- 1广东IT人力外包:数字化转型的加速引擎
- 2JS常用词汇_js单词大全
- 3Stable diffusion——调参归纳_stable diffusion常用起手式汇总
- 4MySQL笔记(十):MySQL管理
- 5数据分析之Numpy模块详解
- 6实例解释遇到前端报错时如何排查问题_前端组件报错找不到具体位置
- 7两种方法快速实现基于bert预训练模型的分类任务,kashgari和keras_bert_闫广庆 nlp
- 8大学英语期末测试_for thousands of years, people have known that the
- 9华为端口聚合命令_华为S5735交换机基本设置-端口聚合lacp
- 10Spring Security 对登录密码进行加密传输Java + Vue_spring security+vue实现密码加密
whisper使用_whisper.transcribe
赞
踩
github: https://gitcode.com/openai/whisper/overview
1. 直接调用 语音识别
,transcribe()方法会读取整个文件,并使用一个30秒的滑动窗口对音频进行处理,对每个窗口进行自回归序列到序列的预测。
官网readme调用1
import whisper
model = whisper.load_model("base") # 加载模型
result = model.transcribe("audio.mp3") # 指定音频路径 识别
print(result["text"]) # 输出识别结果
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
load_model方法在__init__.py文件中有定义
{'text': ' 你一定會笑著說 二百克芝麻能力好耐架', 'segments': [{'id': 0, 'seek': 0, 'start': 0.0, 'end': 2.0, 'text': ' 你一定會笑著說', 'tokens': [50365, 10930, 24272, 6236, 11600, 19382, 4622, 50465], 'temperature': 0.0, 'avg_logprob': -0.5130815124511718, 'compression_ratio': 0.8253968253968254, 'no_speech_prob': 0.12529681622982025}, {'id': 1, 'seek': 0, 'start': 2.0, 'end': 5.5, 'text': ' 二百克芝麻能力好耐架', 'tokens': [50465, 220, 11217, 31906, 24881, 13778, 251, 38999, 8225, 13486, 2131, 4450, 238, 7360, 114, 50640], 'temperature': 0.0, 'avg_logprob': -0.5130815124511718, 'compression_ratio': 0.8253968253968254, 'no_speech_prob': 0.12529681622982025}], 'language': 'yue'}
- 1
2. 语种识别 whisper.detect_language()和whisper.decode()
以下是使用whisper.detect_language()和whisper.decode()的示例用法,这些方法提供对模型的更低级别访问。更低级别可以说是更底层的调用。
官网readme调用2
import whisper model = whisper.load_model("base") # 加载预训练的语音识别模型,这里使用了名为"base"的模型。 # load audio and pad/trim it to fit 30 seconds audio = whisper.load_audio("audio.mp3") audio = whisper.pad_or_trim(audio) # 对加载的音频进行填充或裁剪,使其适合30秒的滑动窗口处理。 # make log-Mel spectrogram and move to the same device as the model mel = whisper.log_mel_spectrogram(audio).to(model.device) # 将音频转换为对数梅尔频谱图,并将其移动到与模型相同的设备(如GPU)上进行处理。 # detect the spoken language _, probs = model.detect_language(mel) # 使用模型进行语言检测,返回检测到的语言和对应的概率。 # 打印检测到的语言,选取概率最高的语言作为结果。 print(f"Detected language: {max(probs, key=probs.get)}") # decode the audio # 置解码的选项,如语言模型、解码器等。 options = whisper.DecodingOptions() # 使用模型对音频进行解码,生成识别结果。 result = whisper.decode(model, mel, options) # print the recognized text # 打印识别结果,即模型识别出的文本内容。 print(result.text)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
3. 指定要识别的语种做语音识别
from whisper import load_model
from whisper.transcribe import transcribe
model = load_model(model_path, device=device)
# 指定model 音频路径 要识别的语言类型 yue--粤语
result = transcribe(model, audio_path, language="yue")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
whisper 源码的transcribe函数
def transcribe( model: "Whisper", audio: Union[str, np.ndarray, torch.Tensor], *, verbose: Optional[bool] = None, temperature: Union[float, Tuple[float, ...]] = (0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0), compression_ratio_threshold: Optional[float] = 2.4, logprob_threshold: Optional[float] = -1.0, no_speech_threshold: Optional[float] = 0.6, condition_on_previous_text: bool = True, initial_prompt: Optional[str] = None, word_timestamps: bool = False, prepend_punctuations: str = "\"'“¿([{-", append_punctuations: str = "\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、", clip_timestamps: