热门标签
热门文章
- 1windows的cmd命令中如何使用延迟方法【ping -n 30 127.0.0.1 > null】_ping -n 3 127.0.0.1>nul
- 2JS中的惰性函数_js 惰性函数
- 3自动驾驶系统概述
- 4html+css_css
- 5python小波包分解_小波包获得某个节点信号的几个细节问题
- 6修改system.img的文件的权限和属性:使用make.ext4fs的方法_system.ext4.win
- 7Win10 配置ADB安装2023.7.12版本_adb windows
- 8Redis学习笔记:基础篇数据结构与对象_embstr 是哪两个单词
- 9大数据毕业设计 opencv指纹识别系统 - python 图像识别_基于opencv的毕业设计
- 10LocalDB的使用详解
当前位置: article > 正文
Python BiLSTM_CRF医学文本标注,医学命名实体识别,NER,双向长短记忆神经网络和条件随机场应用实例,BiLSTM_CRF实现代码_bilstm-crf代码
作者:小小林熬夜学编程 | 2024-04-05 21:28:25
赞
踩
bilstm-crf代码
具体参考的哪一位大神的代码记不清了,在此表示感谢一下:
进入正题
- import torch
- import torch.autograd as autograd
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.optim as optim
1.设置随机种子
torch.manual_seed(1)2.torch.max(input, dim) 函数
output = torch.max(input, dim)
输入
input是softmax函数输出的一个tensordim是max函数索引的维度0/1,0是每列的最大值,1是每行的最大值
输出
- 函数会返回两个
tensor,第一个tensor是每行的最大值,softmax的输出中最大的是1,所以第一个tensor是全1的tensor;第二个tensor是每行最大值的索引。
- def argmax(vec):
- _,idx = torch.max(vec,1)
- return idx.item()
3.将 idxs(位置下标)的列表转化为tensor格式
- def prepare_sequence(seq, to_ix):
- idxs = [to_ix[w] for w in seq]
- return torch.tensor(idxs, dtype=torch.long)
4. LogSumExp(LSE)技巧,主要解决计算Softmax或CrossEntropy2时出现的上溢(overflow)或下溢(underflow)问题。
LSE被定义为参数指数之和的对数:

