电路中运放的内部结构图
- 8如何使用RxJava 2.x开发Android应用?_反应式编程实战:使用rxjava 2.x开发android应用
- 9人工智能基础部分15-自然语言处理中的数据处理上采样、下采样、负采样是什么?_文本 下采样的区别
- 10编译MOTR的时候,报错:error: cannot call member function ‘void std::basic_string<_CharT, _Traits, _Alloc>::_R_msda.ms_deform_attn_forward
.net6数据结构与算法_.net数据结构和算法
赞
踩
前言
程序 = 数据结构 + 算法;
数据:其实就是程序的核心,程序就是为了解决问题,管理数据。
数据结构:就是一个容器,用来存放数据,不同的数据结构有不同的特点,为了更好的完成数据的存储和管理。
算法:是指解题方案的准确而完整的描述,是一系列解决问题的清晰命令,算法代表着用系统的方法描述解决问题的策略机制。
一、简单认识数组
线性数据结构:数据在内存上是连续摆放的。
Array:连续的摆放的数据结构。
特点:节约空间,查找也快,增删慢,定长。
增删慢:是因为需要要新开辟一个空间。
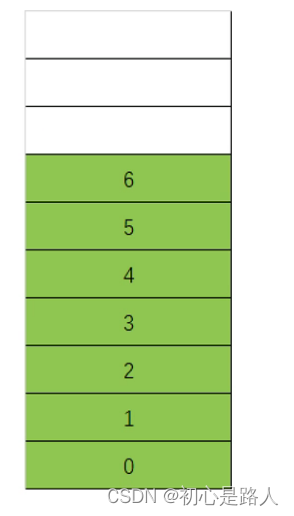
1.1 Array
int[] intArray = new int[3];
intArray[0] = 123:
string[] stringArray = new string[] ["123","234};
- 1
- 2
- 3
1.2 多维Array
int[,] a= new int[3,4] {
{0,1,2, 3} , // 初始化索引号为 0 的行
{4,5,6,7}, // 兴初始化索引号为 1 的行
{8,9,1011} //初始化索引号为 2 的行
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
1.3 锯齿Array
int[][] a = new int[2][];
a[0] = new int[] [ 1,2,3 1;
a[l] = new int[] [ 2 ];
- 1
- 2
- 3
二、链表结构
数据结构分为线性结构(例如数组)和非线性结构,线性结构分为数组和链表(栈和队列)–元素的前后都只有一条数据。
顺序存储:开辟一段连续的空间,数据连续摆放
链式存储:每个数据都是独立的,彼此之间会有一个引用指向
非线性结构:多维数组,树,图 —元素前后可能有多个
1. 单项链表
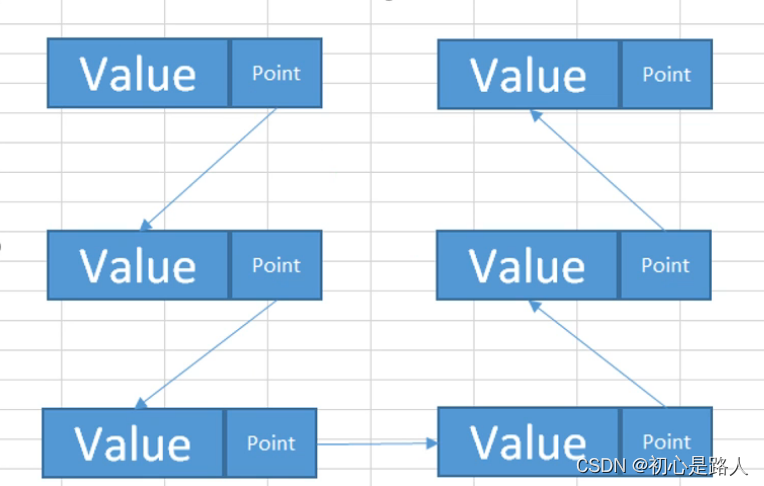
private class CustomNode<T>
{
public T Element;//当前的值
public CustomNode<T> NextNode;//下个节点
public CustomNode()
{
Element = default(T);
NextNode = null;
}
public CustomNode(T theElement)
{
Element = theElement;
NextNode = null;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
添加数据:
private class CustomeLinkedList<T> { private CustomNode<T> _CurrentHeader; public CustomeLinkedList() { this._CurrentHeader = new CustomNode<T>(default(T)); } public CustomeLinkedList(CustomNode<T> header) { this._CurrentHeader = header; } public void Add(T t) { //这里添加节点时,结合上面 CustomNode<T>类一起 CustomNode<T> node = new CustomNode<T>(t); node.NextNode = _CurrentHeader; //1.为当前节点的NextNode为开辟一个空间。2.把上一条数据的Element作为当前数据的NextNode节点 _CurrentHeader = node; //把当前节点保存,作为下一个节点的NextNode } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
链表与数组的区别:
