热门标签
热门文章
- 1Hume获5000万美元融资,推出首个“情商”AI聊天助手
- 2.NET中的IO操作基础介绍
- 3如何搭建一个 tts 语言合成模型_tts模型训练
- 4微信小程序--多种类型日期选择器(年月、月日...)_微信小程序时间筛选
- 5HarmonyOS学习第二课:关于横向滚动视图的一些想法_harmonyos div 滚动
- 6ChatGPT扩展系列之跨平台桌面客户端ChatBox
- 7SSM+Vue+Element-UI实现网上跳蚤市场_uview跳蚤市场
- 8手把手教你做小型机器狗,毕业设计。必看_机器狗编程制作教程
- 98、MapReduce实现WordCount单词统计_wordcount只统计长度超过2的单词怎么设计mapreduce函数
- 102024年的七大前端Web开发趋势_2024 年 7 个 web 前端开发趋势
当前位置: article > 正文
基于python语言dlib库和opencv库的视频眨眼检测_python眨眼识别
作者:2023面试高手 | 2024-03-27 14:27:58
赞
踩
python眨眼识别
功能说明:
基于python编程语言,使用dlib 和opencv开发的视频眨眼检测。
环境:
* python 3.6.8
* opencv 3.4.2.16
* dlib 19.7.0
原理:
1.使用opencv-python读取处理视频图像
2.使用线程机制处理人脸检测关键点
3.根据dlib算法检测到的关键点计算眼部特征,通过欧氏距离计算确定是睁眼还是闭眼
4.统计闭眼次数并在视频图片中绘制结果
原始代码:
- # 基于opencv-python和dlib库的视频眨眼检测
-
- # 导入工具包
- from scipy.spatial import distance as dist
- from collections import OrderedDict
- import numpy as np
- import argparse
- import time
- # pip install dlib==19.6.1 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
- import dlib
- # pip install opencv-python==3.4.1
- import cv2
-
- # 关键点排序
- FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS = OrderedDict([
- ("mouth", (48, 68)),
- ("right_eyebrow", (17, 22)),
- ("left_eyebrow", (22, 27)),
- ("right_eye", (36, 42)),
- ("left_eye", (42, 48)),
- ("nose", (27, 36)),
- ("jaw", (0, 17))
- ])
-
-
- # http://vision.fe.uni-lj.si/cvww2016/proceedings/papers/05.pdf
- def eye_aspect_ratio(eye):
- """
- 计算眼睛上下关键点欧式距离
- :param eye:眼睛关键点位置
- :return: 眼睛睁开程度
- """
- # 计算距离,竖直的
- A = dist.euclidean(eye[1], eye[5])
- B = dist.euclidean(eye[2], eye[4])
- # 计算距离,水平的
- C = dist.euclidean(eye[0], eye[3])
- # ear值
- ear = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
- return ear
-
-
- # 输入参数
- ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
- ap.add_argument("-p", "--shape-predictor", required=True,
- help="path to facial landmark predictor")
- ap.add_argument("-v", "--video", type=str, default="",
- help="path to input video file")
- args = vars(ap.parse_args())
- print(args)
- # 设置判断参数
- EYE_AR_THRESH = 0.3 # 低于该值则判断为眨眼
- EYE_AR_CONSEC_FRAMES = 3
-
- # 初始化计数器
- COUNTER = 0
- TOTAL = 0
-
- # 检测与定位工具
- print("[INFO] loading facial landmark predictor...")
- detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
- #predictor = dlib.shape_predictor(args["shape_predictor"])
- predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
- # 分别取两个眼睛区域
- (lStart, lEnd) = FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS["left_eye"]
- (rStart, rEnd) = FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS["right_eye"]
-
- # 读取视频
- print("[INFO] starting video stream thread...")