输入可以看成是一个n维的向量,输出是一个标量。
- def log_sum_exp(vec):
- max_score = vec[0, argmax(vec)]
- max_score_broadcast = max_score.view(1, -1).expand(1, vec.size()[1])
- return max_score + \
- torch.log(torch.sum(torch.exp(vec - max_score_broadcast)))
5.双向长短记忆神经网络和条件随机场
- class BiLSTM_CRF(nn.Module):
-
- def __init__(self, vocab_size, tag_to_ix, embedding_dim, hidden_dim):
- super(BiLSTM_CRF, self).__init__()
- self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
- self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
- self.vocab_size = vocab_size
- self.tag_to_ix = tag_to_ix
- self.tagset_size = len(tag_to_ix)
-
- self.word_embeds = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
- self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim // 2,
- num_layers=1, bidirectional=True)
-
- # Maps the output of the LSTM into tag space.
- # 将 LSTM 的输出映射到标签空间。
- self.hidden2tag = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, self.tagset_size)
-
- # Matrix of transition parameters. Entry i,j is the score of
- # transitioning *to* i *from* j.
- # 转换参数矩阵。 条目 i,j 是转换 *to* i *from* j.
- self.transitions = nn.Parameter(
- torch.randn(self.tagset_size, self.tagset_size))
-
- # These two statements enforce the constraint that we never transfer
- # to the start tag and we never transfer from the stop tag
- # 这两个语句强制我们从不转移到开始标签并且我们从不从停止标签转移的约束
- self.transitions.data[tag_to_ix[START_TAG], :] = -10000
- self.transitions.data[:, tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]] = -10000
-
- self.hidden = self.init_hidden()
-
- def init_hidden(self):
- return (torch.randn(2, 1, self.hidden_dim // 2),
- torch.randn(2, 1, self.hidden_dim // 2))
-
- def _forward_alg(self, feats):
- # Do the forward algorithm to compute the partition function
- init_alphas = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000.)
- # START_TAG has all of the score.
- init_alphas[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0.
-
- # Wrap in a variable so that we will get automatic backprop
- forward_var = init_alphas
-
- # Iterate through the sentence
- for feat in feats:
- alphas_t = [] # The forward tensors at this timestep
- for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
- # broadcast the emission score: it is the same regardless of
- # the previous tag
- emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(
- 1, -1).expand(1, self.tagset_size)
- # the ith entry of trans_score is the score of transitioning to
- # next_tag from i
- trans_score = self.transitions[next_tag].view(1, -1)
- # The ith entry of next_tag_var is the value for the
- # edge (i -> next_tag) before we do log-sum-exp
- next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score
- # The forward variable for this tag is log-sum-exp of all the
- # scores.
- alphas_t.append(log_sum_exp(next_tag_var).view(1))
- forward_var = torch.cat(alphas_t).view(1, -1)
- terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
- alpha = log_sum_exp(terminal_var)
- return alpha
-
- def _get_lstm_features(self, sentence):
- self.hidden = self.init_hidden()
- embeds = self.word_embeds(sentence).view(len(sentence), 1, -1)
- lstm_out, self.hidden = self.lstm(embeds, self.hidden)
- lstm_out = lstm_out.view(len(sentence), self.hidden_dim)
- lstm_feats = self.hidden2tag(lstm_out)
- return lstm_feats
-
- def _score_sentence(self, feats, tags):
- # Gives the score of a provided tag sequence
- score = torch.zeros(1)
- tags = torch.cat([torch.tensor([self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]], dtype=torch.long), tags])
- for i, feat in enumerate(feats):
- score = score + \
- self.transitions[tags[i + 1], tags[i]] + feat[tags[i + 1]]
- score = score + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG], tags[-1]]
- return score
-
- def _viterbi_decode(self, feats):
- backpointers = []
-
- # Initialize the viterbi variables in log space
- init_vvars = torch.full((1, self.tagset_size), -10000.)
- init_vvars[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0
-
- # forward_var at step i holds the viterbi variables for step i-1
- forward_var = init_vvars
- for feat in feats:
- bptrs_t = [] # holds the backpointers for this step
- viterbivars_t = [] # holds the viterbi variables for this step
-
- for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
- # next_tag_var[i] holds the viterbi variable for tag i at the
- # previous step, plus the score of transitioning
- # from tag i to next_tag.
- # We don't include the emission scores here because the max
- # does not depend on them (we add them in below)
- next_tag_var = forward_var + self.transitions[next_tag]
- best_tag_id = argmax(next_tag_var)
- bptrs_t.append(best_tag_id)
- viterbivars_t.append(next_tag_var[0][best_tag_id].view(1))
- # Now add in the emission scores, and assign forward_var to the set
- # of viterbi variables we just computed
- forward_var = (torch.cat(viterbivars_t) + feat).view(1, -1)
- backpointers.append(bptrs_t)
-
- # Transition to STOP_TAG
- terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
- best_tag_id = argmax(terminal_var)
- path_score = terminal_var[0][best_tag_id]
-
- # Follow the back pointers to decode the best path.
- best_path = [best_tag_id]
- for bptrs_t in reversed(backpointers):
- best_tag_id = bptrs_t[best_tag_id]
- best_path.append(best_tag_id)
- # Pop off the start tag (we dont want to return that to the caller)
- start = best_path.pop()
- assert start == self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG] # Sanity check
- best_path.reverse()
- return path_score, best_path
-
- def neg_log_likelihood(self, sentence, tags):
- feats = self._get_lstm_features(sentence)
- forward_score = self._forward_alg(feats)
- gold_score = self._score_sentence(feats, tags)
- return forward_score - gold_score
-
- def forward(self, sentence): # dont confuse this with _forward_alg above.
- # Get the emission scores from the BiLSTM
- lstm_feats = self._get_lstm_features(sentence)
-
- # Find the best path, given the features.
- score, tag_seq = self._viterbi_decode(lstm_feats)
- # return score, tag_seq
- return tag_seq

