热门标签
热门文章
- 1大模型: 提示词工程(prompt engineering)_大模型的提示词作用是什么
- 2手把手做一个公众号GPT智能客服【二】实现微信公众号回复(订阅送源码!)_微信公众号回复消息接入大模型
- 3[问答]-ARM文档中的†和‡的含义_是什么意思
- 4【Vue】创建vue项目 npm ERR! code CERT_HAS_EXPIRED npm ERR! errno CERT_HAS_EXPIRED
- 5数据挖掘入门项目二手交易车价格预测之特征工程
- 6全连接网络(FC)、前馈神经网络(BP)、多层感知机(MLP)、人工神经网络(ANN)指的是一个东西吗_全连接神经网络和前馈神经网络
- 7从62%到5%‼️找人降重算代写吗_人工降重属于代写吗
- 8Pytorch模型部署开发板所遇到的坑....._torch模型部署到开发板
- 9《Python+Kivy(App开发)从入门到实践》自学笔记:第三章 图形绘制目录及知识点概览_kivy从入门到实践pdf
- 10从0开始实现一个Auto-GPT在WSL2环境中的部署和运行_wsl2 gptfast
当前位置: article > 正文
机器学习:分类决策树(Python)_决策树分类器python
作者:小丑西瓜9 | 2024-03-28 19:36:40
赞
踩
决策树分类器python
一、各种熵的计算
entropy_utils.py
- import numpy as np # 数值计算
- import math # 标量数据的计算
-
-
- class EntropyUtils:
- """
- 决策树中各种熵的计算,包括信息熵、信息增益、信息增益率、基尼指数。
- 统一要求:按照信息增益最大、信息增益率最大、基尼指数增益最大
- """
- @staticmethod
- def _set_sample_weight(sample_weight, n_samples):
- """
- 扩展到集成学习,此处为样本权重的设置
- :param sample_weight: 各样本的权重
- :param n_samples: 样本量
- :return:
- """
- if sample_weight is None:
- sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_samples)
- return sample_weight
-
- def cal_info_entropy(self, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算样本的信息熵
- :param y_labels: 递归样本子集中类别集合或特征取值
- :param sample_weight: 各样本的权重
- :return:
- """
- y = np.asarray(y_labels)
- sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))
- y_values = np.unique(y) # 样本中不同类别值
- ent_y = 0.0
- for val in y_values:
- p_i = len(y[y == val]) * np.mean(sample_weight[y == val]) / len(y)
- ent_y += -p_i * math.log2(p_i)
- return ent_y
-
- def conditional_entropy(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算条件熵,给定特征属性的情况下,信息熵的计算
- :param feature_x: 某个样本特征
- :param y_labels: 递归样本子集中的类别集合
- :param sample_weight: 各样本的权重
- :return:
- """
- x, y = np.asarray(feature_x), np.asarray(y_labels)
- sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))
- cond_ent = 0.0
- for x_val in np.unique(x):
- x_idx = np.where(x == x_val) # 某个特征取值的样本索引集合
- sub_x, sub_y = x[x_idx], y[x_idx]
- sub_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_idx]
- p_k = len(sub_y) / len(y)
- cond_ent += p_k * self.cal_info_entropy(sub_y, sub_sample_weight)
- return cond_ent
-
- def info_gain(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算信息增益
- :param feature_x:
- :param y_labels:
- :param sample_weight:
- :return:
- """
- return self.cal_info_entropy(y_labels, sample_weight) - \
- self.conditional_entropy(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight)
-
- def info_gain_rate(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算信息增益率
- :param feature_x:
- :param y_labels:
- :param sample_weight:
- :return:
- """
- return self.info_gain(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight) / \
- self.cal_info_entropy(feature_x, sample_weight)
-
- def cal_gini(self, y_label, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算当前特征或类别集合的基尼值
- :param y_label: 递归样本子集中类别集合或特征取值
- :param sample_weight:
- :return:
- """
- y = np.asarray(y_label)
- sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))
- y_values = np.unique(y)
- gini_val = 1.0
- for val in y_values:
- p_k = len(y[y == val]) * np.mean(sample_weight[y == val]) / len(y)
- gini_val -= p_k ** 2
- return gini_val
-