1.数据是随机摆放,通过引用串联,不是连续摆放的
2.不适合索引访问,头结点,尾节点,上下个节点比较方便
3.不限制长度,随时可以增删方便,数组需要重新调整空间
4.链表查找数据会慢,需要一个一个去找
适用场景:
1.动态数据集合:当你需要一个能够频繁添加或删除元素的集合时,单向链表是一个好选择,因为它可以在O(1)时间内添加或删除节点。
2.内存空间利用:与数组相比,链表更好地利用内存,因为它不需要预先分配固定大小的内存空间。链表节点可以在需要时动态分配,在处理大小未知或经常变化的数据集时非常有用。
3.实现队列:单向链表非常适合实现队列数据结构,其中元素按照FIFO(先进先出)的顺序处理。你可以在链表的一端添加元素,在另一端移除元素。
4.简单场景下的内存优化:相比双向链表,单向链表可以节省内存,因为它只存储指向下一个节点的引用,而不是前后节点的引用。
2. 双向链表
框架内置的LingkedList;双链表相对于单链表就是多一个数据指向,就是既可以往前搜索,也可以往后搜索
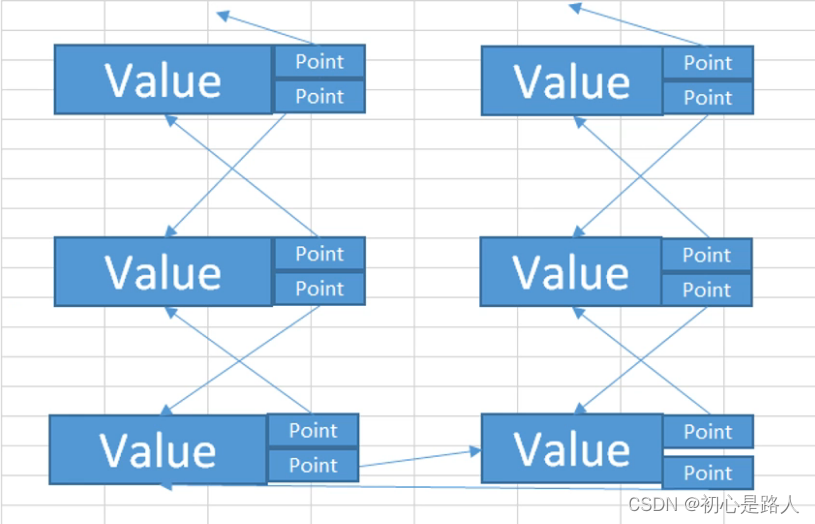
//1.链表的声明以及节点的定义 LinkedList<string> link = new LinkedList<string>(); //定义链表 LinkedListNode<string> node1 = new LinkedListNode<string>("A1"); //第一个节点 LinkedListNode<string> node2 = new LinkedListNode<string>("A2"); //第二个节点s LinkedListNode<string> node3 = new LinkedListNode<string>("A3"); LinkedListNode<string> node4 = new LinkedListNode<string>("A4"); //2.节点的加入 link.AddFirst(node1); //加入第一个节点 //绑定节点关系 link.AddAfter(node1, node2); link.AddAfter(node2, node3); link.AddAfter(node3, node4); //3.计算包含的数量 Console.WriteLine(link.Count); //4.显示 LinkedListNode<string> current = link.First; while (current != null) { Console.WriteLine(current.Value); current = current.Next; } //5.查找 LinkedListNode<string> temp = link.Find("jiajia2"); if (temp != null) { Console.WriteLine("找到这个节点" + temp.Value); } //6.定位最后节点 temp = link.Last; Console.WriteLine("最后这个节点" + temp.Value); //7.一些删除操作 link.RemoveFirst(); link.Remove("A2"); link.Clear();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
源码的头节点添加逻辑(其实就是一些绑定关系逻辑),具体源码在VS工具安装个插件ILSpay自己查看了:
public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value)
{
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head == null)
{
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
}
else
{
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
}
return result;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
private void InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(LinkedListNode<T> newNode)
{
Debug.Assert(head == null && count == 0, "LinkedList must be empty when this method is called!");
newNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
查找节点:
public LinkedListNode<T>? Find(T value) { LinkedListNode<T>? node = head; EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default; if (node != null) { if (value != null) { do { if (c.Equals(node!.item, value)) { return node; } node = node.next; } while (node != head); } else { do { if (node!.item == null) { return node; } node = node.next; } while (node != head); } } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
删除节点:
public bool Remove(T value) { LinkedListNode<T>? node = Find(value); if (node != null) { InternalRemoveNode(node); return true; } return false; } public void Remove(LinkedListNode<T> node) { ValidateNode(node); InternalRemoveNode(node); } public void RemoveFirst() { if (head == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.LinkedListEmpty); } InternalRemoveNode(head); } public void RemoveLast() { if (head == null) { throw new InvalidOperationException(SR.LinkedListEmpty); } InternalRemoveNode(head.prev!); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
internal void InternalRemoveNode(LinkedListNode<T> node) { Debug.Assert(node.list == this, "Deleting the node from another list!"); Debug.Assert(head != null, "This method shouldn't be called on empty list!"); if (node.next == node) { Debug.Assert(count == 1 && head == node, "this should only be true for a list with only one node"); head = null; } else { node.next!.prev = node.prev; node.prev!.next = node.next; if (head == node) { head = node.next; } } node.Invalidate(); count--; version++; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
3. 循环链表
就是头尾连接,双向链表头尾再指向一下。怎么说呢,giao!就是头部的上一个节点是为空的,但是在循环链表中就是把头部节点的上一个空节点指向最后一个节点,头尾连接一下下。
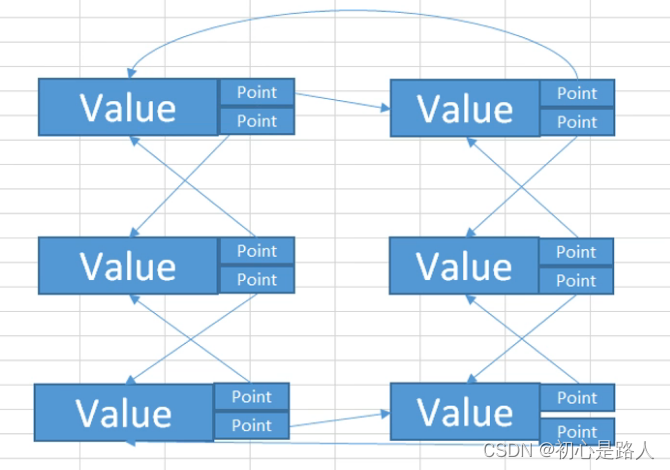
4. 总结
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续,非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
1.单向–双向–循环,其实就是对象包含了1到两个引用指向其他节点,就能通过某个节点,完成对整个链表全部对象的访问!!
2.用来实现堆栈(Queue)比较方便
问:C#默认使用数组,为啥不用链表?