- #vs = cv2.VideoCapture(args["video"])
- vs = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
- #vs = FileVideoStream(args["video"]).start()
- time.sleep(1.0)
-
-
- def shape_to_np(shape, dtype="int"):
- # 创建68*2
- coords = np.zeros((shape.num_parts, 2), dtype=dtype)
- # 遍历每一个关键点
- # 得到坐标
- for i in range(0, shape.num_parts):
- coords[i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
- return coords
-
-
- # 遍历每一帧
- while True:
- # 预处理
- frame = vs.read()[1]
- if frame is None:
- break
-
- (h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
- width = 1200
- r = width / float(w)
- dim = (width, int(h * r))
- frame = cv2.resize(frame, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
- gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
- # 检测人脸
- rects = detector(gray, 0)
-
- # 遍历每一个检测到的人脸
- for rect in rects:
- # 获取坐标
- shape = predictor(gray, rect)
- shape = shape_to_np(shape)
-
- # 分别计算ear值
- leftEye = shape[lStart:lEnd]
- rightEye = shape[rStart:rEnd]
- leftEAR = eye_aspect_ratio(leftEye)
- rightEAR = eye_aspect_ratio(rightEye)
-
- # 算一个平均的
- ear = (leftEAR + rightEAR) / 2.0
-
- # 绘制眼睛区域
- leftEyeHull = cv2.convexHull(leftEye)
- rightEyeHull = cv2.convexHull(rightEye)
- cv2.drawContours(frame, [leftEyeHull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
- cv2.drawContours(frame, [rightEyeHull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
-
- # 检查是否满足阈值
- if ear < EYE_AR_THRESH:
- COUNTER += 1
-
- else:
- # 如果连续几帧都是闭眼的,总数算一次
- if COUNTER >= EYE_AR_CONSEC_FRAMES:
- TOTAL += 1
-
- # 重置
- COUNTER = 0
-
- # 显示
- cv2.putText(frame, "Blinks: {}".format(TOTAL), (10, 30),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
- cv2.putText(frame, "EAR: {:.2f}".format(ear), (300, 30),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
-
- cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
- key = cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF
-
- if key == 27:
- break
-
- vs.release()
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

运行该代码进行调用摄像头检测和读取本地视频检测的命令如下:
- python detect_blinks.py -p shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat -v test.mp4
- python detect_blinks.py -p shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat -v 0
原始代码需要借助于命令行参数才可以运行,后来经过修改后,可以直接在编译器中运行的,代码如下:
- # 视频眨眼检测
- # 导入工具包
- from scipy.spatial import distance as dist
- from collections import OrderedDict
- import numpy as np
- import argparse
- import time
- # pip install dlib==19.6.1 -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
- import dlib
- # pip install opencv-python==3.4.1
- import cv2
-
- # 关键点排序
- FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS = OrderedDict([
- ("mouth", (48, 68)),
- ("right_eyebrow", (17, 22)),
- ("left_eyebrow", (22, 27)),
- ("right_eye", (36, 42)),
- ("left_eye", (42, 48)),
- ("nose", (27, 36)),
- ("jaw", (0, 17))
- ])
-
-
- # http://vision.fe.uni-lj.si/cvww2016/proceedings/papers/05.pdf
- def eye_aspect_ratio(eye):
- """
- 计算眼睛上下关键点欧式距离
- :param eye:眼睛关键点位置
- :return: 眼睛睁开程度
- """
- # 计算距离,竖直的
- A = dist.euclidean(eye[1], eye[5])
- B = dist.euclidean(eye[2], eye[4])
- # 计算距离,水平的
- C = dist.euclidean(eye[0], eye[3])
- # ear值
- ear = (A + B) / (2.0 * C)
- return ear
-
- # 设置判断参数
- EYE_AR_THRESH = 0.3 # 低于该值则判断为眨眼
- EYE_AR_CONSEC_FRAMES = 3
-
- # 初始化计数器
- COUNTER = 0
- TOTAL = 0
-
- # 检测与定位工具
- print("[INFO] loading facial landmark predictor...")
- detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector()
- predictor = dlib.shape_predictor('shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat')
-
- # 分别取两个眼睛区域
- (lStart, lEnd) = FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS["left_eye"]
- (rStart, rEnd) = FACIAL_LANDMARKS_68_IDXS["right_eye"]
-
- # 读取视频
- print("[INFO] starting video stream thread...")