- def conditional_gini(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算条件基尼指数
- :param feature_x:
- :param y_labels:
- :param sample_weight:
- :return:
- """
- x, y = np.asarray(feature_x), np.asarray(y_labels)
- sample_weight = self._set_sample_weight(sample_weight, len(y))
- cond_gini = 0.0
- for x_val in np.unique(x):
- x_idx = np.where(x == x_val) # 某个特征取值的样本索引集合
- sub_x, sub_y = x[x_idx], y[x_idx]
- sub_sample_weight = sample_weight[x_idx]
- p_k = len(sub_y) / len(y)
- cond_gini += p_k * self.cal_gini(sub_y, sub_sample_weight)
- return cond_gini
-
- def gini_gain(self, feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 计算基尼指数增益
- :param feature_x:
- :param y_labels:
- :param sample_weight:
- :return:
- """
- return self.cal_gini(y_labels, sample_weight) - \
- self.conditional_gini(feature_x, y_labels, sample_weight)
-
-
- # if __name__ == '__main__':
- # y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 50)
- # entropy = EntropyUtils()
- # ent = entropy.cal_info_entropy(y)
- # print(ent)
-

二、连续特征数据的离散分箱
data_bin_wrapper.py
- import numpy as np
-
-
- class DataBinsWrapper:
- """
- 连续特征数据的离散化,分箱(分段)操作,根据用户传参max_bins,计算分位数,以分位数分箱(分段)
- 然后根据样本特征取值所在区间段(哪个箱)位置索引标记当前值
- 1. fit(x)根据样本进行分箱
- 2. transform(x)根据已存在的箱,把数据分成max_bins类
- """
- def __init__(self, max_bins=10):
- self.max_bins = max_bins # 分箱数:10%,20%,...,90%
- self.XrangeMap = None # 箱(区间段)
-
- def fit(self, x_samples):
- """
- 根据样本进行分箱
- :param x_samples: 样本(二维数组 n * k),或一个特征属性的数据(二维 n * 1)
- :return:
- """
- if x_samples.ndim == 1: # 一个特征属性,转换为二维数组
- n_features = 1
- x_samples = x_samples[:, np.newaxis] # 添加一个轴,转换为二维数组
- else:
- n_features = x_samples.shape[1]
-
- # 构建分箱,区间段
- self.XrangeMap = [[] for _ in range(n_features)]
- for idx in range(n_features):
- x_sorted = sorted(x_samples[:, idx]) # 按特征索引取值,并从小到大排序
- for bin in range(1, self.max_bins):
- p = (bin / self.max_bins) * 100 // 1
- p_val = np.percentile(x_sorted, p)
- self.XrangeMap[idx].append(p_val)
- self.XrangeMap[idx] = sorted(list(set(self.XrangeMap[idx])))
-
- def transform(self, x_samples, XrangeMap=None):
- """
- 根据已存在的箱,把数据分成max_bins类
- :param x_samples: 样本(二维数组 n * k),或一个特征属性的数据(二维 n * 1)
- :return:
- """
- if x_samples.ndim == 1:
- if XrangeMap is not None:
- return np.asarray(np.digitize(x_samples, XrangeMap[0])).reshape(-1)
- else:
- return np.asarray(np.digitize(x_samples, self.XrangeMap[0])).reshape(-1)
- else:
- return np.asarray([np.digitize(x_samples[:, i], self.XrangeMap[i])
- for i in range(x_samples.shape[1])]).T
-
-
-
- # if __name__ == '__main__':
- # x = np.random.randn(10, 5)
- # print(x)
- # dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=5)
- # dbw.fit(x)
- # print(dbw.XrangeMap)
- # print(dbw.transform(x))

三、可视化分类边界函数
plt_decision_funtion.py
- import matplotlib.pylab as plt
- import numpy as np
-
-
- def plot_decision_function(X, y, clf, acc=None, title_info=None, is_show=True, support_vectors=None):
- """
- 可视化分类边界函数
- :param X, y: 测试样本与类别
- :param clf: 分类模型
- :param acc: 模型分类正确率
- :param title_info: 可视化标题title的额外信息
- :param is_show: 是否在当前显示图像,用于父函数绘制子图
- :param support_vectors: 扩展支持向量机
- :return:
- """
- if is_show:
- plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
- # 根据特征变量的最小值和最大值,生成二维网络,用于绘制等值线