(1).随机访问 vs. 插入/删除效率:
数组: 提供O(1)的随机访问,即可以通过索引直接访问元素。但在插入或删除元素时,可能需要移动其他元素,导致O(n)的时间复杂度。
链表: 链表的插入和删除操作通常更为高效,特别是在列表中间插入或删除元素。然而,随机访问时的性能较差,因为必须按顺序遍历链表,导致O(n)的时间复杂度。
(2).内存布局和空间开销:
数组: 在内存中是连续存储的,因此对于随机访问具有较好的缓存性能。但需要预分配固定大小的内存,可能导致浪费或不足。
链表: 链表的节点可以动态分配,避免了固定大小的内存预分配,但每个节点都需要额外的指针字段,增加了内存开销。
(3).使用场景和操作模式:
如果你的应用程序主要涉及随机访问元素,例如通过索引检索数组元素,那么数组可能更为适用。
如果你的应用程序涉及频繁的插入和删除操作,特别是在集合中间进行操作,链表可能更为适用。
C#提供了List类,它基于动态数组实现,同时也提供了LinkedList类,它基于链表实现。选择使用哪种数据结构通常取决于具体的操作需求和性能优化目标。在实际应用中,也可以考虑使用其他集合类型,如Dictionary<TKey, TValue>或HashSet,这些集合类型根据不同的场景提供了更优化的性能。
三、树结构
树是由边连接的一系列节点,一种非线性的数据结构,可以把数据按照等级模式存储起来。包含有根节点,父节点,子节点,叶节点。无父为根,有子为父,有父为子,无子为叶。
1.二叉树
每个节点最多拥有不超过两个子节点的树定义为二叉树。
完全二叉树:若二叉树中最多只有最下面两层的节点的度小于2,并且最下面一层的节点(叶节点)都一次排列在该层最左边的位置上,具有这样的结构特点的树结构成为完全二叉树。
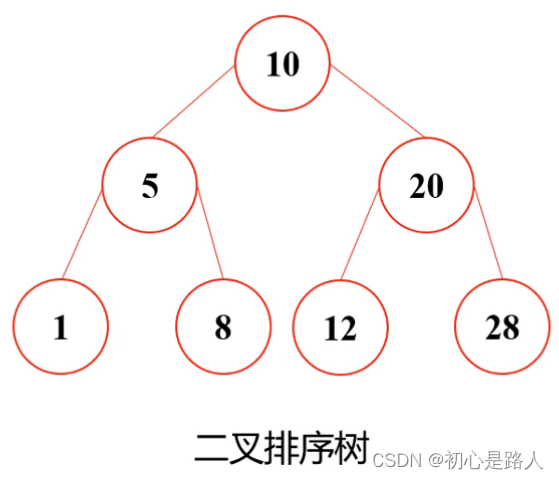
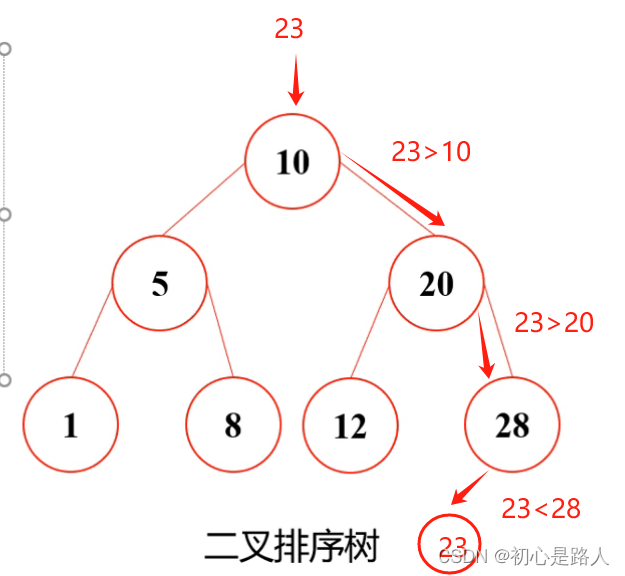
2.二叉查找树(排序树)
1.若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上的所有节点的值均小于根节点的值
2.若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上的所有节点的值均大于根节点的值
3.二叉排序树的左右子树也都是二叉排序树
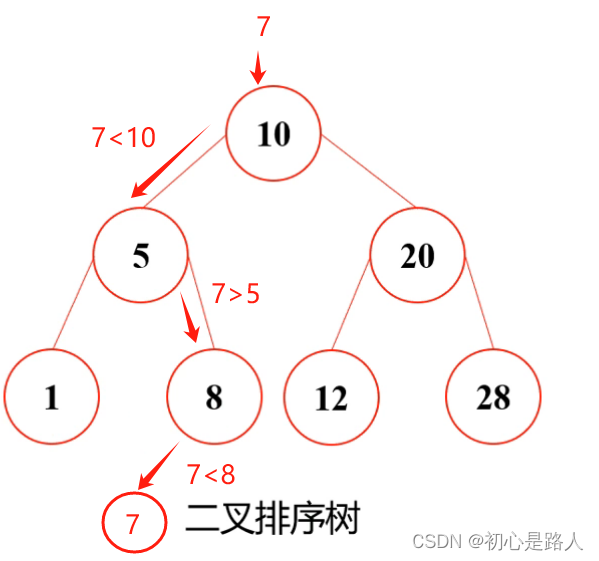
我少年你脑瓜子有点嗡嗡的吧!来,给你解答。
举个栗子:假如我要摆个7,我要放在哪呢?首先7<10,按照第1点的规则,要摆在左边=》》然后7>5,根据第2点的规则,摆在右边 =》》 但是右边7<8,按照第1点的规则,最后得出,7摆在下面8的左边。如果下面还有值以此类推!!!