Union[str, List[float]] = "0", hallucination_silence_threshold: Optional[float] = None, **decode_options, ): """ Transcribe an audio file using Whisper Parameters ---------- model: Whisper The Whisper model instance audio: Union[str, np.ndarray, torch.Tensor] The path to the audio file to open, or the audio waveform verbose: bool Whether to display the text being decoded to the console. If True, displays all the details, If False, displays minimal details. If None, does not display anything temperature: Union[float, Tuple[float, ...]] Temperature for sampling. It can be a tuple of temperatures, which will be successively used upon failures according to either `compression_ratio_threshold` or `logprob_threshold`. compression_ratio_threshold: float If the gzip compression ratio is above this value, treat as failed logprob_threshold: float If the average log probability over sampled tokens is below this value, treat as failed no_speech_threshold: float If the no_speech probability is higher than this value AND the average log probability over sampled tokens is below `logprob_threshold`, consider the segment as silent condition_on_previous_text: bool if True, the previous output of the model is provided as a prompt for the next window; disabling may make the text inconsistent across windows, but the model becomes less prone to getting stuck in a failure loop, such as repetition looping or timestamps going out of sync. word_timestamps: bool Extract word-level timestamps using the cross-attention pattern and dynamic time warping, and include the timestamps for each word in each segment. prepend_punctuations: str If word_timestamps is True, merge these punctuation symbols with the next word append_punctuations: str If word_timestamps is True, merge these punctuation symbols with the previous word initial_prompt: Optional[str] Optional text to provide as a prompt for the first window. This can be used to provide, or "prompt-engineer" a context for transcription, e.g. custom vocabularies or proper nouns to make it more likely to predict those word correctly. decode_options: dict Keyword arguments to construct `DecodingOptions` instances clip_timestamps: Union[str, List[float]] Comma-separated list start,end,start,end,... timestamps (in seconds) of clips to process. The last end timestamp defaults to the end of the file. hallucination_silence_threshold: Optional[float] When word_timestamps is True, skip silent periods longer than this threshold (in seconds) when a possible hallucination is detected Returns ------- A dictionary containing the resulting text ("text") and segment-level details ("segments"), and the spoken language ("language"), which is detected when `decode_options["language"]` is None. """ dtype = torch.float16 if decode_options.get("fp16", True) else torch.float32 if model.device == torch.device("cpu"): if torch.cuda.is_available(): warnings.warn("Performing inference on CPU when CUDA is available") if dtype == torch.float16: warnings.warn("FP16 is not supported on CPU; using FP32 instead") dtype = torch.float32 if dtype == torch.float32: decode_options["fp16"] = False # Pad 30-seconds of silence to the input audio, for slicing mel = log_mel_spectrogram(audio, model.dims.n_mels, padding=N_SAMPLES) content_frames = mel.shape[-1] - N_FRAMES