热门标签
热门文章
- 1springboot使用的设计模式_springboot设计模式
- 2【AI不惑境】计算机视觉中注意力机制原理及其模型发展和应用
- 3高并发高负载系统架构_高负载系统是什么
- 4Python在数据分析与可视化中的深度实践
- 5C#实现微信自动发送消息_c#发送微信消息
- 6python自然语言处理—中文分词技术_python 词素划分
- 7回文日期(蓝桥杯第十一届省赛B组)(C/C++)_蓝桥杯 2020年省赛b组 回文日期
- 8Spring Boot:简化Spring应用程序的开发_springboot如何简化开发
- 9NLP / LLMs中的Temperature 是什么?_nlp temperature
- 10马尔柯夫预测法
当前位置: article > 正文
【linux课设】自主实现shell命令行解释器
作者:不正经 | 2024-03-30 10:46:17
赞
踩
【linux课设】自主实现shell命令行解释器
shell和bash的关系
shell是命令解释器,它接收用户的命令并将其传递给内核去执行。bash,即GNU Bourne-Again Shell,是shell的一种实现方式,也是大多数linux系统下默认的shell。
bash的原理
大多数的指令进程(除了内建命令)都是bash的子进程。当我们要执行一条类似ls -a指令时,bash会提前fork出一个子进程,然后让子进程去执行指令。这是我们进程程序替换的思想。当然,中间的过程涉及到进程创建、虚拟内存、进程替换的细节,本篇文章不做叙述,感兴趣的可以去看我之前的博客,希望能对你有帮助。
我们可以画出bash进程执行指令的过程图来帮助理解:
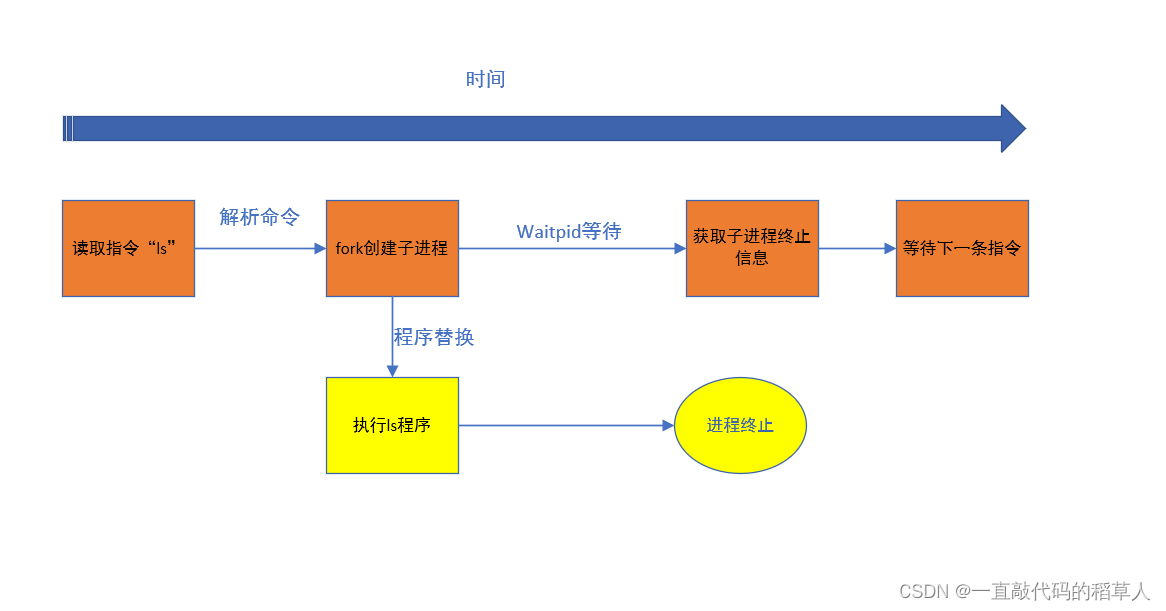
在上图中,bash几乎一直在循环做以下动作:
1.获取指令
2.解析命令行
3.fork创建子进程
4.命令程序替换子进程
5.等待子进程终止
…
既然知道了bash的基本原理,我们同样也可以模拟以上动作来写一个mini版的shell
代码实现
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #include<errno.h> #define SIZE 100 #define COMMAND_SIZE 200 #define ZEOR '\0' #define ARGV_NUM 32 #define SKIP " " #define SkipPath(p) do{p+=strlen(p)-1; while(*p!='/'){p--;}}while(0) char* gArgv[ARGV_NUM];//指令参数 char cwd[SIZE*2];//当前路径的环境变量键值对 int lastcode=0; const char* GetUserName(){//获取环境变量中的值 const char* name=getenv("USER"); if(name==NULL){ return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHome(){//获取家目录 const char* home=getenv("HOME"); if(home==NULL){ return "/"; } return home; } const char* GetHostHome(){//获取主机名 const char* hostname=getenv("HOSTNAME"); if(hostname==NULL){ return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd(){//获取当前路径 const char* cwd=getenv("PWD"); if(cwd==NULL){ return "None"; } return cwd; } //输出命令行 void MakeCommandLineAndPrint(){ char line[SIZE]; const char* name=GetUserName(); const char* hostname=GetHostHome(); const char* cwd=GetCwd(); SkipPath(cwd); snprintf(line,sizeof(line),"[%s@%s %s]> ",name,hostname,cwd=strlen(cwd)==1?"