- 1log2的快速算法_log2快速计算
- 2《虚拟仿真实验教学解决方案(BJBR)》(Yanlz+Unity+SteamVR+VR+AR+MR+HR+??BR??+??CR??+??DR??+??ER??+虚拟仿真+人机交互+立钻哥哥+==)_vr+航母编队展教虚拟仿真实验教学项目
- 3Vue框架介绍简介
- 4ARM与STM32常见面试题【备战春招秋招】
- 5stata:DID双重差分模型基础作业_双重差分模型stata命令
- 6MySQL大数据量分页查询方法及其优化_mysql大数据量分页查询优化
- 7Java基础学习: hutool之CollUtil集合操作工具类
- 8JAVA海外短剧国际版系统源码的使用流程_短剧平台搭建java教程
- 9ROS: 创建机器人仿真模型_ros水下机器人仿真
- 10【NLP】文本LDA主题聚类&主题词生成&PyLDAvis可视化_英文文献lda主题聚类代码
学习笔记——vector容器_vector 取值
赞
踩
vector容器简介——动态数组
vector是将元素置于一个动态数组加以管理的容器。
vector可用vector[idx]或者vector.at(idx)函数取值。
vector在<尾部>插入&删除元素非常快;在<头部>插入&删除元素的时间成本为O(n);在<中间>插入&删除元素也较慢。
vector采用模板类实现,其对象的类型遵循其指定类型。
2.1 vector对象的构造
vetcor对象的默认构造:
- //vetcor对象的默认构造
- vector<int> v; //一个存放int的vector容器
- vector<float> v; //一个存放float的vector容器
- vector<string> v; //一个存放string的vector容器
-
- class CA{};
- vector<CA> v; //一个存放 CA对象 的vector容器
- vector<CA*> v; //一个存放 CA对象指针 的vector容器
vetcor对象的带参数构造:

- //vetcor对象的带参数构造
-
- //第1种:vector(begin,end); 用两个指针
- int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5};
- //将以上数组全部存入vector
- //知识点1:数组名字代表数组首地址,即该指针指向数组第一个元素
- //注意!因为是左闭右开区间,所有右边要比最大索引大
- vector<int> v1(arr, arr+5);
-
- //第2种:vector(n,elem);
- vector<int> v2(3,10); //存储3个10
-
- //第3种:vector(const vector &vec); 用一个容器对象
- vector<int> v3(v1); //v3和v1一样
2.2 vector对象的赋值

- void test_vector02() {
- vector<int> v2(10,10);
- for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) {
- cout << v2[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
- v2.assign(arr, arr + 5);
- for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) {
- cout << v2[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
运行程序后输出:
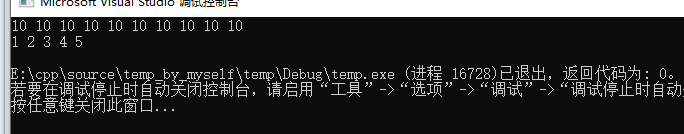
可见:vector.assign(beg,end)函数先清空原对象,再赋值