再举个栗子:假如我要摆个23,我要放在哪呢?首先23>10,按照第2点的规则摆在右边=>>右边23>20,按照第2点的规则,继续往右边走=>>23<28按照第1点的规则摆在左边。以此类推。
代码示例:
private class CustomTreeNode { public int iData { get; set; } //public CustomTreeNode[] Child { get; set; }//任意树 public CustomTreeNode Left { get; set; } public CustomTreeNode Right { get; set; } public void Show() { //这里就是一个递归 this.Left?.Show(); Console.Write(this.iData + " ");//中序遍历 从小到大 this.Right?.Show(); //Console.Write(this.iData + " ");//先序遍历 自身在前 //this.Left?.Show(); //this.Right?.Show(); //this.Left?.Show(); //this.Right?.Show(); //Console.Write(this.iData + " ");//后序遍历 自身在后 } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
public class TreeDemo { public static void Show() { Expression<Func<int, int, int, int>> expression = (i, m, n) => i * 3 + m + 2 + n / 4; CustomTreeNode tree = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 123, Left = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 12, Left = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 11, Left = null, Right = null }, Right = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 12, Left = null, Right = null } }, Right = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 15, Left = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 13, Left = null, Right = null }, Right = new CustomTreeNode() { iData = 17, Left = null, Right = null } } }; CustomBinarySearchTree tree1 = new CustomBinarySearchTree(); tree1.Insert(10); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(5); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(1); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(8); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(20); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(28); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(12); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(6); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(7); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); tree1.Insert(25); tree1.SequentialTraversal(); Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine(tree1.Min()); Console.WriteLine(tree1.Max()); Console.WriteLine(tree1.Find(25).iData); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
public void SequentialTraversal()
{
_Root.Show();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
运行结果大家就自己体验了。多动手,多实践。
2.1 二叉查找树
查找最小值,一直往左边找
public int Min()
{
CustomTreeNode current = this._Root;
while (current.Left != null)
{
current = current.Left;
}
return current.iData;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
查找最大值,一直往右边边找
public int Max()
{
CustomTreeNode current = this._Root;
while (current.Right != null)
{
current = current.Right;
}
return current.iData;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
查找指定值
public CustomTreeNode Find(int i) { CustomTreeNode current = this._Root; while (current != null) { if (i == current.iData) { return current; } if (i > current.iData) { current = current.Right; } else { current = current.Left; } } return null;//没有 }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
删除节点