- x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
- y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
- xi, yi = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.02),
- np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.02))
- y_pred = clf.predict(np.c_[xi.ravel(), yi.ravel()]) # 模型预测值
- y_pred = y_pred.reshape(xi.shape)
- plt.contourf(xi, yi, y_pred, alpha=0.4)
- plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], alpha=0.8, c=y, edgecolors="k")
- plt.xlabel("Feature 1", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
- plt.ylabel("Feature 2", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
- if acc:
- if title_info:
- plt.title("Model Classification Boundary %s \n(accuracy = %.5f)"
- % (title_info, acc), fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
- else:
- plt.title("Model Classification Boundary (accuracy = %.5f)"
- % acc, fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
- else:
- if title_info:
- plt.title("Model Classification Boundary %s"
- % title_info, fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
- else:
- plt.title("Model Classification Boundary", fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
- if support_vectors is not None: # 可视化支持向量,针对SVM
- plt.scatter(X[support_vectors, 0], X[support_vectors, 1],
- s=50, c="None", alpha=0.7, edgecolors="red")
- if is_show:
- plt.show()

四、熵计算的测试
test_entropy.py
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- from utils.entropy_utils import EntropyUtils
- from utils.data_bin_wrapper import DataBinsWrapper
-
-
- data = pd.read_csv("data/watermelon.csv").iloc[:, 1:]
- feat_names = data.columns[:6]
- y = data.iloc[:, -1]
- ent_obj = EntropyUtils()
-
- print("各特征的信息增益如下:")
- for feat in feat_names:
- print(feat, ":", ent_obj.info_gain(data.loc[:, feat], y))
-
- print("=" * 60)
- print("各特征的信息增益率如下:")
- for feat in feat_names:
- print(feat, ":", ent_obj.info_gain_rate(data.loc[:, feat], y))
-
- print("=" * 60)
- print("各特征的基尼指数增益如下:")
- for feat in feat_names:
- print(feat, ":", ent_obj.gini_gain(data.loc[:, feat], y))
-
- print("=" * 60)
- x1 = np.asarray(data.loc[:, ["密度", "含糖率"]])
- print(x1)
- dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=8)
- dbw.fit(x1)
- print(dbw.transform(x1))
-

五、树的结点信息封装
tree_node.py
-
- class TreeNode_C:
- """
- 决策树分类算法,树的结点信息封装,实体类:setXXX()、getXXX()
- """
- def __init__(self, feature_idx: int = None, feature_val=None, criterion_val: float = None,
- n_samples: int = None, target_dist: dict = None, weight_dist: dict = None,
- left_child_Node=None, right_child_Node=None):
- """
- 决策树结点信息封装
- :param feature_idx: 特征索引,如果指定特征属性的名称,可以按照索引取值
- :param feature_val: 特征取值
- :param criterion_val: 划分结点的标准:信息增益(率)、基尼指数增益
- :param n_samples: 当前结点所包含的样本量
- :param target_dist: 当前结点类别分布:0-25%,1-50%,2-25%
- :param weight_dist: 当前结点所包含的样本权重分布
- :param left_child_Node: 左子树
- :param right_child_Node: 右子树
- """
- self.feature_idx = feature_idx
- self.feature_val = feature_val
- self.criterion_val = criterion_val
- self.n_samples = n_samples
- self.target_dist = target_dist
- self.weight_dist = weight_dist
- self.left_child_Node = left_child_Node # 递归
- self.right_child_Node = right_child_Node # 递归
-
- def level_order(self):
- """
- 按层次遍历树...