content_duration = float(content_frames * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE) if decode_options.get("language", None) is None: if not model.is_multilingual: decode_options["language"] = "en" else: if verbose: print( "Detecting language using up to the first 30 seconds. Use `--language` to specify the language" ) mel_segment = pad_or_trim(mel, N_FRAMES).to(model.device).to(dtype) _, probs = model.detect_language(mel_segment) decode_options["language"] = max(probs, key=probs.get) if verbose is not None: print( f"Detected language: {LANGUAGES[decode_options['language']].title()}" ) language: str = decode_options["language"] task: str = decode_options.get("task", "transcribe") tokenizer = get_tokenizer( model.is_multilingual, num_languages=model.num_languages, language=language, task=task, ) if isinstance(clip_timestamps, str): clip_timestamps = [ float(ts) for ts in (clip_timestamps.split(",") if clip_timestamps else []) ] seek_points: List[int] = [round(ts * FRAMES_PER_SECOND) for ts in clip_timestamps] if len(seek_points) == 0: seek_points.append(0) if len(seek_points) % 2 == 1: seek_points.append(content_frames) seek_clips: List[Tuple[int, int]] = list(zip(seek_points[::2], seek_points[1::2])) punctuation = "\"'“¿([{-\"'.。,,!!??::”)]}、" if word_timestamps and task == "translate": warnings.warn("Word-level timestamps on translations may not be reliable.") def decode_with_fallback(segment: torch.Tensor) -> DecodingResult: temperatures = ( [temperature] if isinstance(temperature, (int, float)) else temperature ) decode_result = None for t in temperatures: kwargs = {**decode_options} if t > 0: # disable beam_size and patience when t > 0 kwargs.pop("beam_size", None) kwargs.pop("patience", None) else: # disable best_of when t == 0 kwargs.pop("best_of", None) options = DecodingOptions(**kwargs, temperature=t) decode_result = model.decode(segment, options) needs_fallback = False if ( compression_ratio_threshold is not None and decode_result.compression_ratio > compression_ratio_threshold ): needs_fallback = True # too repetitive if ( logprob_threshold is not None and decode_result.avg_logprob < logprob_threshold ): needs_fallback = True # average log probability is too low if ( no_speech_threshold is not None and decode_result.no_speech_prob > no_speech_threshold ): needs_fallback = False # silence if not needs_fallback: break return decode_result clip_idx = 0 seek = seek_clips[clip_idx][0] input_stride = exact_div( N_FRAMES, model.dims.n_audio_ctx ) # mel frames per output token: 2 time_precision = ( input_stride * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE ) # time per output token: 0.02 (seconds) all_tokens = [] all_segments = [] prompt_reset_since = 0 if initial_prompt is not None: initial_prompt_tokens = tokenizer.encode(" " + initial_prompt.strip()) all_tokens.extend(initial_prompt_tokens) else: initial_prompt_tokens = [] def new_segment( *, start: float, end: float, tokens: torch.Tensor, result: DecodingResult ): tokens = tokens.tolist() text_tokens = [token for token in tokens if token < tokenizer.eot] return { "seek": seek, "start": start, "end": end, "text": tokenizer.decode(text_tokens), "tokens": tokens, "temperature": result.temperature, "avg_logprob": result.avg_logprob, "compression_ratio": result.compression_ratio, "no_speech_prob": result.no_speech_prob, } # show