6.基础参数设置:标注的起始标签和结束标签,词向量的维度(5)和隐藏层(4)设置
- START_TAG = "<START>"
- STOP_TAG = "<STOP>"
- EMBEDDING_DIM = 5
- HIDDEN_DIM = 4
7.序列标注的实例,示例就是两句医学文本,采用的BIO标注方法,B表示实体名词的起始位置,I表示实体名词的非起始位置的字符,O表示其它字符,这是最简单的标注样例。还有比较复杂的标注样例,如下所示:
- # Make up some training data
- training_data = [(
- "高 血 压 容 易 造 成 心 脏 病".split(),
- "B I I O O O O B I I".split()
- ), (
- "心 脏 病 易 造 成 心 肌 梗 死".split(),
- "B I I O O O B I I I".split()
- )]
- print(training_data)

8.数据清洗过程, 建立字典-id
- word_to_ix = {}
- for sentence, tags in training_data:
- # print(tags)
- for word in sentence:
- if word not in word_to_ix:
- word_to_ix[word] = len(word_to_ix)
- print(word_to_ix)

9.标签设置,将标签进行id化,导入模型,开始BiLSTM+CRF模型的训练
- tag_to_ix = {"B": 0, "I": 1, "O": 2, START_TAG: 3, STOP_TAG: 4}
-
- model = BiLSTM_CRF(len(word_to_ix), tag_to_ix, EMBEDDING_DIM, HIDDEN_DIM)
- optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, weight_decay=1e-4)
-
- # Check predictions before training
- # 训练前检查预测
- with torch.no_grad():
- precheck_sent = prepare_sequence(training_data[0][0], word_to_ix)
- precheck_tags = torch.tensor([tag_to_ix[t] for t in training_data[0][1]], dtype=torch.long)
- print('样本一的真实标签:'+ str(precheck_tags.tolist()))
- print('未训练模型的预测:'+ str(model(precheck_sent)))
-
- print('=============开始BiLSTM+CRF模型的训练=============')
- # Make sure prepare_sequence from earlier in the LSTM section is loaded
- for epoch in range(200): # again, normally you would NOT do 300 epochs, it is toy data
- for sentence, tags in training_data:
- # Step 1. Remember that Pytorch accumulates gradients.
- # We need to clear them out before each instance
- model.zero_grad()
-
- # Step 2. Get our inputs ready for the network, that is,
- # turn them into Tensors of word indices.
- sentence_in = prepare_sequence(sentence, word_to_ix)
- targets = torch.tensor([tag_to_ix[t] for t in tags], dtype=torch.long)
-
- # Step 3. Run our forward pass.
- loss = model.neg_log_likelihood(sentence_in, targets)
-
- # Step 4. Compute the loss, gradients, and update the parameters by
- # calling optimizer.step()
- loss.backward()
- optimizer.step()
- if epoch%50 == 0:
- print(f'模型训练第{epoch}轮的Loss值为:{loss[0]}')


10.保存训练好的模型
- # 保存训练好的模型
- output_path = 'ner_trained_model.h5'
- torch.save(model, output_path)
- print('=============训练结束,保存训练好的模型=============\n\n')
生成如下文件

11.加载训练好的模型,进行文本标注,举了一个例子:
test_data = ['高', '血', '压', '容', '易', '造', '成', '心', '脏', '病']
- # 加载训练好的模型
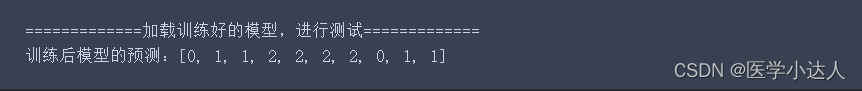
- print('=============加载训练好的模型,进行测试=============')
- test_data = ['高', '血', '压', '容', '易', '造', '成', '心', '脏', '病']
- model_path = 'ner_trained_model.h5'
- trained_ner_model = torch.load(model_path)
- with torch.no_grad():
- precheck_sent = prepare_sequence(test_data, word_to_ix)
- result = model(precheck_sent)
- print('训练后模型的预测:' ,result)
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小小林熬夜学编程/article/detail/368015?site=
推荐阅读
相关标签