/":cwd+1); printf("%s",line); fflush(stdout); } //获取用户命令行 int GetUserCommand(char command[],size_t n){ char* s=fgets(command,n,stdin); if(s==NULL)return -1; command[strlen(command)-1]=ZEOR; return (int)strlen(command); } //命令行分割,获取命令行参数列表 void SplitCommand(char command[],size_t n){ gArgv[0]=strtok(command,SKIP); size_t index=1; char* t=gArgv[0]; while(t!=NULL){ t=strtok(NULL,SKIP); gArgv[index++]=t; } //size_t i=0; //for(;i<index;i++){ // printf("%s\n",gArgv[i]); //} } //cd内建命令 void Cd(){ const char* path=gArgv[1]; if(path==NULL){ path=GetHome(); } //更新当前工作目录 chdir(path);//修改当前进程的工作路径 //更新环境变量 char t[SIZE*2]; getcwd(t,sizeof(t)); snprintf(cwd,sizeof(cwd),"PWD=%s",t); putenv(cwd); } //查看是否是内建命令 int CheckBuiltIn(){ int yes=0; const char* cmd=gArgv[0]; if(strcmp(cmd,"cd")==0){ yes=1; Cd(); } return yes; } // 处理创建子进程失败 void Die(){ exit(1); } //执行指令 void ExeCommand(){ pid_t id=fork(); if(id<0){ Die(); } if(id==0){ //child execvp(gArgv[0],gArgv); exit(errno); }else{ int status=0; pid_t res=waitpid(id,&status,0); if(res>0){ lastcode=WEXITSTATUS(status);//获取子进程退出码信息 if(WIFEXITED(status)){ if(lastcode!=0) printf("%s:%s:%d\n",gArgv[0],strerror(lastcode),lastcode); } } } } int main(){ int quit=0; while(!quit){ //1.输出一个命令行 MakeCommandLineAndPrint(); //2.获取用户命令 char command[COMMAND_SIZE]; int n= GetUserCommand(command,sizeof(command)); if(n<=0)return 1;//输入指令不合法 // printf("%s\n",command); //3.命令行字符串分割 SplitCommand(command,sizeof(command)); //4.查看命令是否是内建命令 int flag=CheckBuiltIn(); if(flag)continue; //5.执行指令 ExeCommand(); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
运用进程创建,进程替换的原理,基本模拟了shell解释命令的过程。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/不正经/article/detail/340292?site
推荐阅读
相关标签