the progress bar when verbose is False (if True, transcribed text will be printed) with tqdm.tqdm( total=content_frames, unit="frames", disable=verbose is not False ) as pbar: last_speech_timestamp = 0.0 # NOTE: This loop is obscurely flattened to make the diff readable. # A later commit should turn this into a simpler nested loop. # for seek_clip_start, seek_clip_end in seek_clips: # while seek < seek_clip_end while clip_idx < len(seek_clips): seek_clip_start, seek_clip_end = seek_clips[clip_idx] if seek < seek_clip_start: seek = seek_clip_start if seek >= seek_clip_end: clip_idx += 1 if clip_idx < len(seek_clips): seek = seek_clips[clip_idx][0] continue time_offset = float(seek * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE) window_end_time = float((seek + N_FRAMES) * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE) segment_size = min(N_FRAMES, content_frames - seek, seek_clip_end - seek) mel_segment = mel[:, seek : seek + segment_size] segment_duration = segment_size * HOP_LENGTH / SAMPLE_RATE mel_segment = pad_or_trim(mel_segment, N_FRAMES).to(model.device).to(dtype) decode_options["prompt"] = all_tokens[prompt_reset_since:] result: DecodingResult = decode_with_fallback(mel_segment) tokens = torch.tensor(result.tokens) if no_speech_threshold is not None: # no voice activity check should_skip = result.no_speech_prob > no_speech_threshold if ( logprob_threshold is not None and result.avg_logprob > logprob_threshold ): # don't skip if the logprob is high enough, despite the no_speech_prob should_skip = False if should_skip: seek += segment_size # fast-forward to the next segment boundary continue previous_seek = seek current_segments = [] # anomalous words are very long/short/improbable def word_anomaly_score(word: dict) -> float: probability = word.get("probability", 0.0) duration = word["end"] - word["start"] score = 0.0 if probability < 0.15: score += 1.0 if duration < 0.133: score += (0.133 - duration) * 15 if duration > 2.0: score += duration - 2.0 return score def is_segment_anomaly(segment: Optional[dict]) -> bool: if segment is None or not segment["words"]: return False words = [w for w in segment["words"] if w["word"] not in punctuation] words = words[:8] score = sum(word_anomaly_score(w) for w in words) return score >= 3 or score + 0.01 >= len(words) def next_words_segment(segments: List[dict]) -> Optional[dict]: return next((s for s in segments if s["words"]), None) timestamp_tokens: torch.Tensor = tokens.ge(tokenizer.timestamp_begin) single_timestamp_ending = timestamp_tokens[-2:].tolist() == [False, True] consecutive = torch.where(timestamp_tokens[:-1] & timestamp_tokens[1:])[0] consecutive.add_(1) if len(consecutive) > 0: # if the output contains two consecutive timestamp tokens slices = consecutive.tolist() if single_timestamp_ending: slices.append(len(tokens)) last_slice = 0 for current_slice in slices: sliced_tokens = tokens[last_slice:current_slice] start_timestamp_pos = ( sliced_tokens[0].