- 1Java架构直通车——SpringBoot run()方法过后发生了什么_springboot start the application run 之后
- 2centos本地yum源配置_centos配置本地yum源
- 3Ubuntu安装ToDesk远程控制软件
- 4❤ vue主要使用的版本和对应体系_vue版本
- 5宇视业软视频及智能业务子系统录像检索配置指导_宇视视频监控管理平台录像怎么看
- 6【CSDN编程竞赛 第六期】我的第一场编程竞赛。_csdn编程比赛
- 7git同一分支上多个commit合成一个的操作_把多个commit合并成一个patch
- 8Java基于springboot的网盘文件管理系统设计与实现_springboot和fastdfs实现网盘应用
- 9Android Studio如何打jar包和aar包并使用_android studio 打jar包
- 10html悬浮广告实现_html制作弹出广告csdn
BPE系列之—— BPE算法
赞
踩
序
- 在看transformer的代码时,看到了这个预处理,记得在最初做cnn情感分类的时候想过如何解决低频词和未登录词的问题,大致看过它,今天正好,趁此机会,学习一下这个算法。
- 此算法在2016年,由《Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units》提出,应用于机器翻译,解决 集外词(OOV)和罕见词(Rare word)问题。
- Neural machine translation (NMT) models typically operate with a fixed vocabulary, but translation is an open-vocabulary problem.
- Previous work addresses the translation of out-of-vocabulary words by backing off to a dictionary.
- In this paper, we introduce a simpler and more effective approach, making the NMT model capable of open-vocabulary translation by encoding rare and unknown words as sequences of subword units
背景
-
前文我们说了seq2seq OOV词的原因和大致解决思路,这里我们从另一个角度简单说一下机器翻译里面OOV的原因:
-
机器翻译是一种自动将源语言转换为目标语言的过程,整个过程一般采用神经网络(encoder-decoder)结构。
-
(1) 需要通过固定的词典对平行语料进行表示,词典大小一般控制在30k-60k,希望减少词表的大小,从而提高时间和空间效率。
-
(2) 同时还希望文本长度尽可能的短,因为文本长度的增加会降低效率并增加神经模型传递信息所需的距离(LSTM),文本越长信息丢失的可能性越大,后面再机器翻译中引入attention以解决此问题。这就导致了很多未登录词(OOV)和罕见词(Rare Words)。
Why is it?
-
Word-level NMT的缺点
-
对于word-level的NMT模型,翻译out-of-vocabulary的单词会回退到dictionary里面去查找。有下面几个缺点:
- 这种技术在实际上使这种假设并不成立。比如源单词和目标单词并不是一对一的,你怎么找呢
- 不能够翻译或者产生未见单词
- 把unknown单词直接copy到目标句子中,对于人名有时候可以。但是有时候却需要改变形态或者直译。
-
我们的目标是建立open-vocabulary的翻译模型,不用针对稀有词汇去查字典(word-level的做法)。事实证明,subword模型效果比传统大词汇表方法更好、更精确。Subword神经网络模型可以从subword表达中学习到组合和直译等能力,也可以有效的产生不在训练数据集中的词汇。本文主要有下面两个贡献
-
open-vocabulary的问题可以通过对稀有词汇使用subword units单元来编码解决
-
采用Byte pair encoding (BPE) 算法来进行分割。BPE通过一个固定大小的词汇表来表示开放词汇,这个词汇表里面的是变长的字符串序列。这是一种对于神经网络模型非常合适的词分割策略。
BPE
- 说在前面:可能是我状态不好,也可能是每个人理解方式不同,原本以为很快就解决这个东西了,但是拖了一下午…看了很多文章,都是晕晕忽忽的…这篇论文给出了github对应代码,但是很“重”,有许多为了优化的操作。
- 我觉得单纯理解是离不开论文的,所以我以我自己最终理解的方式呈现。
解码代码
- 原论文的代码:

- 理解算法最好的方式是看懂算法,看不懂我们就打印出来!