- :return:
- """
- pass
-
- # def get_feature_idx(self):
- # return self.get_feature_idx()
- #
- # def set_feature_idx(self, feature_idx):
- # self.feature_idx = feature_idx
-
-

六、分类决策树算法的实现
decision_tree_C.py
- import numpy as np
- from utils.entropy_utils import EntropyUtils
- from utils.tree_node import TreeNode_C
- from utils.data_bin_wrapper import DataBinsWrapper
-
-
- class DecisionTreeClassifier:
- """
- 分类决策树算法实现:无论是ID3、C4.5或CART,统一按照二叉树构造
- 1. 划分标准:信息增益(率)、基尼指数增益,都按照最大值选择特征属性
- 2. 创建决策树fit(),递归算法实现,注意出口条件
- 3. 预测predict_proba()、predict() --> 对树的搜索
- 4. 数据的预处理操作,尤其是连续数据的离散化,分箱
- 5. 剪枝处理
- """
- def __init__(self, criterion="CART", is_feature_all_R=False, dbw_feature_idx=None,
- max_depth=None, min_sample_split=2, min_sample_leaf=1,
- min_impurity_decrease=0, max_bins=10):
- self.utils = EntropyUtils() # 结点划分类
- self.criterion = criterion # 结点的划分标准
- if criterion.lower() == "cart":
- self.criterion_func = self.utils.gini_gain # 基尼指数增益
- elif criterion.lower() == "c45":
- self.criterion_func = self.utils.info_gain_rate # 信息增益率
- elif criterion.lower() == "id3":
- self.criterion_func = self.utils.info_gain # 信息增益
- else:
- raise ValueError("参数criterion仅限cart、c45或id3...")
- self.is_feature_all_R = is_feature_all_R # 所有样本特征是否全是连续数据
- self.dbw_feature_idx = dbw_feature_idx # 混合类型数据,可指定连续特征属性的索引
- self.max_depth = max_depth # 树的最大深度,不传参,则一直划分下去
- self.min_sample_split = min_sample_split # 最小的划分结点的样本量,小于则不划分
- self.min_sample_leaf = min_sample_leaf # 叶子结点所包含的最小样本量,剩余的样本小于这个值,标记叶子结点
- self.min_impurity_decrease = min_impurity_decrease # 最小结点不纯度减少值,小于这个值,不足以划分
- self.max_bins = max_bins # 连续数据的分箱数,越大,则划分越细
- self.root_node: TreeNode_C() = None # 分类决策树的根节点
- self.dbw = DataBinsWrapper(max_bins=max_bins) # 连续数据离散化对象
- self.dbw_XrangeMap = {} # 存储训练样本连续特征分箱的端点
- self.class_values = None # 样本的类别取值
-
- def _data_bin_wrapper(self, x_samples):
- """
- 针对特定的连续特征属性索引dbw_feature_idx,分别进行分箱,考虑测试样本与训练样本使用同一个XrangeMap
- :param x_samples: 样本:即可以是训练样本,也可以是测试样本
- :return:
- """
- self.dbw_feature_idx = np.asarray(self.dbw_feature_idx)
- x_samples_prop = [] # 分箱之后的数据
- if not self.dbw_XrangeMap:
- # 为空,即创建决策树前所做的分箱操作
- for i in range(x_samples.shape[1]):
- if i in self.dbw_feature_idx: # 说明当前特征是连续数值
- self.dbw.fit(x_samples[:, i])
- self.dbw_XrangeMap[i] = self.dbw.XrangeMap
- x_samples_prop.append(self.dbw.transform(x_samples[:, i]))
- else:
- x_samples_prop.append(x_samples[:, i])
- else: # 针对测试样本的分箱操作
- for i in range(x_samples.shape[1]):
- if i in self.dbw_feature_idx: # 说明当前特征是连续数值
- x_samples_prop.append(self.dbw.transform(x_samples[:, i], self.dbw_XrangeMap[i]))
- else:
- x_samples_prop.append(x_samples[:, i])
- return np.asarray(x_samples_prop).T
-
- def fit(self, x_train, y_train, sample_weight=None):
- """
- 决策树的创建,递归操作前的必要信息处理