说明:当容器为空,vector.size()返回值为0。
vector.resize(num):容器变长,用默认值0填充多的位置;容器变长,截掉多的元素。

Q:vec[idx]如果下标越界可能会导致程序异常终止,但对于初学者,很难看出是因为越界运行停止的。那么如何确保越界一定会提醒呢?
A:使用vec.at(idx)函数,一旦越界一定报错。注意!只是报错,运行也会停止,但会让我们知道为什么停止。
5.1 在末尾插入&删除:
v.push_back(x);//在容器末尾插入
v.pop_back();//在容器末尾删除
5.2 在中间插入&删除:
v.insert(position, x);//在position位置插入x,返回新的<迭代器>
v.insert(position, n, x);//在position位置插入n个x,无返回值
v.insert(position, beg, end);//在position位置插入[beg, end)区间的数据,无返回值
注意:以上position, beg, end都为<指针>,而非<索引下标>
- //容器中插入普通数组
- void test_vector051() {
- vector<int> v5(3, 10);
- int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
- //10 10 10->10 2 3 10 10
- v3.insert(v5.begin() + 1, a + 1, a + 3);
- for (int i = 0; i < v5.size(); i++) {
- cout << v5[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
运行程序后输出:
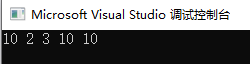
- //容器中插入容器
- void test_vector052() {
- vector<int> v3(3, 10);
- int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
- vector<int> v4(a, a + 5);
- //10 10 10->10 2 3 10 10
- v3.insert(v3.begin() + 1, v4.begin()+1, v4.begin() + 3);
- for (int i = 0; i < v3.size(); i++) {
- cout << v3[i] << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
6.1 vector迭代器的使用
每种容器都定义了一对名为begin()和end()的函数,用于返回迭代器。
- class Person {
- public:
- //构造函数,用列表赋值
- Person(int age, int id) :age(age),id(id){}
- public:
- int age;
- int id;
- };
-
- void test_vector061() {
- //创建类型是Person类的容器v6
- vector<Person> v6;
- Person p1(23, 2112), p2(22, 2111), p3(22, 2110);
- v6.push_back(p1);
- v6.push_back(p2);
- v6.push_back(p3);
-
- //构造一个迭代器对象ite
- vector<Person>::iterator ite;
- ite = v6.begin();
-
- //用迭代器遍历容器v6中的所有元素
- for (ite; ite != v6.end(); ite++) {
- cout << (*ite).age << " " << (*ite).id << " ";//(*ite)取*,即指向对象
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- for_each
- //vector<Person>::iterator pb = v.begin();
- //vector<Person>::iterator pe = v.end();
- //for_each(pb, pe, Print);
- }