public bool Delete(int key) { CustomTreeNode current = this._Root; CustomTreeNode parent = _Root; bool isLeftChild = true; while (current.iData != key) { parent = current; if (key < current.iData) { isLeftChild = true; current = current.Right; } else { isLeftChild = false; current = current.Right; } if (current == null) return false; } if ((current.Left == null) & (current.Right == null)) if (current == this._Root) this._Root = null; else if (isLeftChild) parent.Left = null; else if (current.Right == null) { if (current == this._Root) this._Root = current.Left; else if (isLeftChild) parent.Left = current.Left; else parent.Right = current.Right; } else if (current.Left == null) { if (current == this._Root) this._Root = current.Right; else if (isLeftChild) parent.Left = parent.Right; else parent.Right = current.Right; } else { CustomTreeNode successor = GetSubstitute(current); if (current == this._Root) this._Root = successor; else if (isLeftChild) parent.Left = successor; else parent.Right = successor; successor.Left = current.Left; } return true; } /// <summary> /// 找替补节点 /// </summary> /// <param name="delNode"></param> /// <returns></returns> private CustomTreeNode GetSubstitute(CustomTreeNode delNode) { CustomTreeNode substituteParent = delNode; CustomTreeNode substitute = delNode; CustomTreeNode current = delNode.Right; while (!(current == null)) { substituteParent = current; substitute = current; current = current.Left; } if (!(substitute == delNode.Right)) { substituteParent.Left = substitute.Right; substitute.Right = delNode.Right; } return substitute; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
线性结构:除了头尾元素,每个元素只有一个前置,一个尾巴
非线性结构:一个元素可以跟一个或者多个元素关联。例如:树,图
四、算法
简单介绍三种基础算法:
冒泡排序:双层循环两两交换,直到找出最大值(或最小值)
/// <summary> /// 冒泡排序 /// 先挑最大值 摆在最后面 /// 先挑最小值 摆在最前面? /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> public static void BubbleSort(this int[] arr) { int temp; for (int outer = arr.Length; outer >= 1; outer--) { for (int inner = 0; inner <= outer - 1; inner++) { if (arr[inner] > arr[inner + 1]) { temp = arr[inner]; arr[inner] = arr[inner + 1]; arr[inner + 1] = temp; } } arr.Show(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
选择排序:双层循环,找出最小值(或最大值),直接更头部交换,相对与冒泡排序,移动更少,速度更快
/// <summary> /// 选择排序 /// 依次选择最小的数字放到最左边 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> public static void SelectionSort(this int[] arr) { int min, temp; for (int outer = 0; outer < arr.Length; outer++) { min = outer; for (int inner = outer + 1; inner < arr.Length; inner++) { if (arr[inner] < arr[min]) { min = inner; } } temp = arr[outer]; arr[outer] = arr[min]; arr[min] = temp; arr.Show(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
插入排序:先放一个数据放到位置0,再放第2个,需要比较前面的数据,决定放在左边还是右边,以此类推。速度是最慢的
/// <summary> /// 插入排序 /// 从第2个数开始,跟第一个数对比,放在左边还是右边 /// 循环下去比较,都放在合适的位置 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> public static void InsertionSort(this int[] arr) { int inner, temp; for (int outer = 1; outer < arr.Length; outer++) { temp = arr[outer]; inner = outer; while (inner > 0 && arr[inner - 1] >= temp) { arr[inner] = arr[inner - 1]; inner -= 1; } arr[inner] = temp; arr.Show(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