- :param x_train: 训练样本:ndarray,n * k
- :param y_train: 目标集:ndarray,(n, )
- :param sample_weight: 各样本的权重,(n, )
- :return:
- """
- x_train, y_train = np.asarray(x_train), np.asarray(y_train)
- self.class_values = np.unique(y_train) # 样本的类别取值
- n_samples, n_features = x_train.shape # 训练样本的样本量和特征属性数目
- if sample_weight is None:
- sample_weight = np.asarray([1.0] * n_samples)
- self.root_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建一个空树
- if self.is_feature_all_R: # 全部是连续数据
- self.dbw.fit(x_train)
- x_train = self.dbw.transform(x_train)
- elif self.dbw_feature_idx:
- x_train = self._data_bin_wrapper(x_train)
- self._build_tree(1, self.root_node, x_train, y_train, sample_weight)
- # print(x_train)
-
- def _build_tree(self, cur_depth, cur_node: TreeNode_C, x_train, y_train, sample_weight):
- """
- 递归创建决策树算法,核心算法。按先序(中序、后序)创建的
- :param cur_depth: 递归划分后的树的深度
- :param cur_node: 递归划分后的当前根结点
- :param x_train: 递归划分后的训练样本
- :param y_train: 递归划分后的目标集合
- :param sample_weight: 递归划分后的各样本权重
- :return:
- """
- n_samples, n_features = x_train.shape # 当前样本子集中的样本量和特征属性数目
- target_dist, weight_dist = {}, {} # 当前样本类别分布和权重分布 0-->30%,1-->70%
- class_labels = np.unique(y_train) # 不同的类别值
- for label in class_labels:
- target_dist[label] = len(y_train[y_train == label]) / n_samples
- weight_dist[label] = np.mean(sample_weight[y_train == label])
- cur_node.target_dist = target_dist
- cur_node.weight_dist = weight_dist
- cur_node.n_samples = n_samples
-
- # 递归出口判断
- if len(target_dist) <= 1: # 所有的样本全属于同一个类别,递归出口1
- # 如果为0,则表示当前样本集合为空,递归出口3
- return
- if n_samples < self.min_sample_split: # 当前结点所包含的样本量不足以划分
- return
- if self.max_depth is not None and cur_depth > self.max_depth: # 树的深度达到最大深度
- return
-
- # 划分标准,选择最佳的划分特征及其取值
- best_idx, best_val, best_criterion_val = None, None, 0.0
- for k in range(n_features): # 对当前样本集合中每个特征计算划分标准
- for f_val in np.unique(x_train[:, k]): # 当前特征的不同取值
- feat_k_values = (x_train[:, k] == f_val).astype(int) # 是当前取值f_val就是1,否则就是0
- criterion_val = self.criterion_func(feat_k_values, y_train, sample_weight)
- if criterion_val > best_criterion_val:
- best_criterion_val = criterion_val # 最佳的划分标准值
- best_idx, best_val = k, f_val # 当前最佳特征索引以及取值
-
- # 递归出口的判断
- if best_idx is None: # 当前属性为空,或者所有样本在所有属性上取值相同,无法划分
- return
- if best_criterion_val <= self.min_impurity_decrease: # 小于最小不纯度阈值,不划分
- return
- cur_node.criterion_val = best_criterion_val
- cur_node.feature_idx = best_idx
- cur_node.feature_val = best_val
-
- # print("当前划分的特征索引:", best_idx, "取值:", best_val, "最佳标准值:", best_criterion_val)
- # print("当前结点的类别分布:", target_dist)
-
- # 创建左子树,并递归创建以当前结点为子树根节点的左子树
- left_idx = np.where(x_train[:, best_idx] == best_val) # 左子树所包含的样本子集索引
- if len(left_idx) >= self.min_sample_leaf: # 小于叶子结点所包含的最少样本量,则标记为叶子结点