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin ) end_timestamp_pos = ( sliced_tokens[-1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin ) current_segments.append( new_segment( start=time_offset + start_timestamp_pos * time_precision, end=time_offset + end_timestamp_pos * time_precision, tokens=sliced_tokens, result=result, ) ) last_slice = current_slice if single_timestamp_ending: # single timestamp at the end means no speech after the last timestamp. seek += segment_size else: # otherwise, ignore the unfinished segment and seek to the last timestamp last_timestamp_pos = ( tokens[last_slice - 1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin ) seek += last_timestamp_pos * input_stride else: duration = segment_duration timestamps = tokens[timestamp_tokens.nonzero().flatten()] if ( len(timestamps) > 0 and timestamps[-1].item() != tokenizer.timestamp_begin ): # no consecutive timestamps but it has a timestamp; use the last one. last_timestamp_pos = ( timestamps[-1].item() - tokenizer.timestamp_begin ) duration = last_timestamp_pos * time_precision current_segments.append( new_segment( start=time_offset, end=time_offset + duration, tokens=tokens, result=result, ) ) seek += segment_size if word_timestamps: add_word_timestamps( segments=current_segments, model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, mel=mel_segment, num_frames=segment_size, prepend_punctuations=prepend_punctuations, append_punctuations=append_punctuations, last_speech_timestamp=last_speech_timestamp, ) if not single_timestamp_ending: last_word_end = get_end(current_segments) if last_word_end is not None and last_word_end > time_offset: seek = round(last_word_end * FRAMES_PER_SECOND) # skip silence before possible hallucinations if hallucination_silence_threshold is not None: threshold = hallucination_silence_threshold if not single_timestamp_ending: last_word_end = get_end(current_segments) if last_word_end is not None and last_word_end > time_offset: remaining_duration = window_end_time - last_word_end if remaining_duration > threshold: seek = round(last_word_end * FRAMES_PER_SECOND) else: seek = previous_seek + segment_size # if first segment might be a hallucination, skip leading silence first_segment = next_words_segment(current_segments) if first_segment is not None and is_segment_anomaly(first_segment): gap = first_segment["start"] - time_offset if gap > threshold: seek = previous_seek + round(gap * FRAMES_PER_SECOND) continue # skip silence before any possible hallucination that is surrounded # by silence or more hallucinations hal_last_end = last_speech_timestamp for si in range(len(current_segments)): segment = current_segments[si] if not segment["words"]: continue if is_segment_anomaly(segment): next_segment = next_words_segment( current_segments[si + 1 :] ) if next_segment is not None: hal_next_start = next_segment["words"][0]["start"] else: hal_next_start = time_offset + segment_duration silence_before = ( segment["start"] - hal_last_end > threshold or segment["start"] < threshold or segment["start"] - time_offset < 2.0 ) silence_after = ( hal_next_start - segment["end"] > threshold or is_segment_anomaly(next_segment) or window_end_time - segment["end"] < 2.0 ) if silence_before and silence_after: seek = round( max(time_offset + 1, segment["start"]) * FRAMES_PER_SECOND ) if content_duration - segment["end"] < threshold: seek = content_frames current_segments[si:] = [] break hal_last_end = segment["end"] last_word_end = get_end(current_segments) if last_word_end is not None: last_speech_timestamp = last_word_end if verbose: for segment in current_segments: start, end, text = segment["start"], segment["end"], segment["text"] line = f"[{format_timestamp(start)} --> {format_timestamp(end)}] {text}" print(make_safe(line)) # if a segment is instantaneous or does not contain text, clear it for i, segment in enumerate(current_segments): if segment["start"] == segment["end"] or segment["text"].strip() == "": segment["text"] = "" segment["tokens"] = [] segment["words"] = [] all_segments.extend( [ {"id": i, **segment} for i, segment in enumerate( current_segments, start=len(all_segments) ) ] ) all_tokens.extend( [token for segment in current_segments for token in segment["tokens"]] ) if not condition_on_previous_text or result.temperature > 0.5: # do not feed the prompt tokens if a high temperature was used prompt_reset_since = len(all_tokens) # update progress bar pbar.update(min(content_frames, seek) - previous_seek) return dict( text=tokenizer.decode(all_tokens[len(initial_prompt_tokens) :]), segments=all_segments, language=language, )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326
- 327
- 328
- 329
- 330
- 331
- 332
- 333
- 334
- 335
- 336
- 337
- 338
- 339
- 340
- 341
- 342
- 343
- 344
- 345
- 346
- 347
- 348
- 349
- 350
- 351
- 352
- 353
- 354
- 355
- 356
- 357
- 358
- 359
- 360
- 361
- 362
- 363
- 364
- 365
- 366
- 367
- 368
- 369
- 370
- 371
- 372
- 373
- 374
- 375
- 376
- 377
- 378
- 379
- 380
- 381
- 382
- 383
- 384
- 385
- 386
- 387
- 388
- 389
- 390
- 391
- 392
- 393
- 394
- 395
- 396
- 397
- 398
- 399
- 400
- 401
- 402
- 403
- 404
- 405
- 406
- 407
- 408
- 409
- 410
- 411
- 412
- 413
- 414
- 415
- 416
- 417
- 418
- 419
- 420
- 421
- 422
- 423
- 424
- 425
- 426
- 427
- 428
- 429
- 430
- 431
- 432
- 433
- 434
- 435
- 436
- 437
- 438
- 439
- 440
- 441
- 442
- 443
- 444
- 445
- 446
- 447
- 448
- 449
- 450
- 451
- 452
- 453
- 454
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458
- 459
- 460
- 461
函数解析
1. transcript.py
kimichat:
这段代码是一个Python脚本,它使用了Whisper模型来进行音频转录。Whisper是一个由OpenAI开发的大型语音识别模型,能够处理多种语言和任务。以下是代码的主要功能和组件的逐行解释:
1-7行:导入了所需的库和模块,包括argparse(命令行参数解析)、os(操作系统交互)、traceback(错误跟踪)、warnings(警告信息)、numpy(科学计算)、torch(PyTorch深度学习库)、tqdm(进度条显示)。
9-14行:定义了一些常量和辅助函数,如FRAMES_PER_SECOND(每秒帧数)、HOP_LENGTH(帧跳跃长度)、N_FRAMES(每个音频段的帧数)、N_SAMPLES(音频样本数)、SAMPLE_RATE(采样率)等。
16-25行:定义了log_mel_spectrogram函数,用于将音频信号转换为Mel频率倒谱系数,这是语音识别中常用的特征表示方法。
27-36行:定义了pad_or_trim函数,用于对音频信号进行填充或裁剪,以匹配模型所需的输入长度。
38-55行:定义了transcribe函数,它是脚本的核心,负责加载音频、预处理、使用Whisper模型进行转录,并返回转录结果。它接受多种参数,如verbose(是否显示详细信息)、temperature(采样温度)、compression_ratio_threshold(压缩比阈值)等,这些参数影响转录过程和结果。
57-82行:在transcribe函数中,首先检查设备类型和数据类型(是否使用半精度浮点数),然后对音频进行预处理,包括检测语言、加载tokenizer、处理音频剪辑时间戳等。
84-131行:实现了一个循环,用于处理音频文件的每个剪辑段,进行转录,并更新进度条。
133-174行:在transcribe函数中,还实现了对转录结果的处理,包括添加单词时间戳、处理可能的幻觉(hallucination)和沉默段。
176-198行:定义了cli函数,它使用argparse解析命令行参数,并调用transcribe函数来处理音频文件。
200-206行:在cli函数中,根据用户输入的参数,加载了Whisper模型,并设置了输出格式和目录。
208-213行:实现了对每个音频文件的循环处理,调用transcribe函数进行转录,并将结果写入到文件中。
215-218行:最后,如果这个脚本作为主程序运行,它将执行cli函数,开始命令行界面。
整体来看,这个脚本提供了一个完整的命令行界面,允许用户指定音频文件、模型、输出格式和其他参数,以执行音频转录任务。它使用了Whisper模型的强大功能,能够处理多种语言和语音识别任务。
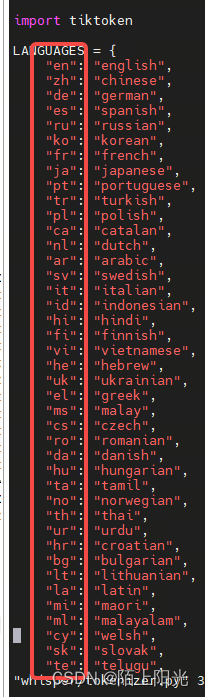
2. tokenizer.py
根据缩写指定要识别的语言
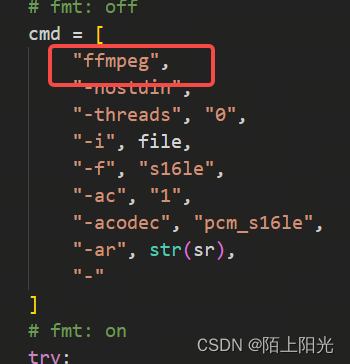
3. audio.py
处理音频用到了ffmpeg命令行工具,在运行环境要安装上ffmpeg命令行工具。
4. __ init__.py
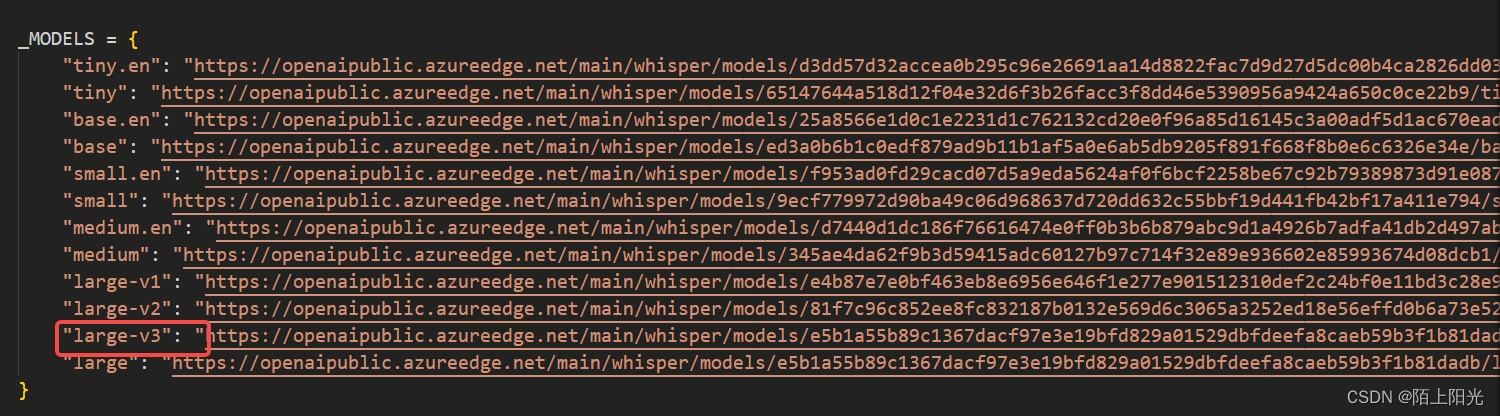
指定要调用的模型, 可以把模型先下载到本地,直接指定模型路径加载本地模型。
grep -H “example” * 匹配内容的同时输出被匹配的文件名。