- vs = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
- time.sleep(1.0)
-
-
- def shape_to_np(shape, dtype="int"):
- # 创建68*2
- coords = np.zeros((shape.num_parts, 2), dtype=dtype)
- # 遍历每一个关键点
- # 得到坐标
- for i in range(0, shape.num_parts):
- coords[i] = (shape.part(i).x, shape.part(i).y)
- return coords
-
-
- # 遍历每一帧
- while True:
- # 预处理
- frame = vs.read()[1]
- if frame is None:
- break
-
- (h, w) = frame.shape[:2]
- width = 1200
- r = width / float(w)
- dim = (width, int(h * r))
- frame = cv2.resize(frame, dim, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
- gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
- # 检测人脸
- rects = detector(gray, 0)
-
- # 遍历每一个检测到的人脸
- for rect in rects:
- # 获取坐标
- shape = predictor(gray, rect)
- shape = shape_to_np(shape)
-
- # 分别计算ear值
- leftEye = shape[lStart:lEnd]
- rightEye = shape[rStart:rEnd]
- leftEAR = eye_aspect_ratio(leftEye)
- rightEAR = eye_aspect_ratio(rightEye)
-
- # 算一个平均的
- ear = (leftEAR + rightEAR) / 2.0
-
- # 绘制眼睛区域
- leftEyeHull = cv2.convexHull(leftEye)
- rightEyeHull = cv2.convexHull(rightEye)
- cv2.drawContours(frame, [leftEyeHull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
- cv2.drawContours(frame, [rightEyeHull], -1, (0, 255, 0), 1)
-
- # 检查是否满足阈值
- if ear < EYE_AR_THRESH:
- COUNTER += 1
-
- else:
- # 如果连续几帧都是闭眼的,总数算一次
- if COUNTER >= EYE_AR_CONSEC_FRAMES:
- TOTAL += 1
-
- # 重置
- COUNTER = 0
-
- # 显示
- cv2.putText(frame, "Blinks: {}".format(TOTAL), (10, 30),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
- cv2.putText(frame, "EAR: {:.2f}".format(ear), (300, 30),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 0, 255), 2)
-
- cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)
- key = cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF
-
- if key == 27:
- break
-
- vs.release()
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()

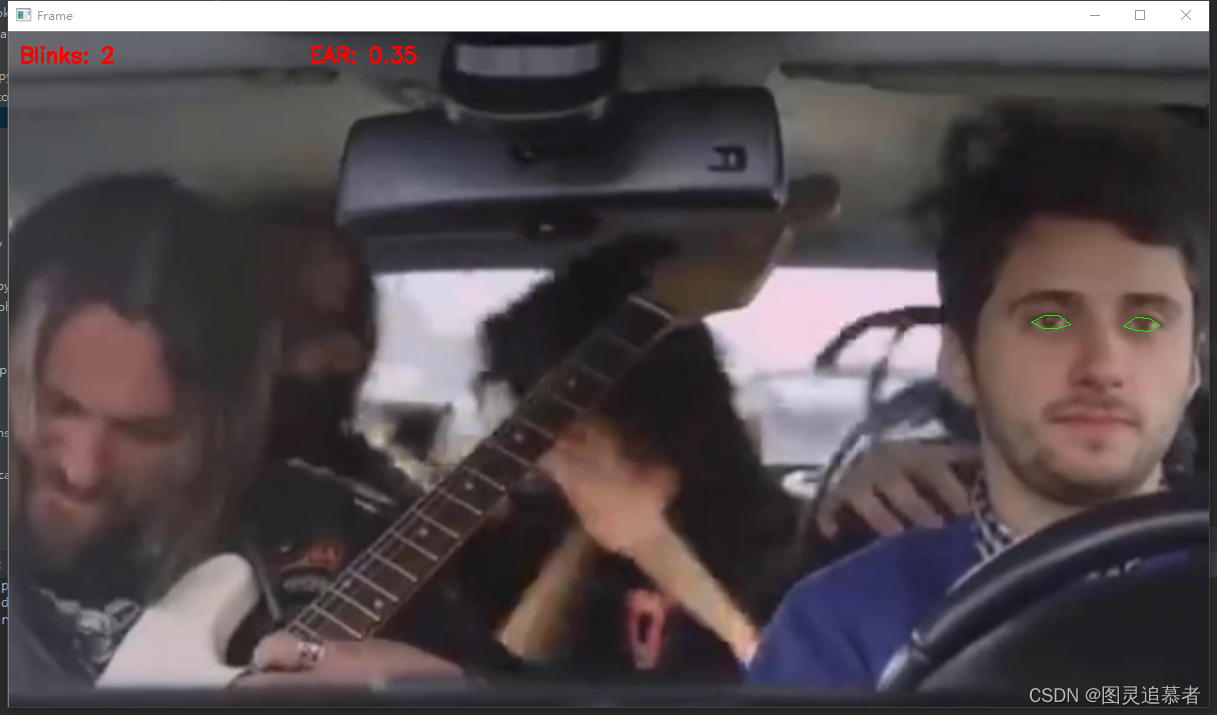
检测效果如下:
下载链接:https://mp.csdn.net/mp_download/manage/download/UpDetailed
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop】
推荐阅读
相关标签