- left_child_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建左子树空结点
- # 以当前结点为子树根结点,递归创建
- cur_node.left_child_Node = left_child_node
- self._build_tree(cur_depth + 1, left_child_node, x_train[left_idx],
- y_train[left_idx], sample_weight[left_idx])
-
- right_idx = np.where(x_train[:, best_idx] != best_val) # 右子树所包含的样本子集索引
- if len(right_idx) >= self.min_sample_leaf: # 小于叶子结点所包含的最少样本量,则标记为叶子结点
- right_child_node = TreeNode_C() # 创建右子树空结点
- # 以当前结点为子树根结点,递归创建
- cur_node.right_child_Node = right_child_node
- self._build_tree(cur_depth + 1, right_child_node, x_train[right_idx],
- y_train[right_idx], sample_weight[right_idx])
-
- def _search_tree_predict(self, cur_node: TreeNode_C, x_test):
- """
- 根据测试样本从根结点到叶子结点搜索路径,判定类别
- 搜索:按照后续遍历
- :param x_test: 单个测试样本
- :return:
- """
- if cur_node.left_child_Node and x_test[cur_node.feature_idx] == cur_node.feature_val:
- return self._search_tree_predict(cur_node.left_child_Node, x_test)
- elif cur_node.right_child_Node and x_test[cur_node.feature_idx] != cur_node.feature_val:
- return self._search_tree_predict(cur_node.right_child_Node, x_test)
- else:
- # 叶子结点,类别,包含有类别分布
- # print(cur_node.target_dist)
- class_p = np.zeros(len(self.class_values)) # 测试样本的类别概率
- for i, c in enumerate(self.class_values):
- class_p[i] = cur_node.target_dist.get(c, 0) * cur_node.weight_dist.get(c, 1.0)
- class_p / np.sum(class_p) # 归一化
- return class_p
-
- def predict_proba(self, x_test):
- """
- 预测测试样本x_test的类别概率
- :param x_test: 测试样本ndarray、numpy数值运算
- :return:
- """
- x_test = np.asarray(x_test) # 避免传递DataFrame、list...
- if self.is_feature_all_R:
- if self.dbw.XrangeMap is not None:
- x_test = self.dbw.transform(x_test)
- else:
- raise ValueError("请先创建决策树...")
- elif self.dbw_feature_idx is not None:
- x_test = self._data_bin_wrapper(x_test)
- prob_dist = [] # 用于存储测试样本的类别概率分布
- for i in range(x_test.shape[0]):
- prob_dist.append(self._search_tree_predict(self.root_node, x_test[i]))
- return np.asarray(prob_dist)
-
- def predict(self, x_test):
- """
- 预测测试样本的类别
- :param x_test: 测试样本
- :return:
- """
- x_test = np.asarray(x_test) # 避免传递DataFrame、list...
- return np.argmax(self.predict_proba(x_test), axis=1)
-
- def _prune_node(self, cur_node: TreeNode_C, alpha):
- """
- 递归剪枝,针对决策树中的内部结点,自底向上,逐个考察
- 方法:后序遍历
- :param cur_node: 当前递归的决策树的内部结点
- :param alpha: 剪枝阈值
- :return:
- """
- # 若左子树存在,递归左子树进行剪枝
- if cur_node.left_child_Node:
- self._prune_node(cur_node.left_child_Node, alpha)
- # 若右子树存在,递归右子树进行剪枝
- if cur_node.right_child_Node:
- self._prune_node(cur_node.right_child_Node, alpha)
-
- # 针对决策树的内部结点剪枝,非叶结点
- if cur_node.left_child_Node is not None or cur_node.right_child_Node is not None:
- for child_node in [cur_node.left_child_Node, cur_node.right_child_Node]:
- if child_node is None:
- # 可能存在左右子树之一为空的情况,当左右子树划分的样本子集数小于min_samples_leaf