import re, collections # 返回字典key中char 组合的频率 def get_stats(vocab): pairs = collections.defaultdict(int) for word, freq in vocab.items(): symbols = word.split() for i in range(len(symbols)-1): pairs[symbols[i],symbols[i+1]] += freq return pairs def merge_vocab(pair, v_in): v_out = {} bigram = re.escape(' '.join(pair)) p = re.compile(r'(?<!\S)' + bigram + r'(?!\S)') for word in v_in: w_out = p.sub(''.join(pair), word) v_out[w_out] = v_in[word] return v_out # 频率词典 vocab = {'l o w </w>' : 5, 'l o w e r </w>' : 2,'n e w e s t </w>':6, 'w i d e s t </w>':3} pairs = get_stats(vocab) print(pairs) best = max(pairs, key=pairs.get) print(best) print(merge_vocab(best, vocab))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
结果:
defaultdict(<class 'int'>, {('e', 'w'): 6, ('l', 'o'): 7, ('s', 't'): 9, ('e', 's'): 9, ('r', '</w>'): 2, ('w', 'e'): 8, ('d', 'e'): 3, ('w', 'i'): 3, ('e', 'r'): 2, ('n', 'e'): 6, ('o', 'w'): 7, ('w', '</w>'): 5, ('i', 'd'): 3, ('t', '</w>'): 9})
('s', 't')
{'l o w e r </w>': 2, 'l o w </w>': 5, 'n e w e st </w>': 6, 'w i d e st </w>': 3}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
-
我个人打印的时候,原代码里的一个循环给去。代码大致思路就是:
-
- input一个频率词典。(这个词典的word被弄成了类似于 'l o w < /w>'的方式,注意空格)。
-
- 每次循环,我都会合并这个词典里,pair_char最大的那对char,效果可以看上面的输出
-
- 根据我设置的循环次数,对这个词典循环1和2(注意,2操作会改变vocab的)。
-
这里面重要的不是这个vocab,重要的是每一次最大的那个pair-char,循环N此后,我们会得到N个它,类似于:
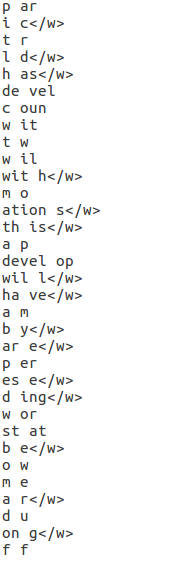
有一个不得不提的细节
我们评估两种应用BPE的方法:
- 学习两个独立的编码,一个用于源词汇,一个用于目标词汇,
- 学习联合两个词汇的编码(我们称之为联合BPE)。
- 前者具有在文本和词汇量方面更紧凑的优点,并且具有更强的保证每个 subword 单元已在相应语言的训练文本中被看到,而后者提高了源词汇和目标词汇之间分词的一致性。 如果我们独立地应用BPE,则相同的名称可能在两种语言中被不同地分段,这使得神经网络模型更难以学习 subword 单元之间的映射。 为了提高英语和俄语之间分词的一致性,尽管有不同的字母表,我们将俄语词汇用ISO-9音译成拉丁字符,然后将BPE合并操作音译回西里尔语,将它们应用到俄语培训文本中,以学习联合BPE编码。
解码
上面的操作类似于学习:pair-char,接下来我们需要使用它,可以理解为解码:
-
解码是也是按在词的范围中进行编码的,首先将词拆成一个一个的字符,然后按照训练得到的codec文件中的字符对来合并。
-
解码效果可以参考下图:
原始数据
foreign minister abdus sattar made the above remarks when xinhua reporters interviewed him this afternoon at the diaoyutai state guest house where he is staying .
president jiang has also paid visits to factories , farms , or cultural facilities and has met with representatives of overseas chinese and foreign nationals of chinese descent .
- 1
- 2
解码后数据
foreign minister ab@@ du@@ s sattar made the above remarks when xinhua reporters interviewed him this afternoon at the di@@ ao@@ yu@@ tai state guest house where he is staying .
president jiang has also paid visits to fac@@ tories , f@@ arms , or cultural facilities and has met with representatives of overseas chinese and foreign nationals of chinese desc@@ ent .
- 1
- 2
编码代码逻辑
- 本人就本论文的github代码的逻辑进行简单陈述,个人没有细看逻辑,这里给出宏观解决。
- 我个人认为这部分应该叫编码,因为我input的是我的密码本(pair-char)和我的明文。
- 有了密码本(注意,这个密码本从上到下的顺序是有意义的,哪个pair-char先找出来,就在上面)。利用密码本的pair-char加上这个pair-char对应的位置去进行"加密",同样注意,这个位置越小优先集合越高,也就是在这个文件中越靠前优先级越高(你可以思考一下为什么?)编程
- 对句子里单词循环编码(也就是我是一个一个单词编码的)(当然,编码前也需要做和解码时同样的预处理,low 单词变成 'l o w ')
我们就整个思路总结一下,一个很不恰当的比喻:
- 整个过程有这么一丝味道:
- 我在一个很大的数据集上训练,我得到了一个密码本。
- 现在我有一大段的明文,我需要用密码本对它进行加密,好,那我就对照这密码本,一个单词一个单词来加密。
- 我们可以和决策树的思路对比一下,建树的时候我是就整个数据集的信息建立的,用它去预测的时候却是一个一个样本,从根节点流入寻找它落到那个叶子节点上,Oh虽然这个对比没啥用…
注意
- 我看到很多人说解码时出来的vocab有用的,丝毫没有提到pair-char的重要性,个人看原代码传参数,其实就只用到了pari-char,没有vocab这个参数,所以我才有了上面行文里的见解,如果我的观点有误,请指教(ps:最后我还是被逼看了源码,虽然没细看)
参考
[ 1 ] Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units
[ 2 ]论文翻译版本
[ 3 ]神经网络机器翻译下的字符级方法
[ 4 ]subword-units
[ 5 ]SentencePiece,subword-nmt,bpe算法
[ 6 ]seq2seq模型中的未登录词处理
[ 7 ]NLP中的传统语言模型与神经语言模型
[ 8 ]NLP 笔记 - 平滑方法(Smoothing)小结
[ 9 ]使用BPE算法处理未登录词