扩展:
自组织查找算法:
自组织查找算法,简单说明就是,每查找相同的值一次,这个值就会往前移动一个索引,也是热数据的一种方式
public static int SequentialSearchWithSelfOrganizing(this int[] arr, int sValue) { for (int index = 0; index < arr.Length - 1; index++) { if (arr[index] == sValue) { if (index > 0) { int temp = arr[index - 1]; arr[index - 1] = arr[index]; arr[index] = temp; arr.Show(); } return index; } } return -1; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
1. 希尔排序算法
希尔排序是对插入排序算法的改进,先分组对比,大致有序之后再插入排序,效率更高
- 插入排序在对几乎已经排好序的数据操作时,效率高,即可以达到线性排序的效率(对数据样本要求高)
- 但是插入排序一般来说是低效的,因为插入排序每次只能将数据移动一位
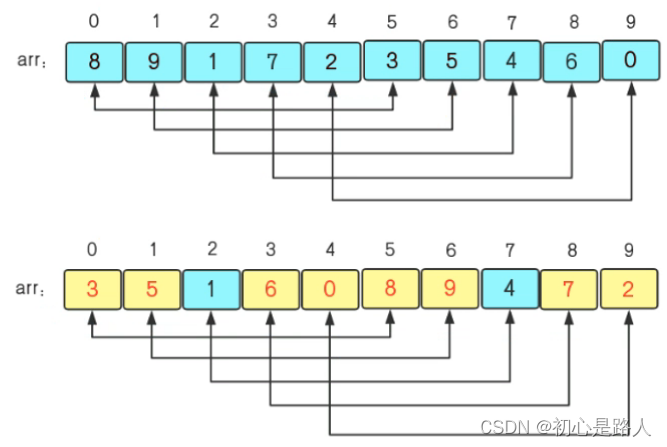
private static void ShellSort(this int[] arr) { int inner = 0; int temp = 0; int increment = 0; //除以3,是因为3是综合下得到的比较适合的分组数量,延用就行了 while (increment <= arr.Length / 3)//10--4 20 13 { increment = increment * 3 + 1; } while (increment > 0)//4--1 { for (int outer = increment; outer <= arr.Length - 1; outer++) { temp = arr[outer]; inner = outer; while ((inner > increment - 1) && arr[inner - increment] >= temp) { arr[inner] = arr[inner - increment]; inner -= increment; } arr[inner] = temp; arr.Show(); }//increment=1时就是插入排序一样的代码 increment = (increment - 1) / 3; arr.Show(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
总结:思路简单,实现方便,性能不错,数据量影响不大,但是复杂度不稳定,跳跃式的,更数据样本有关。
希尔排序算法经常被认为是一种很好的高级排序算法。这是因为它时分容易实现,甚至是对于包含好几万个元素的数据集合而言其性能也是可以接受的
2. 归并排序算法(二分法)
归并排序(二分法)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,就是不断拆分成最小个体,再进行排序。但是需要开辟空间来不断进行分组比较,持续合并。
分治策略:将问题分成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各个答案“修补”在一起,即分而治之。
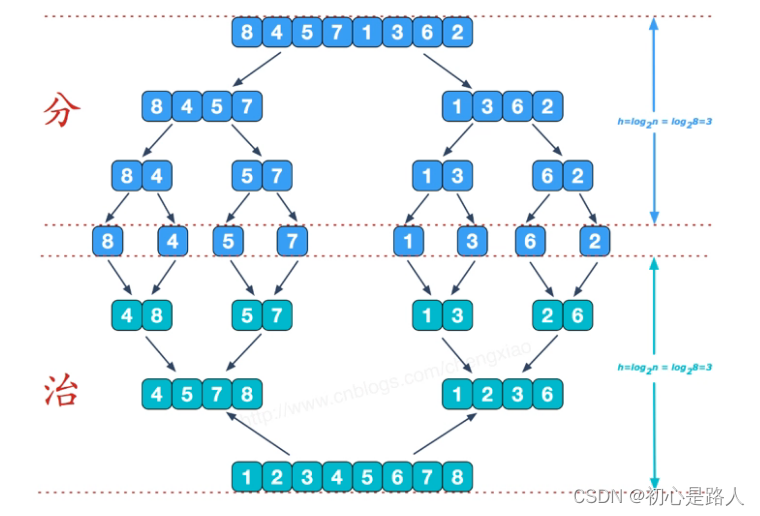
/// <summary> /// 归并排序 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> public static void MergeSort(this int[] arr) { int[] temp = new int[arr.Length];//准备空数组 PartSort(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1, temp); } /// <summary> /// 递归分治 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> /// <param name="left"></param> /// <param name="right"></param> /// <param name="temp"></param> private static void PartSort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) { if (left < right) { int middle = (left + right) / 2; PartSort(arr, left, middle, temp);//左边归并排序 PartSort(arr, middle + 1, right, temp);//右边归并排序 Merge(arr, left, middle, right, temp);//合并操作 } } private static void Merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) { int i = left; int j = mid + 1; int t = 0; while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if (arr[i] <= arr[j]) { //temp[t++] = arr[i++]; temp[t] = arr[i]; t++; i++; } else { //temp[t++] = arr[j++]; temp[t] = arr[j]; t++; j++; } } while (i <= mid) { temp[t++] = arr[i++];//将左边剩余元素填充进temp中 } while (j <= right) { temp[t++] = arr[j++];//将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中 } t = 0; while (left <= right) { arr[left++] = temp[t++];//将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中 } arr.Show(); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
总结:超稳定的排序,它也是一种时分高效的排序,利用二叉树特性O(N*logN)!!!