- continue
- if child_node.left_child_Node is not None or child_node.right_child_Node is not None:
- return
- # 计算剪枝前的损失值,2表示当前结点包含两个叶子结点
- pre_prune_value = 2 * alpha
- for child_node in [cur_node.left_child_Node, cur_node.right_child_Node]:
- # 计算左右叶子结点的经验熵
- if child_node is None:
- # 可能存在左右子树之一为空的情况,当左右子树划分的样本子集数小于min_samples_leaf
- continue
- for key, value in child_node.target_dist.items(): # 对每个叶子结点的类别分布
- pre_prune_value += -1 * child_node.n_samples * value * np.log(value) * \
- child_node.weight_dist.get(key, 1.0)
- # 计算剪枝后的损失值,当前结点即是叶子结点
- after_prune_value = alpha
- for key, value in cur_node.target_dist.items(): # 当前待剪枝的结点的类别分布
- after_prune_value += -1 * cur_node.n_samples * value * np.log(value) * \
- cur_node.weight_dist.get(key, 1.0)
- if after_prune_value <= pre_prune_value: # 进行剪枝操作
- cur_node.left_child_Node = None
- cur_node.right_child_Node = None
- cur_node.feature_idx, cur_node.feature_val = None, None
-
- def prune(self, alpha=0.01):
- """
- 决策树后剪枝算法(李航)C(T) + alpha * |T|
- :param alpha: 剪枝阈值,权衡模型对训练数据的拟合程度与模型的复杂度
- :return:
- """
- self._prune_node(self.root_node, alpha)
- return self.root_node
-

七、分类决策树算法的测试
test_decision_tree_C.py
- import pandas as pd
- from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
- from sklearn.datasets import load_iris, load_breast_cancer
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
- from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
-
-
- # data = pd.read_csv("data/watermelon.csv").iloc[:, 1:]
- # X = data.iloc[:, :-1]
- # y = data.iloc[:, -1]
-
- # iris = load_iris()
- # X, y = iris.data, iris.target
-
- # bc_data = load_breast_cancer()
- # X, y = bc_data.data, bc_data.target
-
- nursery = pd.read_csv("data/nursery.csv").dropna()
- X, y = np.asarray(nursery.iloc[:, :-1]), np.asarray(nursery.iloc[:, -1])
-
- y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(y)
-
- X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0, stratify=y)
-
- depth = np.linspace(2, 12, 11, dtype=np.int64)
- accuracy = []
-
- for d in depth:
- dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(is_feature_all_R=False, max_depth=d)
- dtc.fit(X_train, y_train)
- y_pred_labels = dtc.predict(X_test)
- acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_labels)
- # print(acc)
- accuracy.append(acc)
- # dtc = DecisionTreeClassifier(dbw_feature_idx=[6, 7], max_bins=8, max_depth=2)
- # dtc.fit(X, y)
- # y_pred_prob = dtc.predict_proba(X)
- # print(y_pred_prob)
-
- # print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred_labels))
-
- plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
- plt.plot(depth, accuracy, "ko-", lw=1)
- plt.show()
-


test_decision_tree_C_2.py
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