6.2 vector迭代器的失效
插入时失效:
- void test_vector062() {
- vector<int> v;
- v.push_back(1);
- v.push_back(2);
- v.push_back(3);
- v.push_back(4);
-
- vector<int>::iterator t = v.begin() + 3;
- cout << *t << endl;
-
- //要想使运行不终止,t = v7.insert(t, 8); 因为insert()返回新的<迭代器>
- v.insert(t, 8);
- cout << *t << endl;
- }
运行程序,在输出一个4之后(即执行完line 9),程序就报错:
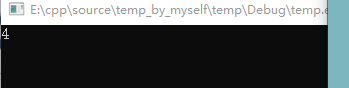
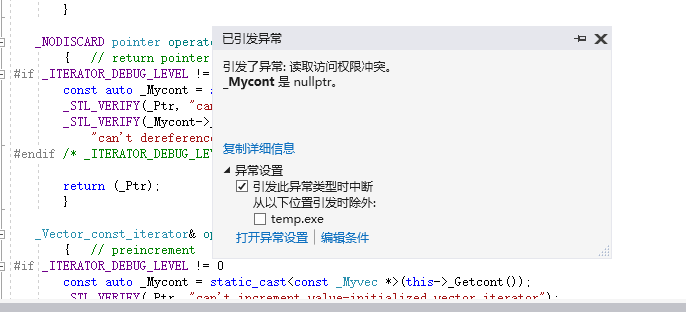
这是因为编译器在运行时,insert()操作是新开辟了一个空间,并将原来的值复制过去。但<迭代器>t仍在原位置,故报错。
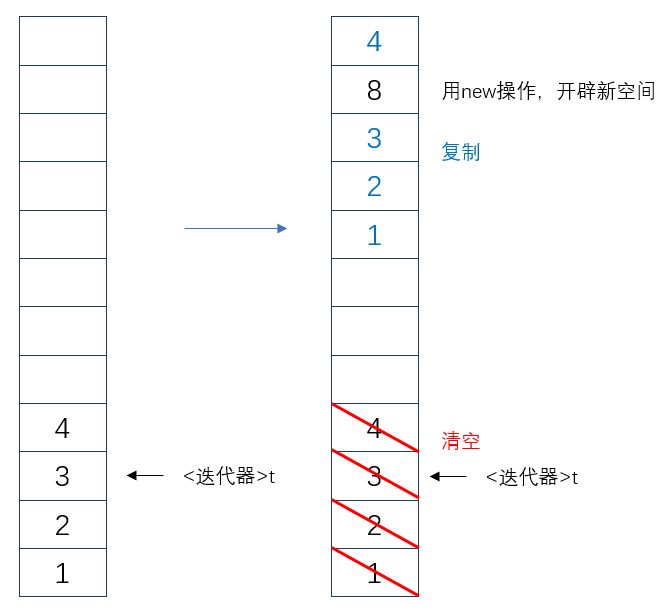
Summary:若在使用insert(pos, elment)函数时,用到了<迭代器>,那么一定要给<迭代器>重新赋值insert(pos, elment)函数的返回值。
删除时失效:
- void test_vector062_2() {
- vector<int> v = { 1,2,3,3,3,4,5,6 };
- vector<int>::iterator it;
- for (it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
- {
- if (*it == 3)
- v.erase(it);
- }
-
- for (it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " ";
- cout << endl;
- }
运行程序报错:
因为erase()函数是把后面的数据移到前面。用覆盖实现删除。
在G++里,erase()函数覆盖删除时,<迭代器>it依然在移动,就会造成只删除一半的3;
而在VS编译器里,利用erase()函数删除,会直接认为<迭代器>it失效。
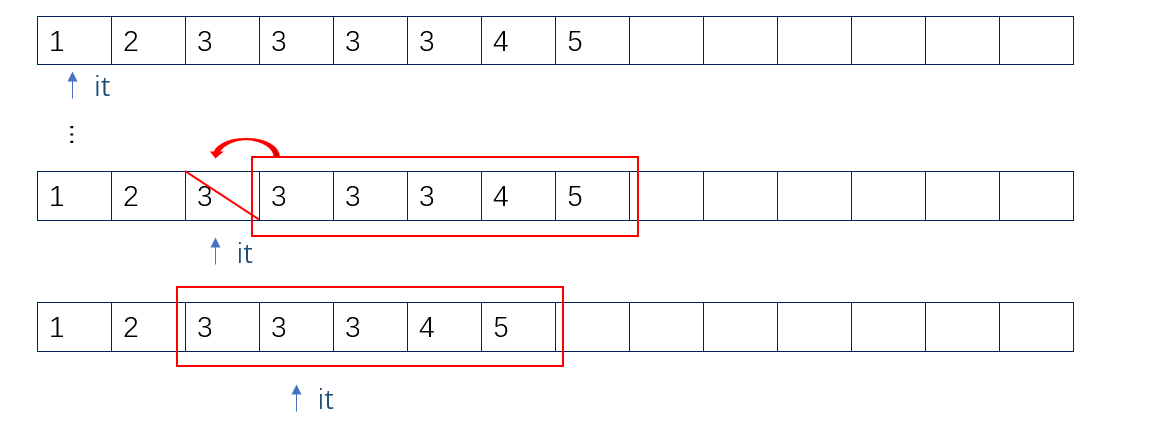
为了不管什么编译器里都实现“删掉所有的3“的操作,应当改为:
- //不管什么编译器,都不会报错
- void test_vector062_3() {
- vector<int> v = { 1,2,3,3,3,4,5,6 };
- vector<int>::iterator it =v.begin();
- while (it != v.end())
- {
- if (*it == 3)
- it=v.erase(it);
- else
- it++;
- }
-
- for (it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
- cout << *it << " ";
- cout << endl;
- }

Summary:若在使用erase()函数时,为了保证<迭代器>不失效,一定要给<迭代器>重新赋值erase()函数的返回值。