3. 快速排序算法
速度最快的高级排序算法!!!额!!!.net内置排序的算法
思路:分治+递归,分区,再区分,再分去,再合并,也是一种冒泡排序的进化!
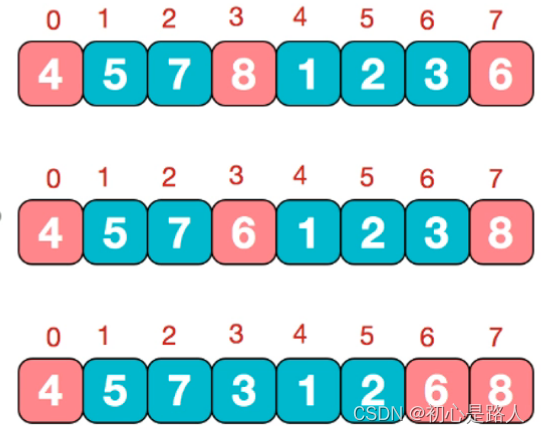
过程:
1.选三个数,头A,尾部B,任意一个数C,然后做好大小排序ACB
2.变成A0000000…CB
3.从索引1开始,一次跟C比较,小的放在左边,大的放在CB中间
4.C的左边都比C小,C的右边都比C大,两边再分别进行123步骤(递归)
public static void QuickSort(this int[] arr) { QuickSortRecursion(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1); } /// <summary> /// 递归排序单个数组 /// </summary> /// <param name="arr"></param> /// <param name="left"></param> /// <param name="right"></param> private static void QuickSortRecursion(int[] arr, int left, int right) { if (left < right) { SetReference(arr, left, right);//获取参照物 int referenceIndex = right - 1; int i = left; int j = right - 1; while (true) { while (arr[++i] < arr[referenceIndex]) { } while (j > left && arr[--j] > arr[referenceIndex]) { } if (i < j) { Swap(arr, i, j); //i是将来的参照值,如果分区不对交换下位置 arr.Show(); } else { break; } } if (i < right) { Swap(arr, i, right - 1); //i是将来的参照值,如果分区不对交换下位置 arr.Show(); } //从左往右找大于参考值,从右往左找小于参考值,然后交换,保证小的在一块,大的在一块,最后把参考值移到中间去 QuickSortRecursion(arr, left, i - 1); //中间值不用排,只排左边 QuickSortRecursion(arr, i + 1, right); //中间值不用排,只排右边 } } private static void SetReference(int[] arr, int left, int right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (arr[left] > arr[mid]) { Swap(arr, left, mid); } if (arr[left] > arr[right]) { Swap(arr, left, right); } if (arr[right] < arr[mid]) { Swap(arr, right, mid); } arr.Show(); Swap(arr, right - 1, mid); arr.Show(); } //交换位置 private static void Swap(int[] arr, int a, int b) { int temp = arr[a]; arr[a] = arr[b]; arr[b] = temp; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
总结:
具体执行还是需要通过代码和返回步骤结果推断,思路会更加清晰。
1 .net类库的默认排序就是快拍,数据多才有优势,数据少无意义
2.分而治之,最关键就是参照物的选择,可以头,尾,中,简而言之就是第一个数据,最后一条数据和中间一条数据做参照
3.针对于大量且通常无序的数据集合而言是非常有优势的,如果数据集合很小,或者数据相对有序的,快排的意义较小
总结
线性存储:数组-,链表,堆栈+队列-hash
非线性存储:二维数组,树,图,…
内存分配:一个进程就是一个堆,堆里面的数据是连续紧密摆放的,多线程并的,线性或者非线性的,其实内存都不一定在一起,只有数据类是在一起的,链表、树、图都是随机分布。数据结构只是封装了一个访问方式,人为的组织了一下数据的关系,而不是物理上的关系。
数组类:物理上是在一起的,但是封装了不同的API提供了不同的特性。
其实所谓的数据结构跟存储(内存)没有关系,只是为了简化算法!!!!
如有补充或者有差异的地方,麻烦再评论下面指出,共勉!!!!!