- from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
- from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
- from utils.plt_decision_function import plot_decision_function
-
-
- # 生成数据
- data, target = make_classification(n_samples=100, n_features=2, n_classes=2, n_informative=1, n_redundant=0,
- n_clusters_per_class=1, class_sep=0.8, random_state=21)
- # print(data)
- # print(target)
-
- cart_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(is_feature_all_R=True)
- cart_tree.fit(data, target)
- y_test_pred = cart_tree.predict(data)
- print(classification_report(target, y_test_pred))
- plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10))
- plt.subplot(221)
- acc = accuracy_score(target, y_test_pred)
- plot_decision_function(data, target, cart_tree, acc=acc, is_show=False, title_info="By CART UnPrune")
-
- # 剪枝处理
- alpha = [1, 3, 5]
- for i in range(3):
- cart_tree.prune(alpha=alpha[i])
- y_test_pred = cart_tree.predict(data)
- acc = accuracy_score(target, y_test_pred)
- plt.subplot(222 + i)
- plot_decision_function(data, target, cart_tree, acc=acc, is_show=False,
- title_info="By CART Prune α = %.1f" % alpha[i])
- plt.tight_layout()
- plt.show()



test_decision_tree_C_3.py
- import copy
-
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from decision_tree_C import DecisionTreeClassifier
- from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer, load_iris
- from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
- from utils.plt_decision_function import plot_decision_function
- from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
-
-
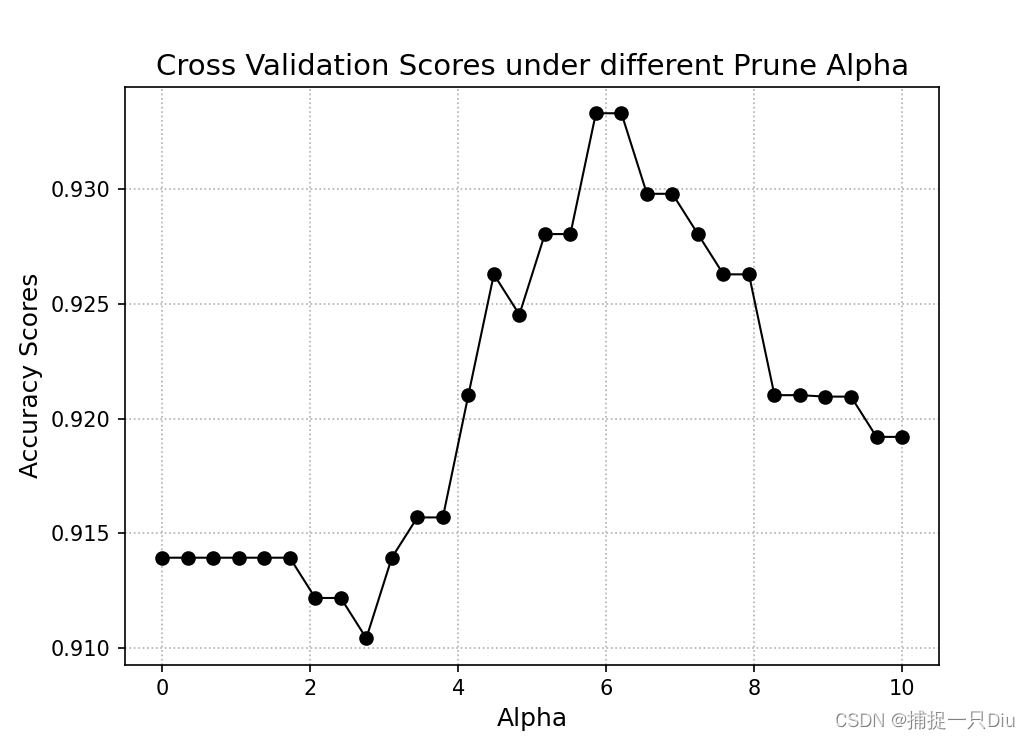
- bc_data = load_breast_cancer()
- X, y = bc_data.data, bc_data.target
- alphas = np.linspace(0, 10, 30)
- accuracy_scores = [] # 存储每个alpha阈值下的交叉验证均分
- cart = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="cart", is_feature_all_R=True, max_bins=10)
- for alpha in alphas:
- scores = []
- k_fold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10).split(X, y)
- for train_idx, test_idx in k_fold:
- tree = copy.deepcopy(cart)
- tree.fit(X[train_idx], y[train_idx])
- tree.prune(alpha=alpha)
- y_test_pred = tree.predict(X[test_idx])
- scores.append(accuracy_score(y[test_idx], y_test_pred))
- del tree
- print(alpha, ":", np.mean(scores))
- accuracy_scores.append(np.mean(scores))
-
- plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
- plt.plot(alphas, accuracy_scores, "ko-", lw=1)
- plt.grid(ls=":")
- plt.xlabel("Alpha", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
- plt.ylabel("Accuracy Scores", fontdict={"fontsize": 12})
- plt.title("Cross Validation Scores under different Prune Alpha", fontdict={"fontsize": 14})
- plt.show()
-

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小丑西瓜9/article/detail/330911?site
推荐阅读
相关标签


